Paleolithic & Neolithic Man: AP World History
advertisement

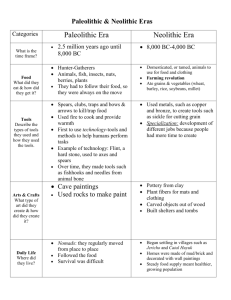
Paleolithic and Neolithic Man Unit 1 AP World History Agenda for today 1. Bell Ringer 2. Expectations for the Class - Textbooks 3. Lecture: Paleolithic and Neolithic Man - Interpretation of Cave Paintings. 4. The Lemon Tree assignment 5. Timeline Activity: Advancement of Man 6. Map Activity: Spread of humans. 7. HW: Vocabulary assignment. The First Humans Homo Sapiens emerge 250,000 years ago. Small clans develop, and every generation moves 2-3 miles. World is populated around 10000 BCE “Africa Theory” All human development began in Africa, moved outward. Hunter-Gatherer Societies Paleo- Old Stone Hunter-gatherers Patterns develop Form clans of 30 Moved frequently Rough gender equality Women stayed closer to camp, while men hunted. Adapting was necessary for survival. Neolithic Revolution 10000-4000 BCE Food is produced instead of gathered. Animals domesticated over time. Settled into communities. These were still relatively nomadic. Growth of Farming Permanent settlements develop with better farming. Catal Huyuk Home placement Food surplus leads to more time for leisure. Polytheistic Religious traditions, “Mother Earth”. Consequences Settlement leads to trade, but also a need for protection. Specialization of labor. Men remained in the field, while women were relegated to household tasks. Gender inequality develops. Eventually, the patriarchal society and the need for protection would change the village. Analyze the lifestyle of Paleolithic man, and how it differed from Neolithic man.