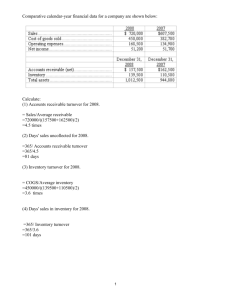
Problem 13-4B
1) Current Ratio
Current Assets
Current Liabilities
6,100 + 6,900+ 15,100 + 13,500 + 2,000
=
11,500+3,300+2,600
=
=
43,600
17,400
= 2.5 : 1
2) Acid-Test Ratio
𝑄𝑢𝑖𝑐𝑘 𝐴𝑠𝑠𝑒𝑡𝑠
𝐶𝑢𝑟𝑟𝑒𝑛𝑡 𝐿𝑖𝑎𝑏𝑖𝑙𝑡𝑖𝑒𝑠
𝐶𝑢𝑟𝑟𝑒𝑛𝑡 𝐴𝑠𝑠𝑒𝑡𝑠 − 𝐼𝑛𝑣𝑒𝑛𝑡𝑜𝑟𝑖𝑒𝑠 − 𝑃𝑟𝑒𝑝𝑎𝑖𝑑 𝐸𝑥𝑝𝑒𝑛𝑠𝑒𝑠
=
𝐶𝑢𝑟𝑟𝑒𝑛𝑡 𝐿𝑖𝑎𝑏𝑖𝑙𝑖𝑡𝑖𝑒𝑠
43,600 − 13,500 − 2,000
=
17,400
=
=
28,100
17,400
= 1.6 : 1
3) Days’ sales uncollected
=
𝐴𝑐𝑐𝑜𝑢𝑛𝑡𝑠 𝑅𝑒𝑐𝑒𝑖𝑣𝑎𝑏𝑙𝑒
× 365
𝑁𝑒𝑡 𝐶𝑟𝑒𝑑𝑖𝑡 𝑆𝑎𝑙𝑒𝑠
15,100
=
× 365
315,500
= 17.5 𝑑𝑎𝑦𝑠
4) Inventory Turnover
=
𝐶𝑜𝑠𝑡 𝑜𝑓 𝐺𝑜𝑜𝑑𝑠 𝑆𝑜𝑙𝑑
𝐴𝑣𝑒𝑟𝑎𝑔𝑒 𝐼𝑛𝑣𝑒𝑛𝑡𝑜𝑟𝑦
=
236,100
(17,400 + 13,500)/2
= 15.3
5) Days’ sales in Inventory
=
365 𝑑𝑎𝑦𝑠
𝐼𝑛𝑣𝑒𝑛𝑡𝑜𝑟𝑦 𝑇𝑢𝑟𝑛𝑜𝑣𝑒𝑟 𝑅𝑎𝑡𝑖𝑜
=
365
15.3
= 23.9 𝑑𝑎𝑦𝑠
6) Debt-to-Equity Ratio
=
𝐷𝑒𝑏𝑡
𝐸𝑞𝑢𝑖𝑡𝑦
=
30,000
70,100
= 0.43 ∶ 1
7) Times Interest Earned
=
𝐸𝑎𝑟𝑛𝑖𝑛𝑔𝑠 𝑏𝑒𝑓𝑜𝑟𝑒 𝐼𝑛𝑡𝑒𝑟𝑒𝑠𝑡 & 𝑇𝑎𝑥𝑒𝑠
𝐼𝑛𝑡𝑒𝑟𝑒𝑠𝑡
28,000 + 2,200
=
2,200
= 13.7 times
8) Profit Margin Ratio
𝑁𝑒𝑡 𝑃𝑟𝑜𝑓𝑖𝑡
× 100
𝑆𝑎𝑙𝑒𝑠
23,800
=
× 100
315,500
=
=7.5%
9) Total Asset Turnover
=
𝑁𝑒𝑡 𝑆𝑎𝑙𝑒𝑠
𝐴𝑣𝑒𝑟𝑎𝑔𝑒 𝑇𝑜𝑡𝑎𝑙 𝐴𝑠𝑠𝑒𝑡𝑠
=
315,500
(94,900 + 117,500)/2
=
315,500
106,200
=3
10) Return on Total Assets
=
𝑁𝑒𝑡 𝑃𝑟𝑜𝑓𝑖𝑡
× 100
𝐴𝑣𝑒𝑟𝑎𝑔𝑒 𝑇𝑜𝑡𝑎𝑙 𝐴𝑠𝑠𝑒𝑡𝑠
=
23,800
× 100
(94,900 + 117,500)/2
