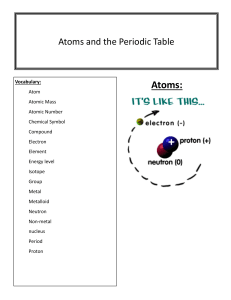
Atomic Theory Democritus first suggested the existence of the atom but it took almost two millennia before the atom was placed on a solid foothold as a fundamental chemical object by John Dalton (1766-1844). Although two centuries old, Dalton's atomic theory remains valid in modern chemical thought. Dalton's Atomic Theory 1) All matter is made of atoms. Atoms are indivisible and indestructible. 2) All atoms of a given element are identical in mass and properties 3) Compounds are formed by a combination of two or more different kinds of atoms. 4) A chemical reaction is a rearrangement of atoms. Modern atomic theory is, of course, a little more involved than Dalton's theory but the essence of Dalton's theory remains valid. Today we know that atoms can be destroyed via nuclear reactions but not by chemical reactions. Also, there are different kinds of atoms (differing by their masses) within an element that are known as "isotopes", but isotopes of an element have the same chemical properties. Many heretofore unexplained chemical phenomena were quickly explained by Dalton with his theory. Dalton's theory quickly became the theoretical foundation in chemistry. Postulates of Dalton's atomic theory Table of Contents 1. Postulates 2. Drawbacks of Dalton's atomic theory of matter 3. Merits of Dalton's atomic theory 4. Contributors John Dalton, a British school teacher, published his theory about atoms in 1808. His findings were based on experiments and the laws of chemical combination. Postulates 1. All matter consists of indivisible particles called atoms. 2. Atoms of the same element are similar in shape and mass, but differ from the atoms of other elements. 3. Atoms cannot be created or destroyed. 4. Atoms of different elements may combine with each other in a fixed, simple, whole number ratios to form compound atoms. 5. Atoms of same element can combine in more than one ratio to form two or more compounds. 6. The atom is the smallest unit of matter that can take part in a chemical reaction. Drawbacks of Dalton's atomic theory of matter The indivisibility of an atom was proved wrong: an atom can be further subdivided into protons, neutrons and electrons. However an atom is the smallest particle that takes part in chemical reactions. According to Dalton, the atoms of same element are similar in all respects. However, atoms of some elements vary in their masses and densities. These atoms of different masses are called isotopes. For example, chlorine has two isotopes with mass numbers 35 and 37. Dalton also claimed that atoms of different elements are different in all respects. This has been proven wrong in certain cases: argon and calcium atoms each have an atomic mass of 40 amu. These atoms are known as isobars. According to Dalton, atoms of different elements combine in simple whole number ratios to form compounds. This is not observed in complex organic compounds like sugar (C12H22O11). The theory fails to explain the existence of allotropes; it does not account for differences in properties of charcoal, graphite, diamond. Merits of Dalton's atomic theory The atomic theory explains the laws of chemical combination. Dalton was the first person to recognize a workable distinction between the fundamental particle of an element (atom) and that of a compound (molecule). Dalton's Atomic Theory Model Back to Top Dalton was developed the theory of the structure of matter and this theory is known as Dalton’s atomic theory. His research was based on experiments and also from law of chemical combination. Dalton’s atomic theory was quickly explained the many heretofore unexplained chemical phenomena. Dalton’s atomic theory quickly became the theoretical foundation in chemistry. The essence of Dalton’s atomic theory was valid, but the modern atomic theory was little more involved than Dalton’s theory. Dalton’s atomic theory stated that: 1. All the matter is made of atoms which are tiny particles and indivisible. 2. All the given atom of the element is identical in mass, size, shape, and in other properties. 3. All different elements have different types of atoms and also different in their mass, size, shape, and in other properties. 4. All the atom of an element cannot be made or destroyed. 5. Chemical combination of two or more different atoms of different elements are formed the new compound. 6. Chemical reactions only give a rearrangement of atoms. 7. Atoms are combined with each other in small whole number. 