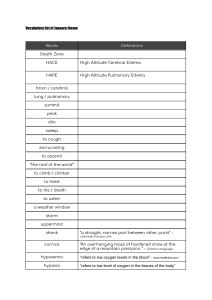
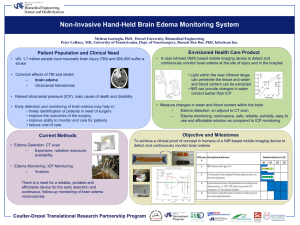
Basic Head -to-Toe Assessment by Straight A Nursing CATEGORY STEPS NOTES INTRODUCTION Greeting Greet patient, introduce yourself, perform hand hygiene Safety Raise bed to a comfortable height for you; check patient’s arm band or verify name by asking; ensure patient not in any acute distress. Pain Location, intensity, quality, radiation, duration, any relieving/exacerbating factors LOC How much stimulus does it take to rouse the patient or are they awake and alert? LOC ranges from awake to somnolent, lethargic, stuporous, then comatose. Orientation Name, date, location, situation. Skin Assess for color, moisture, temperature. Normal is warm, dry, no discoloration.” Some abnormal findings are pale, dusky, jaundiced, clammy, diaphoretic, cool, hot. Facial droop Assess for facial droop; have the patient smile HEAD Periorbital edema There are many causes for this including nephrotic syndrome and thyroid disorders. Pupils PERRLA: Pupils equal, round, reactive to light AND accommodation. Eyes Assess the sclera for discoloration, look for drainage, swelling, inflammation. Neck Cough Look for retractions of neck muscles (indicated accessory muscle use); assess for distended neck veins which can be caused by right heart failure and pulmonary hypertension. Assess for sputum; if present, assess color, consistency and amount. NG tube Check placement and patency; assess for skin breakdown at nares Nasal cannula Check for appropriate placement and FiO2; assess for skin breakdown at ears, cheekbones and nares Hand grip Assess for equal grips by having patient squeeze your hands simultaneously Radial pulses Should be strong and regular Nail beds Assess for capillary refill; should be less than 3 seconds IV site Assess patency and dressing; assess for phlebitis (red, warm, tender) and infiltration (edema, cool, maybe fluid leaking, maybe pallor). PICC site Assess dressing; assess for edema, redness and warmth (signs of DVT). Skin turgor Should quickly return to original state (may be decreased in elderly). AV fistula Assess for bruit (audible) and thrill (palpable) CARDIAC Heart sounds Listen at apex for S1 and S2; S3, S4 and murmurs are abnormal findings. Apex is located left side, MCL, 4th-5th ICS. Two nurses one checks apical while other checks radial; count for one full minute RESPIRATORY Apical/Radial pulse RRPD Lung sounds Listen in three places: anterior, lateral and posterior IS Have patient use the incentive spirometer if available; assess for level obtained WOB Assess for work of breathing and shortness of breath. If patient can’t speak more than a few words at a time, this is indicative of shortness of breath. Work of breathing is seen as accessory muscle use, labored breathing. Crepitus Assess for crepitus if pt is at risk (chest tube, central line, trauma) Appearance Assess abdominal appearance (flat, rounded, distended, etc.) Listen Listen to bowel sounds. More frequently than q 5 seconds is hyperactive; less frequent than q 15 seconds is hypoactive; no sounds in 2 minutes is absent (must listen in each quadrant). Don’t forget to turn off NGT suction prior if using. Feel Palpate abdomen by pressing about 1cm; normal is soft and nontender. Query Ask about passing gas, last BM, appetite, nausea. Catheter Assess Foley catheter if present; ensure patency. Urine Assess urine color, clarity and for presence of sediment, clots or mucus. Voiding If voiding, ask about burning, frequency and amount Pulses Assess pedal pulses at posterior tibial and dorsals pedis Edema Start at the feet and assess upwards until edema ends; pitting edema vs non-pitting edema. Color Look at color of feet; pale, mottled or dusky indicates per perfusion. ARMS/HANDS ABDOMEN RENAL LEGS Respiratory rate, rhythm, depth, presences of air movement 0000001 Basic Head -to-Toe Assessment by Straight A Nursing CATEGORY BACK CLOSURE STEPS NOTES Temperature Assess temperature of feet. Cold extremities are a sign of poor perfusion and could indicate ischemia. Nail beds Sensation Assess for capillary refill at the nail beds (be careful with diabetic patients who have neuropathy). Assess for sensation; ask patient about numbness and tingling Wounds If patient has PVD or is diabetic, inspect feet carefully for wounds. Homan’s Sign Assesses for presence of DVT; not commonly done Ankle strength Have patient press feet against your hands in dorsiflexion and plantar flexion. Edema Assess for dependent edema, especially at sacrum. Skin breakdown Assess for redness at bony prominences or other signs of skin breakdown. Position Reposition patient if needed, lower bed, ensure it is locked and raise side rails (if using) Safety Place call light and overbed table within reach Equipment Check that O2 and suction are functioning. Say goodbye Ask patient if there’s anything else they need; let them know when you will return; perform hand hygiene. 0000002