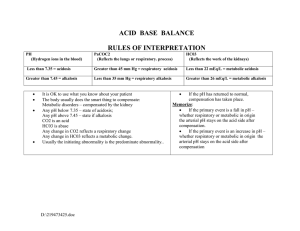
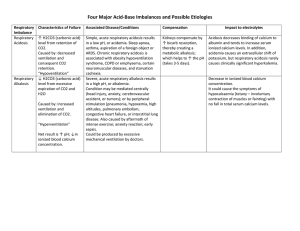
Pathophysiology Exam 1 Study Guide: Chapters 2-4, 7-11 Chapter 2: Integrated Body Processes • Histology - examines cells poorly differentiated • Hyperplasia - increased # of cells in tissues/organs • Metaplasia - replace one cell type by another - Example: GERD - gastroesophageal reflux disease, aka Barrett’s esophagus) • Dysplasia - abnormal cell growth • Neoplasia - new abnormal growth • Apoptosis - programmed cell death “specific time” • Necrosis - cells die when stressors or insults overwhelm their ability to survive Types Hypoxic Cell (irreversible cell damage) Free Radical Causes of Cell Injury Meaning - Blood cannot deliver enough oxygen (vasoconstricted) - Single unpaired electron in outer orbit causes instability - Direct trauma Physical Agents - Endogenous biological substances - Exogenous synthetic substances Chemical - Microorganisms Infectious Agents Immunological Reactions Genetic Defects Nutritional Imbalances - Immune system overreacts and attacks own cells - Damaged DNA transcribes to RNA which sends flawed instructions to ribosomes - Insufficient proteins, carbs, vitamins, and minerals Examples/Causes - Anemia (ex: hemoglobin 7 goes to heaven) - Lactic Acid (ex: marathon runner who gets muscle cramps because of cellular acidosis) - Smoke - Pesticides - Gunshot wound - Temp. extremes (frostbite/burn) - Excessive noises - Hypertension (ex: lead to heart attack, blood clot, aneurysm) - Endo: normal metabolic byproducts not correctly working (ex: high glucose, high sodium, etc.) - Exo: external agents (ex: UV rays, drugs, radiation, poison) - Bacteria - Viruses - Fungi - Protozoa (parasite) - Helminths (worms) - Allergies - Autoimmune diseases (RA) - Defective RNA causes diseases - Obesity - Starvation - Malnutrition Chapter 3: Fluid, Electrolyte, and Acid-Base Homeostasis • Karyotype - visual of all the chromosomes pairs • Down’s Syndrome - extra chromosome (23) Syndrome/Disease/Disorder Trait - Dominant Marfan’s Cystic Fibrosis Sickle Cell (AB hemoglobin) - Recessive - Xlinked Recessive Symptoms [think: Abraham Lincoln] - Back pain - Vision problems - Heart issues - Wheezes - Fatigue Chapter 4: Infection and Inflammation - Genomics: study of interactions of all the nucleotides sequences, not just genes, within an organism (related to basics of hereditary) Alarm Selye’s Stress Response Theory - Central Nervous System (CNS) - Sympathetic Nervous System (SNS) - Adrenal Gland Stimulus - Fight or Flight Reaction Resistance Exhaustion • Venous Stasis - blood is stagnant and susceptible to clotting (deep vein thrombosis - DVT) - Example: pt. in the hospital for several months on bedrest, lack of blood flow, blood is stagnant, can lead to DVT/PE • Orthostatic Hypotension - pt. BP falls at least 20mmHG within 3 minutes as they stand, sit, lay down after prolong period of bedrest • Pressure Ulcers: skin breakdown and tissue ischemia (inadequate blood supply) - Vulnerable to bacterial contamination and infection; extend into bloodstream and cause septicemia (infection in bloodstream) - Extensive healing process (several weeks or months: especially stage 4) Chapter 7: Pulmonary Disorders • Water is found in 3 different fluid compartments (60% total body weight): - Intracellular fluid (ICF): 40% of body weight - Extracellular fluid (ECF): 20% of body weight - Interstitial fluid (ISF) • Oncotic Pressure (aka Colloid Pressure) - pressure due to albumin in the blood - Purpose: used to evaluate nutritional status • RAAS (Renin-Angiotensin (I and II)-Aldosterone System) - when there is a in circulation or in BP the kidneys activate RAAS - Purpose: regulates arterial blood pressure • Electrolyte Locations [think: PISO - potassium inside cell sodium outside cell] - Potassium (ICF) - Sodium (ECF) • Calcium Imbalances - calcium and phosphate levels have inverse relationship (usually kidney issues) so hypocalcemia will cause hyperphosphatemia • Fluid Volume Measurement - important