8. Combination or separation of atoms is responsible for chemical reactions. Dalton’s atomic theory is a model developed to explain the properties and behavior of atoms and it had the weight of careful chemical measurement behind it. Dalton’s atomic theory was based on that the atom of different element could be differentiated by difference in their weight. Using of this theory, Dalton rationalized the various law of chemical combination. Dalton’s were said that all atoms of an elements were identical and that is particular they had the same mass, so that the element is pure. He also said that atoms of each element were different from one another, since elements were differed from one another in particular, they had different mass. The atoms of different elements are bonded to one another and they are not easily separated from one another, so the compounds are pure substance. When the compound contains a fixed ratio of atoms and each atom has its own characteristic weight, so the compounds have constant composition. Each atom can fix the weight ratio of one element to the other. Postulates of Dalton's Atomic Theory Back to Top Postulates of Dalton’s atomic theory can used to explain the behavior of matter: 1. All matter is composed of small tiny particles called atoms. In Greek the word atom is termed as indivisible. The atoms can not be further broken down. 2. All atoms are indivisible, indestructible, and unchangeable. Atom of an element cannot be created, divided, destroyed, or split into smaller particles or transformed into atoms of other elements or transformed into other atoms in a chemical reaction. They are simply rearrangement of new compound. Dalton’s atomic theory based this hypothesis on the law of conservation of mass and on centuries of experimental evidence. 3. All the elements are characterized by mass of their atoms. All atoms of an element have identical weights and also atoms of different elements have different weight. 4. When the elements are reacts, their atoms are combining in simple whole number ratios to form compounds. For example 1 atom of A plus 1 atom of B, 2 atoms of A plus 3 atoms of B, etc., this postulate of Dalton’s atomic theory suggested a practical strategy for determining relative atomic weight from elemental percentages in compounds. 5. When the elements are reacts, their atoms are some times combining in more than one simple whole number ratios to form different compounds. For example carbon and oxygen combined to form both carbon monoxide as well as carbon dioxide. In carbon monoxide one atom of carbon combined with one atom of oxygen and in carbon dioxide one atom of carbon combined with two atom of oxygen. So the ratio of carbon and oxygen in CO is 1:1 and in CO2 is 1:2. This postulates of Dalton’s atomic theory can also explain why the weight ratio of nitrogen to oxygen in various nitrogen was them selves simple multiples of each other. Merits of Dalton's Atomic Theory Back to Top Some Merits of Dalton's Atomic Theory are given below: Dalton’s atomic theory used to explained many things. Mainly this theory was used to explain the laws of chemical combination. Dalton’s atomic theory was quickly explained the many heretofore unexplained chemical phenomena. Dalton’s atomic theory quickly became the theoretical foundation in chemistry. Drawbacks of Dalton's Atomic Theory of Matter Back to Top Dalton’s atomic theory was described that the atom is the ultimate, discrete and indivisible particle called atom of matter. This theory was never put to experimental tests, nor was they ever used to explain scientific truth. The new researches were proved that the Dalton’s atomic theory was not fully correct, due to the following drawbacks: 1. Atoms of the same or different types have a strong ability to combine together to form a new group of atoms. For example nitrogen, hydrogen, oxygen gases exist in nature as a group of two atoms. These are indicates the smallest unit capable of independent existence is a group of atoms, but not an atom. 2. The atom can no longer be considered indivisible. Atoms can be sub divided into sub atomic particles like proton, neutron, and electron. 3. The discovery of isotopes indicated that all the atoms of the same element are not perfectly identical in all respects. Atoms of the same element having different masses are called as isotopes. For example 1H1, 1H2, 1H3. Atoms of different elements are not different in all respects; atoms of different elements having same atomic mass are called as isobar. For example argon and calcium atoms have same atomic mass of 40. 4. This Dalton's atomic theory of matter does not give reason for why certain substances, should differ in their properties even though they contain atoms of the same element. For example, charcoal, graphite and diamond all are made of only by carbon, but they all are having a different property. 5. All the compounds do not have small number of atoms. 6. Atoms can be destroyed or break down by fission process in nuclear reactor. 7. It fails to explain Gay-Lussac’s law of gaseous volume and the existence of allotropes. 8. This theory also not given ultimate difference between the particle of an element and the small particle of a compound. Best Answer: The following of Dalton's theories are no longer valid: 1) All matter is made of indivisible and indestructible atoms 2) All atoms of a given element are identical in their physical and chemical properties