Art History Midterm Study Guide: Prehistoric to Aegean
advertisement

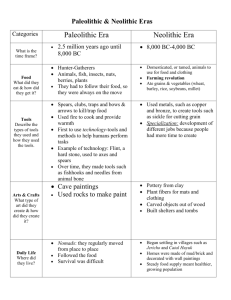
2ASP20 Page 1 MIDTERM STUDY LIST – 85 points Chapters 1-4, Prehistoric, Mesopotamia, Egypt and Aegean This midterm will open on Monday, May 11th at 12AM and close on Friday, May 15th at 11PM. Students will have access to their textbooks and notes; however, they will only have 50 minutes on each section (multiple choice and short responses). The exam consists of 60 multiple choice questions and 5 short response questions taken from the assigned readings, PowerPoint lectures and videos. To prepare for the exam: • Read the textbook and review over your notes. • For each image listed: memorize the artist/architect (if known), the associated period or culture. • Know the iconography (meaning or subject of the artwork, if there is one), the function of the work (if known), and, the location for architecture. • Know the main characteristics of these artistic or historical periods: Paleolithic, Neolithic, Sumer, Akkad, Neo-Sumer, Babylon, Assyria, and Neo-Babylon, Cycaldes, Minoans, Mycenaeans. For example, were people hunter-gathers or farmers, warring or peaceful? How were the beliefs of the society reflected in objects? What structures were built and what materials were used in construction? Vocabulary: memorize the vocabulary to define a word or use in an answer Ch1: Paleolithic, Neolithic, sculpture-in-the-round, zoomorphic, Composite/Twisted perspective, ground line, post and lintel, megalith, Neolithic Revolution Ch2: hierarchical scale, register, votive offering, ziggurat Ch3: Ka, mastaba, nemes headdress, uraeus, mortuary temple, hypostyle hall Ch4: Fresco, Corbel Arch, Megaron, Labyrinth, Tholos Tomb Dates: 45-30,000 BCE – First works of art appear 26th – 25th c. BCE – Building of the pyramids People: Sir Leonard Woolley, Naram-Sim, Queen Hatshepsut, Akhenaton, Tutankhamen Art Images: Chapter 1: 1. Nude woman (Venus of Willendorf), (Paleolithic) 2. Hall of the Bulls, Lascaux, Dordogne, France (Paleolithic) 3. Stonehenge, Salisbury Plain, Wiltshire, England (Neolithic) 4. Landscape with volcanic eruption, Çatal Höyük, Turkey, (Neolithic) Chapter 2: 5. Statuettes of two worshipers, (Sumer) 6. Standard of Ur (Peace and War sides), (Sumer) 7. Victory Stele of Naram-Sin, (Akkad) 8. Ziggurat, Ur, Iraq, (Neo-Sumer/Third Dynasty of Ur) 9. Ashurbanipal Hunting Lions, relief from the south palace of Ashurbanipal, Nineveh, Iraq, (Assyrian) Chapter 3: 10. Imhotep, Stepped Pyramid of Djoser, Saqqara, Egypt, (Early Dynastic) 11. Khafre enthroned, (Old Kingdom) 2ASP20 Page 2 12. Nebamum hunting fowl, Tomb of Nebamum, (New Kingdom) 13. Mortuary temple of Hatshepsut, Deir el-Bahri, Egypt, (New Kingdom) 14. Akhenaton, Nefertiti, and three daughters,(Amarna) 15. Death mask of Tutankhamen, Thebes, Egypt, (Post-Amarna) Chapter 4: 16. Figurine of a woman, from Syros, Greece (Cycladic) 17. Bull-leaping, from the palace at Knossos (Crete), Greece, Fresco (Minoan) 18. Harvester Vase, from Hagia Triada (Crete) (Minoan) 19. Treasury of Atreus, Mycenae, Greece (Mycenaean) 20. Lion Gate, Mycenae, Greece (Mycenaean) Study Questions: Be able to respond to these questions, using specific examples of works viewed and art vocabulary. • Name two developments that differentiate the Paleolithic from the Neolithic periods? • What aspects of the Nude Woman, Venus of Willendorf are emphasized? What does this indicate about the figurine’s purpose? • What were two important innovations developed by the Sumerians? • How does a ziggurat differ from a stepped Pyramid? • What do the reliefs of the palace of Ashurbanipal at Nineveh depict and why? • What is unique about the Harvester vase?