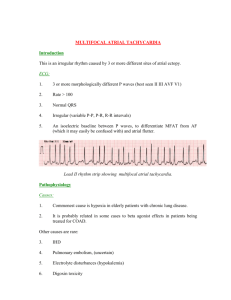
Arrhythmia: Definition, Types, Risk Factors, and Nursing Care
advertisement

Arrhythmia BSN 4B - Group 5 Table of contents 01 Definition 05 Diagnostic Tests 02 Key Points & Classification 06 Pathophysiology 03 Risk Factors 07 Clinical Manifestations 04 Etiology 08 Nursing Intervention 01 Definition What is Arrhythmia? Cardiac Rhythm Cardiac rhythm is the pattern or pace of the heartbeat. The usual cardiac rhythm is called Normal Sinus Rhythm Characteristic of Normal Sinus Rhythm •Heart rate is between 60 and 100 beats/minute. •The SA node initiates the impulse (upright P wave before each QRS complex). •Impulse travels to the AV node in 0.12 to 0.2 second (the PR interval). •The ventricles depolarize in 0.12 second or less (the QRS complex). •Each impulse occurs regularly (evenly spaced). What is Arrhythmia? •Arrhythmias result from abnormal electrical conduction or automaticity that changes heart rate and rhythm. It Vary in severity, from those that are mild asymptomatic, and require no treatment (such as sinus arrhythmia, in which heart rate increases and decreases with respiration) to catastrophic ventricular fibrillation, which requires immediate intervention. • Also called as Dysrhythmia. 02 Key Points & Classifications Key Points & Classifications •Arrhythmias are classified according to their origin; •Arrhythmia originating in the atria •Arrhythmia originating in AV node •Arrhythmia originating in the ventricles •Their effect on cardiac output and blood pressure, partially influenced by the site of origin, determines their clinical significance. •The volume of blood ejected from the heart per minute, may be greatly compromised when a rhythm disturbance develops. Sinus Arrhythmia Sinus arrhythmia occurs when the sinus node creates an impulse at an irregular rhythm; the rate usually increases with inspiration and decreases with expiration. Sinus Bradycardia Sinus Tachycardia Sinus bradycardia occurs when the SA node creates an impulse at a slower than normal rate. Sinus tachycardia occurs when the sinus node creates an impulse at a faster than normal rate. Atrial Arrhythmia Premature Atrial Complex Atrial Fibrillation Atrial Flutter A PAC is a single ECG complex that occurs when an electrical impulse starts in the atrium before the next normal impulse of the sinus node Atrial Fibrillation is a common arrhythmia. Several areas in the right atrium initiate impulses resulting in disorganized, rapid activity. Atrial flutter occurs because of a conduction defect in the atrium and causes a rapid, regular atrial impulse at a rate between 250 and 400 bpm. Junctional Arrhythmia Premature Junctional Complex A premature junctional complex is an impulse that starts in the AV nodal area before the next normal sinus impulse reaches the AV node Junctional Rhythm 01 02 Atrioventricular Nodal Reentry Tachycardia Nonparoxysmal Junctional Tachycardia Junctional tachycardia is caused by enhanced automaticity in the junctional area, resulting in a rhythm similar to junctional rhythm, except at a rate of 70 to 120 bpm. Junctional or idionodal rhythm occurs when the AV node, instead of the sinus node, becomes the pacemaker of the heart. 03 04 a common arrhythmia that occurs when an impulse is conducted to an area in the AV node that causes the impulse to be rerouted back into the same area over and over again at a very fast rate. Symptoms of the disease Premature Ventricular Complex Idioventricular Rhythm an impulse that starts in a ventricle and is conducted through the ventricles before the next normal sinus impulse. also called ventricular escape rhythm, occurs when the impulse starts in the conduction system below the AV node. Ventricular Tachycardia Ventricular Asystole defined as three or more PVCs in a row, occurring at a rate exceeding 100 bpm. Commonly called flatline, ventricular asystole is characterized by absent QRS complexes confirmed in two different leads, although P waves may be apparent for a short duration. Ventricular Tachycardia a rapid, disorganized ventricular rhythm that causes ineffective quivering of the ventricles. Conduction Abnormalities First Degree Atrioventricular Block occurs when all the atrial impulses are conducted through the AV node into the ventricles at a rate slower than normal. Second Degree Atrioventricular, Type 1 occurs when there is a repeating pattern in which all but one of a series of atrial impulses are conducted through the AV node into the ventricles. Second Degree Atrioventricular, Type 2 occurs when only some of the atrial impulses are conducted through the AV node into the ventricles. First Degree Atrioventricular Block occurs when no atrial impulse is conducted through the AV node into the ventricles. 