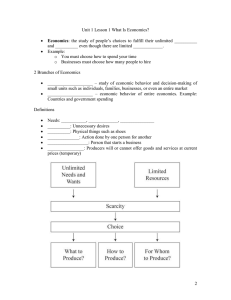
Grade 7 Training manual 2017 EMS: Economics Needs and Wants Term 1 NEEDS AND WANTS Glossary of Terms: Learners must first give an description of the following words in their notebook: CONCEPT DESCRIPTION Needs Wants Primary needs Secondary needs Limited wants Scarcity Physical needs Security needs Goods Services Community Resources Natural resources Labour Capital Factors of production Technical effienciency Effective efficiency Bl. 1 van 12 2 Economics Needs and Wants: Term 1 THE ECONOMY LESSON PLAN Subject: EMS Grade: 7 Educator(s) Signature: Topic: Needs and wants Date: HOD Signature: Term: 1 Week: 8 - 10 Duration: 3 weeks 6 hrs 12 periods of 30 minutes Prior content knowledge: Content: • • • • • • • • • • Links with next lesson History of Money • Goods and services Vocabulary/Important words: Explain the concept of needs. Explain the concept of wants. Describe the differences of needs and wants. How do we satisfy our needs as individuals, families, communities and countries Primary and secondary needs Unlimited wants Limited Resources Impact of differences the community. Impact of differences on the environment. Basic needs Individuals Communities Resources Environment Aims and Objectives of the lesson By the end of the lesson learners will be able to: Differentiate between needs and wants Identify and discuss the needs of individuals, families, communities and countries Distinguish between primary and secondary needs Discuss unlimited wants and give examples Discuss limited resources to satisfy needs and wants Teaching Methods: Discussion Differentiation (Enrichment opportunities/ addressing barriers to learning) Comparing the needs of different individuals, families, communities and countries Bl. 2 van 12 Economics Needs and Wants: Term 1 3 Brainstorming Look for pictures representing the different needs and wants Question and answer Keyword list with different words and explanations Report Allow learners to design own posters on how to conserve our planets natural resources. Poster can be exhibited in the school administration block. Debate Visual aids Allow learners to complete extra activities if time allows or do it as revision. Case Studies Examples from the community Guest speakers ASSESSMENT STRATEGY: Formal Form of assessment: Informal X X Assessment tool: Memo and checklist/Rubric Class work and Assignment (question and answer , report writing , case studies , scenarios , picture interpretation) Teacher Activities • Baseline assessment • Discuss previous knowledge held by learners (what is a need, what is want, list own needs and own wants, needs of local shop/community, etc.) • Educator to develop notes on the following terms for learners to record in class work books: ü Needs ü Wants ü Individuals ü Families ü Communities ü Countries ü Environment • • • • Learning Activities • Learners explain the concepts of needs and wants. • Leaners describes own needs and wants as well as those of the community and environment. • Learners takes down notes from the chalkboard 1&2 Educator discuss and explain the difference between needs and wants Educator to provide notes on the differences of needs and wants • Educator to discuss the four categories of needs and wants. • Educator develop a notes on the four categories of needs and wants namely Survival needs, security needs, social needs, self-esteem needs Learners write down the difference between needs and wants as the educator explain. • Learners complete the class notes on the difference between needs and wants • Learners to participate in classroom discussion on the four categories of needs. Learners to complete notes provided by educator Bl. 3 van 12 4 Economics Needs and Wants: Term 1 Period 3&4 5&6 Describe to learners how people satisfy their needs. Define and discuss with examples the following terms: ü Goods ü Resources ü Unlimited wants ü Scarcity ü Limited resources ü Satisfy ü Non – Renewable Resources ü Renewable resources ü Economic Problem Educator to ensure that learners understand that needs and wants are satisfied by the purchasing of goods and services and in turn goods and services are produced by resources. • Learner to participate in educators description on how needs are satisfied • Learners to ask clarity seeking questions • Learners to participate in discussion of concepts • Learner to undertake activity • Learners are provided with activities to consolidate above knowledge • Discuss the impact needs and wants have on the environment and community. Learners to brainstorm ideas on how to minimize the impact of products on the environment (Limited resources) • Participate in the discussion on the impact needs and wants on the environment and community • Brainstorm ideas on how to minimise the impact of products on the environment • • • • • • Discuss how learners can develop an environmental footprint of one of their favourite things Allow learners to complete assignment in class 7, 8, 9 & 10 11 & 12 • Learners to develop environmental footprint of favourite thing • Learners complete assignment in class Resources Text books Internet Newspapers Magazines Stationery black board Teacher’s comments/reflection: HOD input: monitoring and support: Bl. 4 