measure standard of fluid loss or fluid gain is by weight (ideally same time every day) Pathophysiology Dehydration Hyponatremia (highest risk pt. are post-op & elderly) Hypernatremia Definition - Low H20 volume (hypovolemia) in the ICF and ECF Causes - Hypernatremia - Osmotic diuresis (high glucose levels) - Burns, fever, sweating - Reduced fluid intake - Sodium < 135 (salt loss) - Excess H20 [think: 4Ds] - Diarrhea - Diuretics - Dehydration - Drains (NG, fistula - ulcer/abscess causes tunnel to drain pus) [Tutor Example: hippo - takes in a lot of water which would decrease sodium] - Sodium > 145 - Low H20 (dehydration) (highest risk pt. are breastfed infants & elderly) - Calcium < 8.5 Hypocalcemia (Chvostek’s sign & Trousseau’s sign) - Calcium > 10 (body is weak) Hypercalcemia Hypokalemia - Potassium < 3.5 (slow and low) EKG: Flatten T wave High U wave - Potassium > 5 Hyperkalemia EKG: High T wave Wide QRS [think: CHIMED] - Cushing’s - Hyperventilation - Infection - Medication/meals - Excessive water loss - Diabetes & diuretics [think: LOW CALCIUM] - Low PTH (parathyroid) - Oral inadequate intake - Wound drain - Celiac & Crohns - Acute pancreatitis - Low Vitamin D - Chronic kidney issues - Increased phosphorous - Using meds like laxatives - Mobility issues [think: CHIMPANZEES] - Calcium supplements - Hyperparathyroidism - Iatrogenic (immobility) - Multiple meds - Parathyroid hyperplasia - Alcohol - Neoplasm (breast/lung cancer) - Zollinger Ellison Syndrome - Excess Vitamin D - Excess Vitamin A - Sarcoidosis (organ inflammation) [think: 4Ds] - Diarrhea - Diuretics - Diabetes - Digitalis (treats cong. heart failure) [think: MACHINE] - Medications - Acidosis (metabolic & respiratory) - Cell injury (burns, trauma, etc.) - Hypoaldosteronism (Addison’s) - Intake excess - Nephrons (renal failure) - Extreme exercise Signs/Symptoms - Headaches - Diarrhea - Cramps - Vomiting - Confusion - Thirst [think: SALT LOSS] - Stupor/coma - Anorexia - Lethargy - Tendon reflex decreases - Limp muscles - Orthostatic hypotension - Stomach cramping - Shallow respirations [think: SALTED] - Skin flushed - Agitated - Low urine output - Thirsty - Edema - Dry mouth [think: CANTS] - Convulsions - Arrythmias - Neuromuscular excitability - Tetany (muscle cramps) - Seizures [think: - OANS] - Groans: constipation - Moans: joint pain - Bones: fractures - Stones: kidney stones [think: 6Ls] - Lethargy - Leg cramps - Limp Muscles - Loss of appetite (anorexia) - Lots of urine (polyuria) - Lethal cardiac dysrhythmias [think: MURDER] - Muscle weakness - Urine loss - Respiratory distress - Diarrhea - Elevated BP & HR - Reflexes (flaccid) Chapter 8: Renal and Urological Disorders • Three Buffer Systems: 1. Protein 2. Phosphate 3. Carbon-acid bicarbonate (lungs & kidneys regulate the body’s acid-base balance with this - levels of “compensation”) • Hyperventilation - CO2 which raises pH • Hypoventilation - CO2 which decreases pH (most common cause of respiratory alkalosis) • ABG Values: - Blood pH: 7.35 - 7.45 (lower than 7.35 is acidic, higher than 7.45 is basic) - Partial pressure of oxygen (PO2): 90 - 100 (low levels need oxygen therapy) - Partial pressure of carbon dioxide (PCO2): 35 - 45 (lower than 35 is basic, higher than 45 is acidic) - Bicarbonate ion concentration (HCO3-): 22 - 26 (lower than 22 is acidic, higher than 26 is basic) • Four Acid-Base Disturbances: 1. Respiratory Acidosis 2. Respiratory Alkalosis 3. Metabolic Acidosis (found in: lactic acidosis, ketoacidosis, renal failure) 4. Metabolic Alkalosis Arterial Blood Gas Disorders 7.35 7.4 7.45 Acidosis pH 7.35 CO2 (respiratory) 45 HCO3 (metabolic) 22 Fully Compensated (look at direction of normal pH) Acidosis Normal Alkalosis pH X X Alkalosis 7.45 35 Normal 26 Partially Compensated (X are on opposite sides) Acidosis Normal Alkalosis pH X X Uncompensated (one X is in the middle) Acidosis Normal Alkalosis pH X X Chapter 9: Hormonal and Reproductive Disorders • Inflammation - protective response to an injury • Five Class Signs