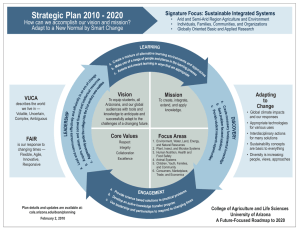
ETHICS TO HANDLE VUCA ENVIRONMENT By: Sagar Tewari A023119819024 B .Tech (A.I.) WHAT IS VUCA ENVIRONMENT ? ● ● ● ● Volatile – Change is rapid and unpredictable in its nature and extent. Uncertain – The present is unclear and the future is uncertain. Complex – Many different, interconnected factors come into play , with the potential to cause chaos and confusion. Ambiguous – There is lack of clarity or awareness about situations. Volatility Volatility is the V component of VUCA. This refers to the different situational social-categorization of people due to specific traits or reactions that stand out during that situation. Volatility is the changing dynamic of social-categorization in a set of environmental situations. The dynamic can change due to any shift in a situation, whether it is social, technical, biological or anything of the like. Studies have been conducted, but it has proven difficult to find the specific component that causes the change in situational socialcategorization. Uncertainty Uncertainty is the U component of VUCA. Uncertainty in the VUCA framework is almost just as it sounds: when the availability or predictability of information in events is unknown. Uncertainty often occurs in volatile environments that are complex in structure involving unanticipated interactions that are significant in uncertainty. Uncertainty may occur in the intention to imply causation or correlation between the events of a social perceiver and a target. Situations where there is either a lack of information to prove why a perception is in occurrence or informational availability but lack of causation are where uncertainty is salient. Complexity Complexity is the “C” component of VUCA. This refers to the different situational social-categorization of people due to specific traits or reactions that stand out during that situation. It refers to the interconnectivity and interdependence of multiple components in a system. The results of a deliberately controlled environment are unexpected because of the non-linear interaction and interdependencies within different groups and categories. Ambiguity Ambiguity is the “A” component of VUCA. This refers to when the general meaning of something is unclear even when an appropriate amount of information is provided. Uncertainty is when relevant information is unavailable and unknown, and ambiguity where relevant information is available but the overall meaning is still unknown. Ambiguity leads to people assuming an answer, and many times this leads assuming ones race, gender, and can even lead to class stereotypes. ETHICS TO HANDLE Volatility • • • • Become adaptive in decision-making Have clarity of vision, short and medium-term Communicate clearly to reduce confusion Determine your intent and resolve Uncertainty • • • • Flexibility to cope with doubt Build commitment and consensus of approach Develop new perspectives Create risk-management ideologies ETHICS TO HANDLE Complexity • • • • Understand the links between cause and effect Simplify processes and procedures Recognize nothing is permanent Encourage development and generation of ideas Ambiguity • • • • Communicate directly and with clarity Seek out and uncover alternative viewpoints Listen to divergent ideas and concepts Learn lessons that can apply in various circumstances