03 Risk Factors What are the risk factors of Arrhythmia? Risk factors ● ● ● Aging Cardiovascular Conditions ○ CAD ○ Heart Failure ○ Cardiomyopathy ○ Hypertension Medicines and Other Substances ○ Smoking ○ Alcohol Consumption ○ Too much caffeine consumption ○ OTC medicines such as those used to treat cough or colds ○ ○ ● Prescription medicine used to treat asthma, heart problems, thyroid problems, and pain Illegal drugs Other Risk Factors ○ Prior heart surgery ○ Diabetes ○ Sleep apnea ○ Chronic Stress ○ Eating disorders ○ Electrolyte imbalances 04 Etiology What causes Arrhythmia? Etiology Congenital Myocardial Ischemia Myocardial Infarction Organic Heart Disease Drug Toxicity Degeneration of Conductive Tissue 05 Diagnostic Tests DIAGNOSTIC TEST Electrocardiography (ECG) allows detection and identification of arrhythmias. 06 Pathophysiology 07 Clinical Manifestations Clinical Manifestations Palpitation: A feeling of skipped heartbeat or that your heart is "running away,' fluttering or doing "flip-flops." Pounding in your chest. Dizziness or feeling lightheaded. Shortness of breath. Chest discomfort. Weakness or fatigue Weakening of the heart muscle or low ejection fraction. 08 Nursing Interventions Nursing Interventions Monitoring and Managing Arrhythmias The nurse regularly evaluates the patient's blood pressure, pulse rate and rhythm, rate and depth of respirations, and breath sounds to determine the arrhythmia’s hemodynamic effect. The nurse also asks the patient about episodes of lightheadedness, dizziness, or fainting as part of the ongoing assessment. ● Administration of anti-arrhythmic medication and evaluation of its effects: ○ ○ ○ ○ ○ Sodium channel blockers Beta - blockers Potassium channel blockers Nondihydropyridine calcium channel blockers Anticoagulants Nursing Interventions Monitoring and Managing Arrhythmias ● ● The nurse may also conduct a 6-minute walk test as prescribed, which is used to identify the patient's ventricular rate in response to exercise. The nurse assesses for factors that contribute to the dysrhythmia (eg, oxygen deficits, acid-base and electrolyte imbalances, caffeine, or non-adherence to the medication regimen). Monitor for ECG changes. Nursing Interventions Monitoring and Managing Arrhythmias ● ● The nurse may also conduct a 6-minute walk test as prescribed, which is used to identify the patient's ventricular rate in response to exercise. The nurse assesses for factors that contribute to the dysrhythmia (eg, oxygen deficits, acid-base and electrolyte imbalances, caffeine, or non-adherence to the medication regimen). Monitor for ECG changes. Nursing Interventions Minimizing Anxiety ● When the patient experiences episodes of dysrhythmia, the nurse stays with the patient and provides assurance of safety and security while maintaining a calm and reassuring attitude. Nursing Interventions Promoting Home and Community-Based Care ● ● ● The nurse clearly explains treatment options to the patient and family. The patient and family need to know what measures to take to decrease the risk of recurrence of the arrhythmia. If the patient has a potentially lethal dysrhythmia, it is also important to establish with the patient and family a plan of action to take in case of an emergency and, if appropriate, to encourage a family member to obtain CPR training. END ;) Thanks! Created by: Denesa Joyce Bustamante Presented by: Group 5 Acosta, Airelle Joyce C. Angeles, Jelyn Nicole G. Bustamante, Denesa Joyce Z. David, Jovert Garcia, Michael Vince G. Lagpao, Moira Abbygaile Musni, Theo Roi N. Ramos, Ariane Mae CREDITS: This presentation template was created by Slidesgo, including icons by Flaticon, and infographics & images by Freepik Icon pack