of Inflammation: 1. Rubor (redness) 2. Tumor (swelling) 3. Calor (heat) 4. Dolor (pain) 5. Loss of function (function laesa) • Five Types of White Blood Cells (WBC): [think: never let monkey eat banana] - Granulocytes (in histology cells appear to have granules) 1. Neutrophils (think: neutrophils means bacterial infection and acute inflammation aka Neutrophilia) - Tutor Example: purulent discharge (pus) after post-op is because of neutrophils 2. Basophils 3. Eosinophils - Agranulocytes 4. Lymphocytes 5. Monocytes (turn into macrophages) • Factors that Affect Healing Process: nutrition status, exercise, rest, oxygen supply, steroid use, diabetes Chapter 10 • Sepsis (septicemia) - infection of the bloodstream when the blood becomes contaminated - Hospitalized pt. is more vulnerable to infection because of illness, surgery, and other invasive procedures (ex: chemo is a procedure) - Rapid process results in lots of death • Iatrogenic - illness caused by medical examination or treatment (usually unwanted treatment - secondary diagnoses) Example: pt. admitted for sore throat gets pneumonia in hospital then gets bed sore • Levels of Defense for Infections: 1. Innate Immunity: immediately prevent the spread and movement of pathogens 2. Adaptive Immunity: developed after exposure to antigens and has memory for antigens, attacks non-self pathogens but sometimes attacks itself in error Example: autoimmune disorders like RA, • Maternal-Fetal Transmission: - Congenital Infection: infectious disease passed from mom to baby 1. Pathogens invade the mother’s bloodstream and placenta can pass into the fetal circulation 2. Mother’s infection can be transferred during childbirth when infected vaginal secretions and membranes come in contact with baby • Group B Streptococcus (GBS) - bacteria found in the intestine, vagina, rectum (pyogenesis) - Gram-positive - Mother rarely shows signs/symptoms but needs antibiotics (usually Penicillin) during labor - Can be deadly to baby; 5% mortality rate Type IgG IgA IgM IgE IgD Immunoglobins (Antibodies) [think: GAMED] Location Important Info - Throughout the bloodstream - Secondary exposure (ex: chickenpox that results in shingles later) - Breast milk, tears, saliva - Protective/preventive role for GI tract, respiratory tract, and genitourinary tract - Throughout bloodstream - First to be made to fight infection - Respiratory, GI tract, mast cells - Allergies - Mature B cells - Early stage/sign, antigen has first entered the body; exists in smallest amounts Chapter 11: Neurological Disorders • Active Acquired Adaptive Immunity - exposure to antigen (causes illness) or through a vaccine (provides immunization) Example: child gets measles infection then build immunity or child who gets the measles vaccine to build immunity • Passive Acquired Adaptive Immunity - pt. is given pre-made fully formed antibodies against an antigen (short term immunity) Example: infant is breastfed and receives fully formed maternally produced antibodies in breastmilk • Systemic Anaphylaxis - severe, life-threatening type I immediate hypersensitivity reaction (immediate EPI injection required) - Signs/Symptoms: hives, coughing, stridor, asthma attack, extreme anxiety, fainting • Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE) - chronic autoimmune inflammatory disease exhibits fever, rash, joint inflammation, damage to the kidneys, lungs, and serosal membranes - Signs/Symptoms: butterfly rash across bridge of nose and cheeks Extra Info from Tutor Session: • Covid (artificial active acquired) - Moderna and Pfizer are RNA rooted (scientific lab created) - Johnson & Johnson is live rooted (antibodies) • Aortic Stenosis - calcification (thrombosis formation) of the aortic valve; narrowing of the valve that impedes blood ejecting Prevention: exercise • Antipyretic - medication used to prevent or reduce fever Future Test Info: • Exam 2: Calcium, Phosphate, Magnesium imbalances • Final: Down’s Syndrome • HESI and Final: Chvostek’s Sign and Trousseau’s Sign