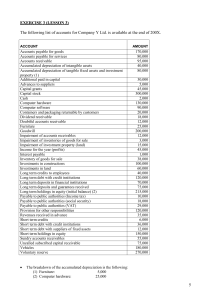
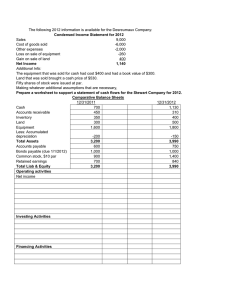
EXERCISE 3 (LESSON 3) The following list of accounts for Company Y Ltd. is available at the end of 200X. ACCOUNT Accounts payable for goods Accounts payable for services Accounts receivable Accumulated depreciation of intangible assets Accumulated depreciation of tangible fixed assets and investment property (1) Additional paid in capital Advances to suppliers Capital grants Capital stock Cash Computer hardware Computer software Containers and packaging returnable by customers Dividend receivable Doubtful accounts receivable Furniture Goodwill Impairment of accounts receivables Impairment of inventories of goods for sale Impairment of investment property (land) Income for the year (profits) Interest payable Inventory of goods for sale Investments in constructions Investments in land Long term credits to employees Long term debt with credit institutions Long term deposits in financial institutions Long term deposits and guarantees received Long term holdings in equity (initial balance) (2) Payable to public authorities (Income tax) Payable to public authorities (social security) Payable to public authorities (VAT) Provision for other responsibilities Revenues received in advance Short term credits Short term debt with credit institutions Short term debt with suppliers of fixed assets Short term holdings in equity Sundry accounts receivables Uncalled subscribed capital receivable Vehicles Voluntary reserve • AMOUNT 170,000 80,000 95,000 40,000 80,000 30,000 5,000 45,000 300,000 2,000 130,000 90,000 20,000 18,000 12,000 25,000 200,000 12,000 3,000 15,000 45,000 1,000 38,000 100,000 60,000 40,000 120,000 70,000 75,000 215,000 10,000 18,000 29,000 120,000 35,000 6,000 36,000 12,000 150,000 55,000 75,000 180,000 270,000 The breakdown of the accumulated depreciation is the following: (1) Furniture: 5,000 (2) Computer hardware: 25,000 5 (3) Vehicles: (4) Investments in constructions: • • • 30,000 20,000 These are shares that have been classified by the company as “available for sale”. There are two groups of shares: Holdings in company A: ¾ Book value (1/1/2007): 42,000 ¾ Market value (31/12/200X): 50,000 Holdings in company B: ¾ Book value (1/1/2007): 173,000 ¾ Market value (31/12/200X): 150,000 These holdings have not yet been valued at fair value. REQUIRED: 1) Register the valuation at fair value of the long term holdings in equity. 2) Prepare the Balance Sheet according to the normal model of the new PGC. EXERCISE 4 (LESSON 3) The following list of accounts for Company Y Ltd. is available at the end of 2008. Advances from customers 3.150 Accounts receivable, bill of exchange 118.600 Short term debt with credit institutions from the discounting of bills of exchange 46.400 Salary payable 800 Adjustments for changes in value of financial instruments available for sale 2.550 Salary paid in advance 2.100 Capital stock 370.000 Uncalled subscribed capital receivable 20.000 Legal reserve 50.000 Accumulated depreciation of intangible assets 2.400 Accumulated depreciation of tangible fixed assets (1) 80.000 Impairment of plant and equipment 8.590 Called subscribed capital receivable 1.260 Cash 146.060 Machinery classified as held for sale 30.000 Debt with suppliers of fixed assets (of the machinery held for sale) 10.000 Accounts payable 7.800 Long term holdings in equity 7.000 Impairment of inventory of finished goods 600 Short term debt with credit institutions 29.890 Interest payable to credit institutions 600 Long-term debt payable to suppliers of fixed assets 48.920 Voluntary reserve 103.881 Short-term debt payable to suppliers of fixed assets 11.420 Computer software10.000 Constructions 460.000 Machinery 200.000 Plant and equipment 100.000 Inventory of raw materials 2.100 Inventory of finished goods 8.100 Inventory of work-in process 2.700 Capital grants 5.600 Provision for other responsibilities 95.000 Payable to public authorities (Income Tax) 49.855 Expenses paid in advance 1.800 Payable to public authorities (VAT) 10.400 Income for the year ¿? (1) The breakdown of the accumulated depreciation is the following: a. Constructions: 50,000 b. Machinery: 20,000 c. Plant and equipment: 10,000 REQUIRED: Prepare the Balance Sheet according to the normal model of the new PGC. 6