=
23,800
× 100
106,200
= 22.4%
11) Return on Common Stockholders’ Equity
=
=
𝑁𝑒𝑡 𝑃𝑟𝑜𝑓𝑖𝑡
× 100
𝐴𝑣𝑒𝑟𝑎𝑔𝑒 𝐸𝑞𝑢𝑖𝑡𝑦 𝑆ℎ𝑎𝑟𝑒ℎ𝑜𝑙𝑑𝑒𝑟𝑠 ′ 𝑓𝑢𝑛𝑑𝑠
23,800
× 100
({35,500 + 18,800} + {35,000 + 35,100})/2
=
23,800
× 100
62,200
= 38.3%
Problem 13-5A
1)
Sr.
No.
a)
Particulars
Barco Company
Current Ratio
=
Current Assets
Current Liabilities
b)
Acid Test Ratio
𝑄𝑢𝑖𝑐𝑘 𝐴𝑠𝑠𝑒𝑡𝑠
𝐶𝑢𝑟𝑟𝑒𝑛𝑡 𝐿𝑖𝑎𝑏𝑖𝑙𝑡𝑖𝑒𝑠
c)
Accounts Receivable Turnover
𝑁𝑒𝑡 𝐶𝑟𝑒𝑑𝑖𝑡 𝑆𝑎𝑙𝑒𝑠
𝐴𝑣𝑒𝑟𝑎𝑔𝑒 𝐴𝑐𝑐𝑜𝑢𝑛𝑡𝑠 𝑅𝑒𝑐𝑒𝑖𝑣𝑎𝑏𝑙𝑒
d)
Inventory Turnover
𝐶𝑜𝑠𝑡 𝑜𝑓 𝐺𝑜𝑜𝑑𝑠 𝑆𝑜𝑙𝑑
𝐴𝑣𝑒𝑟𝑎𝑔𝑒 𝐼𝑛𝑣𝑒𝑛𝑡𝑜𝑟𝑦
e)
𝐴𝑣𝑔. 𝐴𝑐𝑐𝑜𝑢𝑛𝑡𝑠 𝑅𝑒𝑐𝑒𝑖𝑣𝑎𝑏𝑙𝑒
× 365
𝑁𝑒𝑡 𝐶𝑟𝑒𝑑𝑖𝑡 𝑆𝑎𝑙𝑒𝑠
=
238,050
93,300
=2.6 : 1
19,500 + 46,500
61,340
34,000 + 64,600
93,300
= 1.1 ∶ 1
= 1.1 ∶ 1
770,000
(29,800 + 46,500)/2
880,200
(54,200 + 64,600)/2
= 20.2
= 14.8
585,100
(55,600 + 84,440)/2
632,500
(107,400 + 132,500)/2
= 8.4
= 5.3
365
8.4
365
5.3
= 43.5 days
= 68.9 days
Days’ sales in Inventory
Days’ sales uncollected
155,440
61,340
=2.5 : 1
365 𝑑𝑎𝑦𝑠
𝐼𝑛𝑣𝑒𝑛𝑡𝑜𝑟𝑦 𝑇𝑢𝑟𝑛𝑜𝑣𝑒𝑟 𝑅𝑎𝑡𝑖𝑜
f)
Kyan Company
=
38,150
× 365
770,000
= 18.1 days
=
59,400
× 365
880,200
= 24.6 days
Interpretation –
Barco Company is better for short-term credit risk because of the following reasons –
i.
