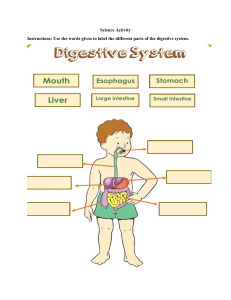
Leaving Certificate Biology Plus Chapter 28 Human nutrition Heterotrophic nutrition involves: • • • • Ingestion (taking in food) Digestion (breaking down food) Absorption (food entering the body) Egestion (removing waste). The human digestive system In the mouth: • The four types of teeth are incisors, canines, premolars and molars • The enzyme amylase digests starch to maltose. The oesophagus: • Is a muscular pipe • Moves food by peristalsis. Peristalsis is a wave of muscular action that forces food through the intestines. Fibre stimulates peristalsis. Peristalsis The stomach: • • • • Stores and digests food Is a muscular bag Churns food to make chyme The stomach lining makes: (i) Mucus (ii) Pepsinogen (becomes pepsin in acid; pepsin digests protein to peptides) (iii) Hydrochloric acid (pH 1–2), which kills bacteria and softens food. The pancreas makes: • Sodium hydrogen carbonate (neutralises acid from the stomach) • The enzymes (i) Amylase (starch to maltose) and (ii) Lipase (lipid to fatty acid and glycerol). The digestive roles of the liver: • Makes bile, which emulsifies fat • Makes sodium hydrogen carbonate to neutralise acid • Stores many nutrients. The duodenum is the main location for digestion. It makes a range of digestive enzymes. The relationship between the alimentary canal and the liver and pancreas In the ileum: • Food is absorbed • There is a lining of numerous villi to increase surface area • Glucose and amino acids are absorbed into the bloodstream and taken to the liver • Fatty acids and glycerol enter the lacteals and are transported in lymph and returned to the bloodstream for distribution around the body. The relationship between the ileum and the liver The appendix and caecum are vestigial (i.e. have lost their former use). The colon reabsorbs water from the waste, forming faeces. The junction of the small and large intestines Symbiotic bacteria in the colon: (i) Make vitamins and digest cellulose (ii) Break down cellulose (iii) Prevent the growth of diseasecausing organisms. The rectum stores faeces. TS of the colon There are seven components of a balanced diet: • • • • • • • Carbohydrate Lipid Protein Minerals Vitamins Fibre Water. The amount of food a person requires depends on age, activity, gender and health. The four food groups and their average number of servings per day are: • • • • Cereals, bread and potatoes (6+) Fruit and vegetables (4+) Milk, cheese and yoghurt (4) Meat, fish and poultry (2). The food pyramid