van 12 Economics Needs and Wants: Term 1 5 What are we going to learn? • • • • • • Analyse the basic needs of individuals, families, communities and countries. Discuss primary and secondary needs Explain how needs are satisfied Discuss the unlimited wants of individuals and the problem of scarcity. Explain why resources are limited Types of effectiveness in use of resources Needs and wants What do you need to survive? • • A need is something you have to have in order to stay alive. A want is something you would like to have but it is not necessary for your survival Basic needs Needs and wants influence our communities through the following ways: • • • • They determine what kind of products and services in the community sold or offered. This may have an impact on how communities work People in poor communities whose basic needs are not provided for, will not apply to spending by failing to support local shops and businesses in their communities. People in wealthier communities will spend money at shops and businesses in their communities so that communities will be more prosperous. Basic, primary and secondary needs Basic or primary needs - Physical needs - Safety needs Secondary needs - Needs that our survival does not depend on. Bl. 5 van 12 6 Economics Needs and Wants: Term 1 Unlimited needs with limited resources • • • • Individuals, families, communities and countries all unlimited wants. We do not have enough resources to meet our needs. Money has evolved to enable people to satisfy more easily their needs and desires. There's a certain amount of money in the world and economic activity can only satisfy a limited number of needs and desires. Economic problem The problem caused by the limited resources they have available to satisfy people's unlimited wants. • • • • natural resources = all the gifts from the nature labour = all the people of a country's capacity to work. capital = money a country for goods and services to produce. production factors = the inputs used to produce goods and services. Types of effectiveness in the use of resources Technical efficiency • Countries must use all the resources (land, labour and capital). Effective efficiency • Countries should produce more of the goods and services where there is a greatest demand. Bl. 6 van 12 Economics Needs and Wants: Term 1 7 CLASSROOM ACTIVITIES ACTIVITY 1: CLASS WORK Word search: Concepts W A N T S A B G H T Y C K L O L U I O P M U N L I M I T E D F J K W Q P D F F T R E C R C G E O E H Y I R R B S W L O B J T M R T W B A E E S R F G G G E R D G A T D M F O H M F F H I A Z P F O O G F H E C M D F F I G T T B A F E H R Y F M B P J I G B Y N L R E V Y Y B Z G E A E B G G M T Y D H D D F Y S H R U T E U T H N P G K E N C P S T A F F P S E T T A V U U Y B S G B F J B N G L K E J H L S I T D D E P Y Q D G I D D H H R T J R J R A J N T U H I U O L D U Y M S N A O S A L R R S T T A S I Y Y S K A U F W U M G K U T K V O Y K J J D T W O X C A T D S U A N F K K S O G B K N E E D S I J Y O E P J I M H O H H R B E Y N C S J L S T M O E C B L L R Q F J H L I F O T D H L K Q O E U R N T G U B G I R O I B P C Y F E S D D R H O I L G P R X G O I S G R K F M Y B O T T I G N O T L T T R G B C R T F P K K B T Y R F P L D L I I S C A R C I T Y H T K F H O I E O N G F H S E C R U O S E R L A F A G L B J U T P Y Y K N H T D G R N D O F T C J D P F F H R R G R A S R N H M U U J B L H N K I E A G D T D N D R O X U E L D G T F E F D S F G I T N Y Y G F A J X L K T N O R U T M S B I V T W A V B R D A D P D N Y F P B C T N C N U C O P A G I E G R S D H K T R A N B N B D C H O I C E Z A V A K J X S N R O L B I L B R O E F R M R B Z S N D N D D R O R D N E T C R L K Z T M G M I L B V N T P F R D F S T O O L S E S S E R V V B R H F S D L T O I P G N E L B M D P W E R D F G T J U I K O L P G F D S A N T S G T Y J I L T J S E H K S O E R T Y U I K L O M V E H I C L E S R T Y U I O P M K L Y R U O B A L CLUES: 1. Something that you want to have, but necessary for survival. 2. Something you can touch and see. 3. The value of the best alternative that could have been chosen, but was not chosen. 4. Goods ready to be sold. 5. Goods that last for years and years. 6. You only have so many needs. 7. Physical and mental activities. 8. First and important part of the economy. 9. An example of a capital good. 10. Money you need to start your own business. 11. Unlimited wants and limited resources. 12. Place on earth where people live. 13. People that cannot satisfy basic needs. 14. An example of a natural resource. 15. Goods that you use to produce more goods. 16. A group of people living together. 17. An alternative selected above another. 18. Something you have to have in order to stay alive. 19. Things you need to satisfy unlimited wants. 20. You have so much wants. Bl. 7 van 12 8 Economics Needs and Wants: Term 1 Activity 2 Study the following cartoon and answer the questions that follows: 1. What does the above cartoon predict? 2. Name the type of scarcity in the cartoon? 3. In which province is the biggest drought in South Africa? 4. Name 3 methods how we can save water. 5. Name the minister of water and sanitation. Bl. 8 van 12 Economics Needs and Wants: Term 1 9 Activity 3 Study the following graph and answer the questions that follows: 1. Which sector needs the most water? 