Higher Accounts Receivable Turnover – It indicates that the company has better
efficiency in collection of account receivables
ii.
Higher Inventory Turnover Ratio – A higher ratio signifies that the inventory is
quickly used and has a lower stay life on shelf indicating better liquidity
iii.
iv.
v.
Lower Days’ sales in inventory - A smaller number indicates that the company is
more efficiently and frequently selling off its inventory.
Less Days’ sales uncollected – The lower figure indicates appropriate credit
standards and adequate collection activities
Liquidity ratios – The company has similar Current Ratio and Acid-Test Ratio in
comparison to Kyan Company
2)
Sr.
No.
Particulars
Barco Company
Kyan Company
Profit Margin Ratio
162,200
× 100
770,000
210,400
× 100
880,200
= 21.1%
=23.9%
770,000
(398,000 + 445,440)/2
880,200
(382,500 + 542,450)/2
a)
𝑁𝑒𝑡 𝑃𝑟𝑜𝑓𝑖𝑡
× 100
𝑆𝑎𝑙𝑒𝑠
Total Assets Turnover
b)
𝑁𝑒𝑡 𝑆𝑎𝑙𝑒𝑠
𝐴𝑣𝑒𝑟𝑎𝑔𝑒 𝑇𝑜𝑡𝑎𝑙 𝐴𝑠𝑠𝑒𝑡𝑠
Return on Total Assets
c)
=
Return on Common
=
880,200
462,475
=1.8
=1.9
162,200
× 100
421,720
210,400
× 100
462,475
= 38.5%
=45.5%
162,200
× 100
(278,300 + 303,300)/2
210,400
× 100
(299,600 + 348150)/2
𝑁𝑒𝑡 𝑃𝑟𝑜𝑓𝑖𝑡
× 100
𝐴𝑣𝑔. 𝑇𝑜𝑡𝑎𝑙 𝐴𝑠𝑠𝑒𝑡𝑠
d)
770,000
421,720
Shareholders’ Equity
𝑁𝑒𝑡 𝑃𝑟𝑜𝑓𝑖𝑡
× 100
𝐴𝑣𝑔. 𝐸𝑞𝑢𝑖𝑡𝑦 𝑓𝑢𝑛𝑑𝑠
=
162,200
× 100
290,800
=55.8%
Price Earnings Ratio
=
e)
𝑀𝑎𝑟𝑘𝑒𝑡 𝑉𝑎𝑙𝑢𝑒 𝑝𝑒𝑟 𝑠ℎ𝑎𝑟𝑒
𝐸𝑎𝑟𝑛𝑖𝑛𝑔𝑠 𝑝𝑒𝑟 𝑠ℎ𝑎𝑟𝑒
Dividend Yields
=16.6
=
f)
𝐷𝑖𝑣𝑖𝑑𝑒𝑛𝑑 𝑝𝑒𝑟 𝑠ℎ𝑎𝑟𝑒
𝑀𝑎𝑟𝑘𝑒𝑡 𝑉𝑎𝑙𝑢𝑒 𝑝𝑒𝑟 𝑠ℎ𝑎𝑟𝑒
× 100
75
4.51
3.81
× 100
75
=5.1%
=
210,400
× 100
323,875
=65%
=
75
5.11
=14.7
3.93
× 100
75
=5.2%
Interpretation –
Kyan Company’s stock is better in terms of its investment potential because of the following
reasons –
i.
Higher rate of return – The company has better Profit Margin Ratio, Return on Total
Assets and Retun on Common Shareholders’ Equity. Thus, it creates a higher income in
proportion to its sales, assets and net worth as compared to Barco Company
ii.
Higher Total Assets Turnover – A higher ratio indicates that the company is making
effective use of its assets for generating sales.
iii.
Higher Dividends Yield – Kyan Company pays higher divided per Rupee of investment
made
iv.
Lower Price Earnings Ratio – Along with the above ratios, a lower Price Earnings Ratio
represents that the company is currently undervalued and the share price is expected
to rise in the future leading to higher returns on investment.