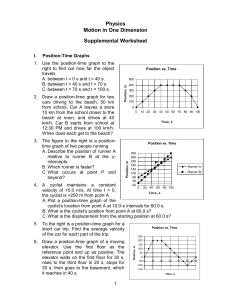
Physics Motion in One Dimension Supplemental Worksheet Position-Time Graphs 2. Draw a position-time graph for two cars driving to the beach, 50 km from school. Car A leaves a store 10 km from the school closer to the beach at noon, and drives at 40 km/h. Car B starts from school at 12:30 PM and drives at 100 km/h. When does each get to the beach? Position vs. Time 500 Position, m 1. Use the position-time graph to the right to find out how far the object travels A. between t = 0 s and t = 40 s. B. between t = 40 s and t = 70 s. C. between t = 70 s and t = 100 s. 3. The figure to the right is a positiontime graph of two people running. A. Describe the position of runner A relative to runner B at the yintercepts. B. Which runner is faster? C. What occurs at point P and beyond? 400 300 200 100 0 0 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100 Tim e, s Position vs. Time Position, m I. 300 260 220 180 140 100 60 20 -20 P Runner A Runner B 4. A cyclist maintains a constant 0 20 40 60 80 100 velocity of +5.0 m/s. At time t = 0, Tim e, s the cyclist is +250 m from point A. A. Plot a position-time graph of the cyclist’s location from point A at 10.0-s intervals for 60.0 s. B. What is the cyclist’s position from point A at 60.0 s? C. What is the displacement from the starting position at 60.0 s? 5. To the right is a position-time graph for a short car trip. Find the average velocity of the car for each part of the trip. 1 250 200 Position, m 6. Draw a position-time graph of a moving elevator. Use the first floor as the reference point and up as positive. The elevator waits on the first floor for 30 s, rises to the third floor in 20 s, stops for 30 s, then goes to the basement, which it reaches in 40 s. Position vs. Time 150 100 50 0 -50 0 10 20 30 -100 -150 Tim e, s 40 50 60 II. Velocity-Time Graphs Velocity vs. Tim e 8. Use the graph to the lower right to find the acceleration of the moving object A. during the first 5 s of travel. B. between the fifth and tenth second of travel. C. between the tenth and the fifteenth second of travel. D. between the twentieth and twentyfifth second of travel. 9. Use the graph to the right to find the distance the moving object travels between A. t = 0 s and t = 5 s. B. t = 5 s and t = 10 s. C. t = 10 s and t = 15 s. D. t = 0 s and t = 25 s. Velocity, m/s 60 50 40 30 20 10 0 0 2 4 6 Tim e, s Velocity vs. Time Velocity, m/s 7. Use the graph to the right to A. determine the acceleration of the moving object. B. calculate the distance the object moved during the first five seconds of motion. 35 30 25 20 15 10 5 0 0 5 10 15 20 25 Time, s 10. The velocity of an automobile changes over an 8.0-s time interval as shown in the table below. A. Plot the velocity-time graph of the motion. B. Determine the displacement of the car during the first 2.0 s. C. What displacement does the car have during the first 4.0 s? D. What displacement does the car have during the entire 8.0 s? E. Find the slope of the line between t = 0 s and t = 4.0 s. What does this slope represent? F. Find the slope of the line between t = 5.0 s and t = 7.0 s. What does this slope indicate? Time, s 0.0 1.0 2.0 3.0 4.0 5.0 6.0 7.0 8.0 Velocity, m/s 0.0 4.0 8.0 12.0 16.0 20.0 20.0 20.0 20.0 2 30 III. Acceleration-Time Graphs Acceleration vs. Time 60 Acceleration, m/s/s 11. Use the acceleration-time graph to the right to calculate the velocity of the object at the end of 10 s. 50 40 30 20 10 0 0 2 4 6 8 10 Time, s 12. Use the acceleration-time graph below to answer the following questions. A. Describe the type of motion between 0-3 s; 3-4 s; 4-8 s; 8-9 s; and 9-10 s. B. What is the acceleration during the first three seconds? Between 4 and 8 s? Between 9 and 10 s? C. How fast did the object travel during the first 3 s? How fast did the object travel between t = 4 s and t = 8 s? Acceleration vs. Time Acceleration, m/s/s 60 50 40 30 20 10 0 0 2 4 6 8 10 Time, s Answers to the Odd-Numbered Problems: 1. 3. A. 400 m; B 0 m; C. -400 m A. Runner A is 60 m ahead of Runner B; B. Runner B is faster; C. Runner B is ahead of Runner A. 5. 20 m/s; 0 m/s; -10 m/s; 10 m/s 7. A. 10 m/s2; B. 125 m 9. A. 75 m; B 150 m; C. 125 m; D. 500 m 11. 500 m/s 3