2. What will happen in this sector if the drought continues in South Africa? 3. Which sector uses the least water? 4. Why does this sector not need so much water? 5. What sector uses the second most water? 6. Where does this water from municipals go? 7. In your opinion, is the drinking water in South Africa safe? Bl. 9 van 12 10 Economics Needs and Wants: Term 1 Activity 4 Read the following article and answer the questions that follows: Western Cape could run out of dam water by 2019 Government has predicted fresh water demand will exceed supply, due to population growth, among other reasons. CAPE TOWN – The Western Cape government says the province could run out of fresh water in dams by 2019 if water resources are not managed properly. Government has predicted fresh water demand will exceed supply, due to population growth and limited water resources. Experts such as those at the World Wildlife Fund (WWF) say the province will survive the current dry season, but they warn government needs to start implementing long-term solutions to increase supply before the situation reaches a critical level. Environmental Affairs MEC Anton Bredell says government will have to look at how it manages water resources in preparation for a population increase in the Western Cape. "Studies show that we're going to run out of water by 2019. Population growth is obviously one of the things we're going to need to manage." Bredell says population growth will affect many sectors. "You need to plan for that, to get ahead of the curve. People use resources. We will need to look at our water resource, but also sanitation, transport, hospitals, clinics, schools and all these things, there will be pressure on it." In 2016 the province had a population of 6.4 million people and Bredell says the population is expected to grow by two million people in the next 15 years, or even sooner. Article by Monique Mortlock (05 March 2017) 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Why would the Western Cape run out of water in 2019? What does the abbreviation WWF stand for? Who is the MEC of Environmental affairs? What other things will also be affected by population growth? What is the current population in the Western Cape? What causes population growth? Bl. 10 van 12 Economics Needs and Wants: Term 1 11 Activity 5 Study the following pictures and identify the different needs and wants. Activity 6 1. Read the stories below. Draw a mind map for each family. Show their basic needs and how they are satisfied. Case study Family in a rural area Jubu lives with his sister, brother and grandparents in a village in KwaZulu-Natal. They have some goats and a vegetable patch. Jabu and his brother look after the goats and gather wood and his sister fetches water from a river 2 km away. The children walk to school when they are not needed to help at home. Their grandmother cooks their food of mealie meal and vegetables on an outside fire. Their home is a thatched-roof hut with one room where they all sleep together. Their grandparents buy clothes and other things they need with their monthly government pension money. Bl. 11 van 12 12 Economics Needs and Wants: Term 1 Family in an urban area Neo lives with his parents in a small house his family rents in a suburb of Johannesburg. His mother is a secretary and his father works in the post office. Neo catches the bus to school every day. Neo’s father buys food from the shops at the nearby shopping centre. While his mother cooks supper of pap, meat and vegetables on the electric stove. Neo does his homework. After supper, he helps to wash dishes, watches some television, has a shower and goes to bed in his bedroom. His parents buy clothes and other things they need and want from shops in the shopping centre with the money from their salaries. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. What are the basic needs of communities and countries? What are primary and secondary needs? What are wants and why are they said to be unlimited? What are resources and what does it mean if they are limited? What should you do if you have a limited resource such as a limited amount of money? Bl. 12 van 12 Economics Needs and Wants: Term 1 13 14 Economics Needs and Wants: Term 1 Economics Needs and Wants: Term 1 15 16 Economics Needs and Wants: Term 1 Economics Needs and Wants: Term 1 17 18 Economics Needs and Wants: Term 1 Economics Needs and Wants: Term 1 19 20 Economics Needs and Wants: Term 1 Economics Needs and Wants: Term 1 21 22 Economics Needs and Wants: Term 1 Economics Needs and Wants: Term 1 23 24 Economics Needs and Wants: Term 1 Economics Needs and Wants: Term 1 25 26 Economics Needs and Wants: Term 1 Economics Needs and Wants: Term 1 27 28 Economics Needs and Wants: Term 1 Economics Needs and Wants: Term 1 29 30 Economics Needs and Wants: Term 1 Economics Needs and Wants: Term 1 31 32 Economics Needs and Wants: Term 1 Economics Needs and Wants: Term 1 33 34 Economics Needs and Wants: Term 1 Economics Needs and Wants: Term 1 35 36 Economics Needs and Wants: Term 1 Economics Needs and Wants: Term 1 37 38 Economics Needs and Wants: Term 1 Economics Needs and Wants: Term 1 39 40 Economics Needs and Wants: Term 1