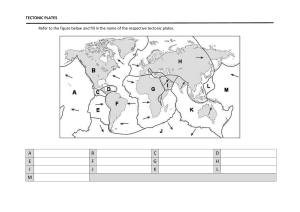
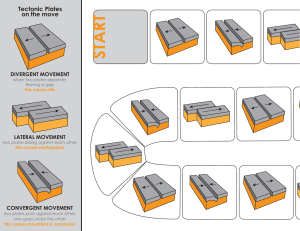
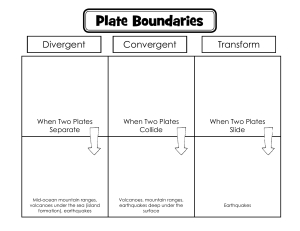
Unit 6 Earth physics By Violet Voon Sound Vibrations (move back and forth) make sound If you hit a drum with greater force, it vibrates more and produces louder sound. Our vocal cord vibrates and produces sound when we speak. Loudness and Pitch • Not all sounds are the same • The bigger the vibrations (amplitude), the louder the sound • The faster the vibrations (frequency), the higher the pitch of the sound. • Thunders can be loud but low pitch • A baby crying is high pitch • Tighten the string of a guitar produces higher pitch • Sound at certain pitch can cause damaging vibrations even the sound is not too loud. Glass can be broken by vibrations from sound. Louder sound has a bigger amplitude. Higher pitch has a higher frequency. Sound wave • When a loud speaker makes a sound, its cone vibrates back and forth. • The air molecules next to the cone move back and forth with the same frequency. • They then push the molecules on the next layer so that they also start vibrating. • These molecules push on the next ones and so on. The molecules only move side to side, but the vibration travels outwards . This is called sound wave. • Sound waves transfer sound energy. How sound travels Medium Speed of sound, m/s Air 340 Water 1497 Steel, iron 5200 • Sound can travel through medium (solid, liquid or gas). • Sound travels the fastest through solid, then liquid, and slowest in gas. • Sound cannot travel through a vacuum, as there is no particles to vibrate to make a sound wave. • The sound of the bell becomes softer and finally cannot be heard when the air in the bell jar is pumped out. Reflection of sound • A sound wave will be reflected when it strikes an obstacle. The reflected sound is called echo. • Sound waves reflect best from large, smooth and flat surface. • Surfaces such as glass, tiles, flat metal and smooth concrete give good reflection of sound. Useful echoes • The use of echo sounding equipment has enabled humans to measure the depth of sea , the presence and distance of an iceberg and the distance of an enemy’s submarine. • Echoes help the bat to work out where the insect is. • Echoes can be used to make images from inside the body. Sound sent into mother’s body echo back out of her body. This is to make the image of unborn baby. • The distance travelled by the sound is double the distance from the object making sound to the reflecting surface. Unwanted echoes • Sometimes echoes are unwanted for example when recording music. • In theatre the audience needs to hear the voices of people on the stage. If there were echoes, the voices would not be clear. • Theatres usually have no large flat surfaces to stop echoes. Ways to reduce echoes 1. Hang Soft Curtains. 2. Add Fluffy Rugs or Carpeting. 3. Add Sound-Absorbing Plants. 4. ring in Some Cushions and Blankets. The shapes on the walls are made to stop echoes The structure and age of the earth •The earth is about 4500 million years old •The earth has a crust of solid rock. •Beneath the crust is the mantle, which is molten rock that can flow. •In the centre is the core. It is made of nickel and iron. The outer core is molten, while the inner core is solid. •The rock found in the crust contain metals and non-metals. •Oxygen is the most abundant element in the earth crust. •The most abundant metal in the earth crust is aluminium Millions years ago, all the land was a large continent. Over millions of years, the land broke up and drifted apart. This idea is called continent drift, by Alfred Wegner a German scientist in 1912. His evidence for this idea was that: 1. The shape of the continents fit together 2. The types of rocks on the different continents match up where they fit together 3. The fossils on the different continents match up when they fit together. But he could not explain how the drift happened, so not everyone believed his ideas. In the 1960s, tectonic plate theory was developed. The earth’s surface is made up of large plates. Some of the plates are under oceans, they are called oceanic plates. Some of the plates form the continents, they