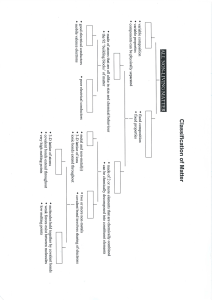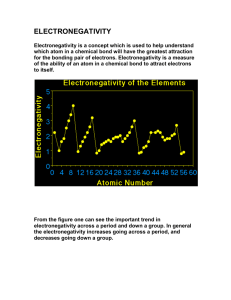
Chemical Bonding Just a quick definition. Electronegativity: The amount of attraction an element has for electrons when forming a Chemical Bond. Metals & Non-Metals Properties of Metals: Typically: Good conductors. Malleable & pliable. High melting point. Solid at room temperature (Hg being an exception). Low electronegativity. Properties of Non-Metals: Typically: Poor conductors. Brittle Low melting point. Liquid High & fragile. or gaseous at room temperature. electronegativity. Side-note: Metalloids Metalloids share characteristics of both metals and nonmetals. They are best known as semiconductors, most notably, Silicon (symbol Si). How they appear on the Periodic Table: Metals vs. Non-metals in Chemical Bonding Metals and non-metals tend to behave differently when they form chemical bonds. This is due mostly to the differing electronegativity. Covalent Bonds: Sharing is Caring Covalent Bonds: When two bound molecules share electrons However, they do not always share equally. In a polar covalent bond, electrons are more attracted to the element with the higher electronegativity. In a non-polar covalent bond, electrons are equally attracted to the two elements. They must have equal (or close to equal) electronegativity. An important note… The most equal sharing of electrons comes from atoms that are the same element. A couple examples: Polar Covalent: Water. The “Universal” Solvent. A couple examples: (Nitrogen) N2 (Carbon Dioxide) CO2 Ionic Bonds: All for me, myself, and I. Occur when electronegativity of the two elements is very different. Occurs most often between a metal and a non-metal. A common example: Salt Where would the electrons want to go? Hydrogen Bonds: The Honorary Bonds. Water molecules are attracted to each other because they are polar. Forms a very weak attraction among molecules.