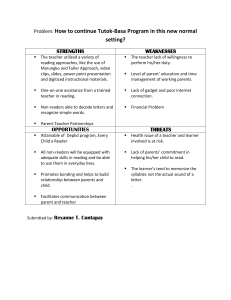
Subject Manual in TLE ICT 7-8 PHILOSOPHY AND RATIONALE Any secondary education technology livelihood and entrepreneurship program should be based on the new Basic Education Curriculum in Technology and Livelihood Education (TLE) for easier assimilation. It should be made more relevant to the present needs of the time. They are revised by integrating new imperatives to the Basic Education Curriculum. New concepts, knowledge and processes are also introduced so that students and teachers will not be left behind in getting across these new elements. The development of the basic skills in the four areas of TLE, namely: (l) Home Economics, (2)Agriculture,(3) Industrial Arts and (4) Entrepreneurship, should be the main concern along with the formation of desirable work values and attitudes. Lessons are made flexible to give the teacher an opportunity to innovate ideas and work processes. It is however important that all suggested activities and projects be pursued ffectively to realize the objectives of the program. Care was exercised to make concepts and thinking and work practices appropriate for the needs, interests and learning abilities of students. The course/subject is intended to help teachers to attain its objective optimally and to experience a sense of achievement in having contributed to the formation of the individual student into knowledgeable, morally responsibleand economically productive human being. TLE program is designed especially for the first year students. It aims to reinforce the work skill training and value orientation of the first year students. FACILITATOR GUIDELINES Here are some tips to help the facilitators get the best from the students and their time in the sessions. Give clear instructions. Give clear instructions in English if you can. Check your instructions. There are many ways of doing this. You can repeat the instructions clearly. If this is not effective, then you will need to make the language of the instructions simpler. Translation is also an effective way of checking instructions. A quick way of involving trainees in this process is to ask them to tell you orally what the instructions are and what they are supposed to do. Demonstration is another excellent way of checking instructions. Finish activities promptly. It can waste a lot of time to wait until every single student/pair/group has finished an activity in their own time. When the majority have finished, tell the remaining student/pair/group they must finish. Allow a few more seconds, then stop the activity. Include everybody. Don’t let the strong participants dominate the sessions. Make sure weaker students are following the session, and don’t get left behind. Be sure to include everybody, including the students who seem less interested in the session. Avoid pointless repetition. Avoid going slowly around the session getting students to take it in turn to do the same thing, such as answering the same question, as this can be a waste of time. It is often more efficient to get students to do thus type of activity in pairs instead. If the class is moving slowly, find out why. Different activity can take different amounts of time to get through the same material. If your session is moving too slowly, try to identify the types of activity which are taking too long. Why are they taking too long? Do the students need more help and support? Feedback technique. Provide feedback in plenary discussion in a positive way. Point out the strength point and then the developing area. Ask the students to express their opinions and motivate them to use the discussed techniques and methodology in their classroom practices. Journal keeping. Read the journals and point out the developing areas that need to be addressed and discussed in the session and change your mode of delivery if required. Distribute the journal with positive comments. Reading practice. Provide opportunity to read and discuss in pair, group and individually. In case of pair reading, allow the pairs to read alternately and in group, everyone to read a part of supplied reading materials one after another and to discuss after every one’s reading. TLE-ICT 7-8 COMPUTER HARDWARE SERVICING The Computer Hardware Servicing NC II program is a vocational program that teaches students how to install, configure and maintain computer systems and networks. It develops students’ skills in diagnosis and troubleshooting of computer systems, as well as in the performance of computer operations. The program enhances a student’s ability in basic computer application programs, MS-DOS/ Windows and Linux installation and PC software and hardware support. Also covered in the program are simple programming and creation of budget projections based on departmental needs. UNIT OBJECTIVES The learner demonstrates understanding basic concepts and underlying theories of computer hardware servicing. Lesson 1: SKILLS IN FOCUS The learner independently demonstrates common competencies in computer hardware servicing as prescribed by TESDA Training Regulations. ACTIVITIES 1. Envisioning the future business career related to computer hardware servicing by creating essay reflections about the learner’s greatest dream business in the future. ASSESSMENT 1. Discuss the relevance of the course 2. Explain basic concepts in computer hardware servicing 3. Explore opportunities in computer hardware servicing as a career RESOURCES DepEd CHS Learning Module Brilliant Computing www.google.com www.youtube.com www.wikipedia.com Lesson 2: SKILLS IN FOCUS The learner recognizes his/her PECs and prepares an activity plan that aligns with the PECs of a practitioner/entrepreneur’s in computer hardware servicing. ACTIVITIES 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Discussion about PECs Perform pair assessment of learner's PECs Perform pair assessment of professional/practitioner's PECs Actual survey questions related to PEC's assessment with other learners Actual survey related