are called continental plates. The plates move slowly on the molten magma underneath them. The plates only move about 4 cm each year. The earthquakes and volcanoes are usually occur at the plate boundaries, the places where tectonic plates meet. Geological change • Geological change happens most frequently at plate boundaries because the tectonic plates are always moving. • Some geological change is very slow, takes millions of years. Some are very sudden and violent. • The picture below shows there are many geological changes and events such as volcanic eruptions and earthquakes t the plate boundaries around the edge of the Pacific Ocean. The area is called Ring of Fire. Movement of plates Plates moving together • One plate may slide underneath the other one. This is called subduction. • The rocks in the crust melt as they move into the mantle. They become part of the mantle Movement of plates Plates moving apart • As tectonic plates drift away from each other, they break and crack when they become too thin. • Lava erupts from the mantle and harden to form new crust with new rocks. This causes a volcano. Movement of plates Plates sliding past • There is a lot of friction between the plates as the plates are large and heavy. • There is always force on the tectonic plates, so the pressure builds up and eventually the pressure causes violent movement. This is an earthquake. Fold mountains • Sometimes when tectonic plates move together, the rocks crumple and fold upwards, this produces fold mountains. • This can happen under the ocean or on land. • The newest fold mountains are between 10 and 25 million years old. Examples : the Himalayas in Asia and the Rocky Mountains in North America. • The oldest fold mountains are more than 200 million years old. Example the Ural Mountains in Russia The Himalayas Rocky Mountains Ural Mountains Volcanoes • Volcanoes are usually formed at the plate boundaries when magma from the mantle rises up through cracks in the Earth crust. • At the Earth’s surface, magma erupts to form lava flows and ash deposits. • Magma is the liquid rock when it is underground, lava is the liquid rock when it is on the surface. • The lava and ash harden as they cool to form new rocks. So each time the volcano erupts, it gets bigger. • Sometimes if the magma is really thick and contains dissolved gas, pressure builds up and the eruption is violent. Gases and rock shoot up through the opening. Violent eruptions can even cause avalanches and earthquakes. Tsunamis also may happen if the volcano is close to sea. • Active volcanoes may erupt anytime; inactive or dormant volcanoes have not erupted for a very long time. Extinct volcanoes will not erupt again. Earthquakes • Some earthquakes are extremely violent and cause a lot of damage. Some are so light that they only register on scientific instruments. • The size or magnitude of the earthquake depend on 1. The size of the faults (cracks) at the plate boundaries 2. How far the rocks move when the earthquake happens. In the largest earthquakes, the rocks can move tens of metres in seconds. How a shadow formed? • Light travels in straight lines called rays. • Light rays cannot pass through an opaque object, it blocks the light from reaching the place behind it, thus a shadow formed. Solar eclipse • A solar eclipse happens when the Moon comes between the Sun and the Earth. •The Moon blocks the sunlight. •The shadow of the Moon forms on Earth. •People in the middle of the shadow (umbra) observe a total solar eclipse. •Away from the middle of the shadow of the Moon, some light rays from the Sun can reach the Earth (penumbra), there is partial solar eclipse. Never look at the Sun directly even when there is an eclipse, it can cause eyes damage •A lunar eclipse happens when the Earth comes between the Sun and the Moon. •The Earth blocks the sunlight. •The shadow of the Earth is formed on the Moon. • It does not happen every month. •The Moon takes 27 days to orbit the Earth but the orbit of the Moon is tilted slightly. It is not exactly the same plane as the orbit of the Earth around the Sun. •It happens only when the Sun, Earth and Moon are in the same straight line .