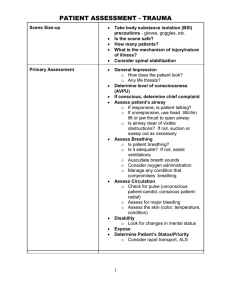
Updated Jan. 2011 1 2000L UNIT ONE Performing Health Assessment Region Assessment Normal Findings Abnormal Findings Stable well nourished, speech clear , AAO x 3, cheerful steady gait, normal ADLs Hypertension, hypotension, fever, increased respiratory rate, ungroomed, in distress, changes in speech, disoriented, unsteady, history of psychiatric problems Color lesions Use ABCD method: A – asymmetry B – border irregular C – color variation D - Diameter Freckles, birthmarks, surgical and trauma scars Rashes, Ecchymosis, erythema, pallor, cyanosis, jaundice Texture, warmth Smooth, warm, dry Rough, indurated (hard), cool, moist Turgor Supple, no tenting Tenting (poor turgor) = breakdown Vascularity Normal skin down Pressure area, petechia Color, texture, distribution Even, smooth General Survey VS, dress, hygiene. overall health and wellbeing, nutritional status, speech, LOC, affect, posture, gait, gross deformities SKIN Indicator of hydration, nutrition, circulation Integumentary System Hair Nails/Hands Alopecia o Nail angle of attachment 160 and convex Appearance Color pink to light brown depending on skin tones, no brittleness, cracking, splinting Yellow: cigarettes, fungal infections, psoriasis Reddish/pink distal band: 20% - cirrhosis, hypoalbuminera 20-60% - renal disease Blue (cyanotic): peripheral disease/hypoxia Black: trauma, bacterial endocarditis Size, shape, position, scalp, tenderness, lesions, masses No headaches, normocephalic Headaches, dizziness, lightheadedness, vertigo Symmetry, facial expressions CN 7 Facial intact Facial sensation CN 5 Trigeminal intact TMJ joint No popping or tenderness Capillary Refill All fingers and toes HEAD Inspection Palpation Face o Clubbing >160 : clubbing from congenital heart disorder, cystic fibrosis or chronic pulmonary diseases (chronic lack of oxygen) Updated Jan. 2011 2 Eyes Inspection Test Extraocular movements (Six Cardinal Fields of Gaze) Do you have any vision problems. Give the client something close and something far to test vision CN 3 Occumlomotor, 4 Trochlear, 6 Abducens intact, no nystagmus, strabismus Visual loss, diplopia, ptosis CN 2 Optic Sclera White or grey color Yellow: jaundice Pink: infection Conjunctivae Pink , moist Pale: anemia Papillary reaction to light and accommodation CN3 intact, PERRLA Neurological deficit External ear and canal Intact Infections, hearing loss, tinnitus, vertigo Palpation Position, symmetry of ears Even Dysphagia, pain, hearing aid Test Palpate mastoid for tenderness None Whisper test CN 8 Acoustic intact Hearing loss Nose Inspect nares Patent, no drainage Mass, deviated septum Inspection Test Check sense of smell CN 1 Olfactory intact Neurological deficit Ears Inspection Updated Jan. 2011 3 Mouth Lips, oral mucosa Pink, moist, smooth Bleeding gums, pain Pharynx Teeth, gingival, palate No caries, pink gums, no inflammation, no tenderness Caries, inflammation, halitosis gingivitis, poor hygiene Inspection Pharynx, tonsils No redness or edema Infection process (URI) Palpation Gag and swallow reflex (“ah”) Cough and speak CN 9 Glossopharyngeal CN10 Vagus/Vagal intact Test Taste on anterior posterior tongue, CN 7Facial and 9 Glossopharyngeal intact Tongue movement (”Say D, L, N, I”) CN 12 Hypoglossal intact NECK Inspect for shape Smooth, symmetrical Respiratory Cardiac Test JVD – Angle of Louis No distention at 45o angle Distention, overload Musculoskeletal Neurological Muscular strength, shrug shoulders, tilt head side to side CN 11 Spinal Accessory Weakness, numbness Inspect Palpation Palpate carotid pulse (with the bell) Even +2 bilaterally Atherosclerosis