to PEC's assessment with that of professional/practitioners Actual alignment procedure of learner's PECs to that of professional/practitioner's PECs. ASSESSMENT Recognize PECs needed in Computer Hardware Servicing 1.1 Assess one’s PECs: characteristics, attributes, lifestyle, skills, traits 1.2 Assess practitioner’s PECs: characteristics, attributes, lifestyle, skills, traits 1.3 Compare one’s PECS with that of a practitioner/ entrepreneur’s 1.4 Align one’s PECS with those of a practitioner/entrepreneur’s RESOURCES DepEd CHS Learning Module Brilliant Computing www.google.com www.youtube.com www.wikipedia.com Lesson 3: SKILLS IN FOCUS The learner independently generates a business idea based on the analysis of environment and market in computer hardware servicing. ACTIVITIES 1. Discussions about SWOT: a) Strength b) Weaknesses c) Opportunities d) Threats 2. Conducting SWOT analysis inside and outside the classroom. a) Other learner's competencies b) Professional/practitioner's competencies. 3. Generating business ideas based on the target customer's needs and wants 4. Generating product design and specifications based on the generated business ideas ASSESSMENT Generate a business idea that relates with a career choice in Computer Hardware Servicing a) b) c) d) e) f) Conduct SWOT analysis Identify the different products/services available in the market Compare different products/services in computer hardware servicing business Determine the profile potential customers Determine the profile potential competitors Generate potential business idea based on the SWOT analysis Prepare hand tools and equipment for computer hardware servicing a) Prepare hand tools and equipment according to function and task requirement RESOURCES DepEd CHS Learning Module Brilliant Computing www.google.com www.youtube.com www.wikipedia.com Lesson 4: SKILLS IN FOCUS The learner independently uses hand tools and equipment for computer hardware servicing. ACTIVITIES 1) Discussions about different hand tools and equipment for computer hardware servicing 2) Perform hand tool preparation and identification based on the given task. ASSESSMENT Prepare hand tools and equipment for computer hardware servicing a) Prepare hand tools and equipment according to function and task requirement RESOURCES DepEd CHS Learning Module Brilliant Computing www.google.com www.youtube.com www.wikipedia.com Lesson 5: SKILLS IN FOCUS The learner consistently observes and practices occupational health and safety procedures in the workplace. ACTIVITIES 1) Discussions about potential hazards and risks in the workplace 2) Conducting hazard check in the workplace 3) Evaluating hazards and risks based of its classifications and effects 4) Generate OHS policies and procedures in controlling the hazards and risks in the workplace. 5) Perform actual drills in preparing controls in OHS policies and procedures ASSESSMENT Identify hazards and Risks a) Explain hazards and risks in the workplace b) Identify hazards and risks indicators in the workplace c) Apply contingency measures in accordance Evaluate hazards and risks a) Determine the effects of hazards and risks b) Classify the types of hazards and risks in the workplace Control hazards and Risks a) Follow OHS Procedures for controlling hazards and risks b) Use personal protective equipment (PPE) c) Follow and observe organizational protocol when providing emergency assistance Maintain occupational health and safety regulations a) Participate in related drills and training b) Prepare OHS personal records in accordance with workplace requirements RESOURCES DepEd CHS Learning Module Brilliant Computing www.google.com www.youtube.com www.wikipedia.com Lesson 6: SKILLS IN FOCUS The learner independently performs accurate measurements and calculations based on a given tasks. ACTIVITIES Perform a discussion about: 1.2 Data storage capacity 1.3 Processor 1.4 Video card ASSESSMENT Perform basic mensuration 1.1 Identify object/s to be measured 1.2 Use the correct specifications as specified in the operating system Carryout mensuration and calculation 2.1 Perform calculation needed to complete task using the four mathematical fundamental operations (addition, subtraction, multiplication and division) 2.2 Employ different techniques in checking accuracy of the computation RESOURCES DepEd CHS Learning Module Brilliant Computing www.google.com www.youtube.com www.wikipedia.com Lesson 7: SKILLS IN FOCUS The learner independently prepares and interprets technical drawings and work plans accurately. ACTIVITIES Perform a discussion about: 1. Basic symbols 2. Basic Elements 2.1 Schematic diagram 2.2 Charts 2.3 Block diagrams 2.4 Layout plans 2.5 Loop diagram 3. Flowchart interpretation 3.1 Types of flowchart ASSESSMENT Identify different kinds of technical drawings 1.1 Identify basic symbols used in technical drawing 1.2 Select technical drawing in accordance with the job requirement Interpret technical drawing 2.1 Identify the basic symbols used in flow charting 2.2 Interpret the symbols used in flow charting 2.3 Create a flowchart that depicts a simple scenario RESOURCES DepEd CHS Learning Module Brilliant Computing www.google.com www.youtube.com www.wikipedia.com Lesson 8: SKILLS IN FOCUS The learner independently prepares and interprets technical drawings and work plans accurately. ACTIVITIES Perform a discussion about: 1. Basic symbols 2. Basic Elements 2.1 Schematic diagram 2.2 Charts 2.3 Block diagrams 2.4 Layout plans 2.5 Loop diagram 3. Flowchart interpretation 3.1 Types of flowchart ASSESSMENT Identify different kinds of technical drawings 1.1 Identify basic symbols used in technical drawing 1.2 Select technical drawing in accordance with the job requirement Interpret technical drawing 2.1 Identify the basic symbols used in flow charting 2.2 Interpret the symbols used in flow charting 2.3 Create a flowchart that depicts a simple scenario RESOURCES DepEd CHS Learning Module Brilliant Computing www.google.com www.youtube.com www.wikipedia.com