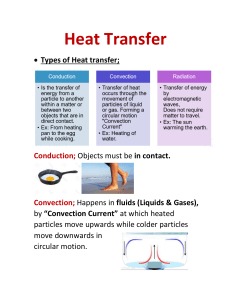
HEAT HEAT Heat is the total kinetic (moving) energy of all molecules. Depends on the mass and energy of the particles! If you have a cup of water the same temperature as the ocean, which has more heat energy? How does heat flow? Heat flows from hot to cold until the heat is balanced which we call equilibrium. A metal cup containing water at 100F is placed in an aquarium containing water at 80F: A) Which way will heat flow? Why? B) When will the flow of heat stop? C) What is it called when heat no longer flows? How is heat measured? It is measured in calories, joules, or BTUs A calorie is the amount of heat used to raise the temperature of one gram of water one degree Celsius. One calorie = 4 joules One Calorie (food)=1000 calories (4,000 J) What is the difference between heat and temperature? Heat is the total amount of kinetic energy available. Temperature is a relative measure of the speed of the particles. Temperature is measured in degrees. Temperature and heat are not the same!!!! What happens when a substance is heated? The speed of the particles increases which causes the space between the particles to increase How does heat affect volume? Volume increases with more heat. More heat means that the molecules are moving faster (more kinetic energy), therefore they bump into one another and spread out. Less heat means less volume! What effect does heat have on density? When a substance is heated, it expands, volume increases therefore it becomes less dense. Temperature Scales The 2 main temperature scales are Celsius and Fahrenheit. Boiling point is 100 C & 212 F Freezing is 0 C & 32 F Kelvin Scale A third temperature scale used mainly for scientific purposes, where absolute 0 is the coldest possible temperature. It starts at 0 (which is absolute 0) Boiling 373 Freezing 273 Absolute Zero Absolute zero is the temperature where there is an absence of heat. There is no motion of molecules. It has not been reached in real life or in a lab, but scientists have gotten very close. ABSOLUTE ZERO Absolute Zero = -460 F Absolute Zero = -273 C Dry Ice = -110 F Coldest Place on Earth = -70 F What is specific heat? The amount of energy needed to raise the temperature of 1 kg of a substance by 1 degree Celsius. The ability of a substance to absorb heat. This property can help identify substances. Example of Specific Heat How much energy does it take to raise the temperature of 2 kilograms of water by 3°C (specific heat of water is 4,184 J/kg°C) Solution: 2 kilograms x 3°C = 6 kg°C 4,184 J/ kg°C x 6 kg°C = 25,104 J What are the 3 states of matter? Solid-has a defined volume and shape. Liquid-defined volume, takes the shape of its container. Gas-no defined shape or volume. Sketch these pictures What is heat of fusion? The amount of energy used to melt one gram of a substance without changing its temperature. What is heat of vaporization? The phase change when a liquid becomes a gas. The energy needed for one gram of a liquid to become a gas without changing the temperature. The particles gain enough energy to permit them to escape the surface of the liquid and become a gas. STOP HERE TAKE THIS QUIZ. SCORES WILL BE COUNTED. LOOK BACK THROUGH THE POWERPOINT AS NEEDED! http://makeaquiz.net/eIAwte CONDUCTION Conduction is the direct transfer of heat. Does conduction happen better in solids, liquids, or gases? Conduction works best through solids! CONVECTION Convection is when warmer less dense material rises and is replaced by cooler, more dense material. It then becomes heated and rises creating a current (or repeating cycle!). RADIATION Radiation involves the transfer of heat through the air or a vacuum! ALL objects radiate heat!