Auscultation Test Lymph nodes No swelling Inflammation, infection Trachea Inspect and palpate – auscultate for bronchial sounds Midline – sounds harsh on expiration Deviation – mass, pneumothorax, enlarged - goiter Thyroid gland Respiratory Moves with trachea with swallowing Spine inspect and check ROM Normal curvature and movement Kyphosis, scoliosis Chest excursion – hands on back, patient inhales and exhales Normal movement of chest cavity Restrictive lung disease Auscultate lung fields for vesicular sounds Clear blowing sounds – heard louder on inspiration Adventitious: crackles, rhonchi, wheezing Also: TB, smoker, cough. Dyspnea, orthopnea, hemoptosis THORAX RESPIRATORY (ANT, POST, LAT) Posterior Inspection Auscultation Updated Jan. 2011 4 Respiratory Thorax, Anterior and Lateral Inspection Auscultation Palpation Auscultate lung fields for Brochovesicular sounds at sternal border th th Vesicular sounds laterally at 5 -6 ICS and at the apex of the lungs located supraclavicular left and right th Cardiovascular PMI palpate at 5 mid-clavicular line Clear and equal inspiration and expiration Clear and equal Adventitious crackles, rhonchi, wheezing No thrills Thorax, Anterior Heart sounds: auscultate (APETA) CHECK ALL SITES WITH BELL AND DIAPHRAGM. CHECK IN 3 POSITIONS: SIT, STAND, L LATERAL a. aortic – 2 nd ICS RSB nd b. pulmonic – 2 ICS LSB rd c. Erb’s point – 3 ICS LSB th d. Tricuspid – 4 ICS LSB th e. Mitral or Apical– 5 ICS mid clavicular Abnormalities in heart sounds can indicate murmurs, CAD and CHF Other cardiac abnormalities: syncope, palpations Louder S-2 Louder S-2 Equal S-1 and S-2 Louder S-1 Louder S-1 Updated Jan. 2011 5 1. the sternum 2. the suprasternal notch 3. the infrasternal notch 4. the xiphoid process of the sternum 5. the sternal angle (of Louis) ABDOMEN Inspect for shape Flat or round, soft and non-tender Distended, hard, or tympanic, presence of ascities pain, tenderness Inspect for scars None Surgical and trauma Movement and abnormalities None Bowel sounds – auscultate four quadrants 5-30 sounds per minute in all four quadrants >30: hyperactive <5: hypoactive Absence of sounds: no sounds for at least 5 minutes Bruit indicate turbulent blood flow (aneurysm?) Palpate lightly for tenderness, masses No tenderness Masses, bladder tenderness Gastrointestinal Inspection Palpation Auscultation EXTREMITIES, Upper Inspect joints for swelling, redness, deformity Inflammation, injury Updated Jan. 2011 6 Musculoskeletal Neurological Inspect and palpate nails, capillary refill, Blanch test Color return in 3 seconds – brisk Inspection Palpation Test Test: sensation – superficial and deep No neurological deficits Test: muscle strength and hand grip, coordination ROM Strong and equal bilaterally Palpate & grade the pules: radial, ulnar, brachial Include spine assessment Strong +2 and equal bilaterally <3 seconds: circulatory problem Atrophy, neurological deficit Extremities, Lower Inspect joints for swelling, redness, deformity Musculoskeletal Neurological Inspect and palpate nails for capillary refill Color return in 3 seconds – brisk Inspection Palpation Test Inspect skin for skin hair distribution temperature edema varicose veins Even Even Warm None None Perform Homan’s Test No pain in calf on dorsiflexion Pain: positive sign for DVT Test for muscle strength Strong, equal, full ROM, adequate sensation Atrophy, neurological deficit Test for sensation: superficial and deep Adequate sensation Palpate & grade the pulses: femoral, popliteal, posterior tibial, & dorsalis pedis pulses Strong +2 and equal bilaterally <3 seconds: circulatory problem Weak or absent indicates poor circulation/DVT