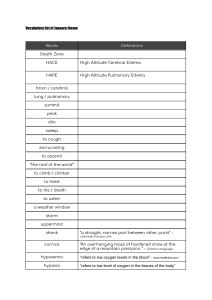
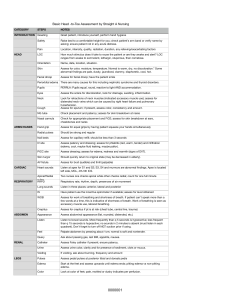
Data Analysis Raw scores for right foot volumes were individually normalized as a percentage of change from their values at time 0, then averaged for each treatment group. The time-course curves for foot volume were subjected to a two-way (treatment × time) repeated measures analysis of variance with Bonferroni’s post hoc t-test. The total foot volume for each treatment was calculated in arbitrary units as the area under the curve (AUC). The following equation was used to determine the percentage inhibition for each treatment. Differences in AUCs were analyzed by ANOVA followed by Student-NewmanKeuls’ post hoc test. ED50 (dose responsible for 50% of the maximal effect) for each drug was determined by using an iterative computer least squares method, with the following nonlinear regression (three-parameter logistic) equation Where X is the logarithm of the dose and Y is the response. Y starts at a (the bottom) and goes to b (the top) with a sigmoid shape. The fitted midpoints (ED50s) of the curves were compared statistically using the F test (Miller, 2003; Motulsky et al., 2003). GraphPad Prism for Windows version .03 (GraphPad Software, San Diego, CA, USA) was used for all statistical analyses and ED50 determinations. P < 0.05 was considered statistically significant. Data were presented as the effect of drugs on the time course and the total edema response (Total edema produced by each treatment is expressed in arbitrary units as AUC of the time-course curves) for 6 h using GraphPad Prism for Windows version 9.92 (GraphPad Software, San Diego, CA, USA). CHAPTER FOUR RESULTS Figures 4.1-4 show the time courses for the effects of Bombax buopozense, Acacia nilotica, Morinda lucida and diclofenac in carrageenan-induced edema. Two-way ANOVA (treatment x time) revealed that, except Acacia nilotica (F18, F (3, 16) = 6.362 P=0.0048, the effect of drug treatment for diclofenac (F18, F (3, 16) = 4.591 P=0.0168), Bombax buopozense (F18, F (3, 16) = 32.25 P<0.0001), and Morinda lucida (F18, F (3, 16) = 15.02 P<0.0001) were significant. Negative Control % change in paw size 20 Acacia nilotica 30mg/kg 15 Acacia nilotica 300mg/kg 10 Acacia nilotica 100mg/kg 5 0 2:00:00 -5 4:00:00 6:00:00 8:00:00 Time (Hours) Figure 4. 1: Effect of Acacia nilotica (30, 100, and 300 mg kg-1; p.o) on time course curve Negative Control % change in paw size 20 Bombax buopozense 30mg/kg 15 Bombax buopozense 300mg/kg 10 Bombax buopozense 100mg/kg 5 0 2:00:00 -5 4:00:00 6:00:00 8:00:00 Time (Hours) Figure 4. 2: Effect of Bombax buopozense (30, 100, and 300 mg kg-1; p.o) on time course curve. Normal saline DICLOFENAC 10mg/kg RED DICLOFENAC 30mg/kg GREEN DICLOFENAC 100mg/kg BLACK % change in paw size 20 15 10 5 0 2:00:00 -5 4:00:00 6:00:00 8:00:00 Time (Hours) Figure 4. 3: Effect of Diclofenac (10, 30, and 100 mg kg-1; p.o) on time course curve. Negative Control % change in paw size 20 Morinda lucida 30mg/kg 15 Morinda lucida Extract 100mg/kg Morinda lucida 300mg/kg 10 5 0 0:00:00 2:00:00 4:00:00 6:00:00 8:00:00 Time (Hours) Figure 4. 4: Effect of Morinda lucida (30, 100, and 300 mg kg-1; p.o) on time course curve. Morinda lucida (30-300 mg kg-1) dose-dependently and significantly reduced, the total foot edema with maximal effect of 35.64±6.470% for Morinda lucida administered prophylactically (Figure 4.5). ✱✱✱✱ ✱ 60 40 20 ML 300mg/kg ML 100mg/kg ML 30mgh/kg 0 Normal Saline Total Oedema (Calc as AUC) ✱✱ Figure 4. 5: Total edema response (AUC) to Morinda lucida in carrageenan-induced paw edema in chicks. Values are meant ± S.D. (n = 5). ***P < 0.001; ** P < 0.01; *P < 0.05 compared to the Normal Saline (One-way ANOVA followed by Newman-Keul’s post hoc test). Acacia nilotica (30-300 mg kg-1) dose-dependently reduced the total foot edema, with a maximal effect of 35.01±5.32% for Acacia nilotica administered prophylactically (Figure 4.6). ✱✱ 60 ✱✱ 40 20 AN 300mg/kg AN 100mg/kg AN 30mgh/kg 0 Normal saline Total Oedema (Calc as AUC) ✱ Figure 4. 6: Total edema response (AUC) to Acacia nilotica in carrageenan-induced paw edema in chicks. Values are meant ± S.D. (n = 5). ***P < 0.001; ** P < 0.01; *P < 0.05 compared to the Normal Saline group (One-way ANOVA followed by Newman-Keul’s post hoc test). Bombax buopozense (30-300 mg kg-1) dose-dependently reduced the total foot edema with a maximal effect of 22.34±3.41% for Bombax buopozense administered prophylactically (Figure 4.7). ✱✱✱✱ 60 ✱✱✱✱ 40 20 BB 300mg/kg BB 100mg/kg BB 30mgh/kg 0 Normal saline Total Oedema (Calc as AUC) ✱✱✱✱ Figure 4. 7: In chicks, total edema response (AUC) to Bombax buopozense in carrageenan-induced paw edema. Valuesare meants ± S.D. (n = 5). ***P < 0.001; ** P < 0.01; *P < 0.05 compared to the Normal Saline (One-way ANOVA followed by Newman-Keul’s post hoc test). The Diclofenac (10-100 mg kg-1) dose-dependently reduced the edema with a maximal effect of 44.58±3.97% (Figure 4.8). ✱ 60 ns 40 20 DICLO 100mg/kg DICLO 30mg/kg DICLO 10mg/kg 0 Normal saline Total Oedema (Calc as AUC) ✱ Figure 4. 8: Total edema response (AUC) to Diclofenac in carrageenan-induced paw edema in chicks. Values are meant ± S.D. (n = 5). ***P < 0.001; ** P < 0.01; *P < 0.05 compared to the Normal Saline (One-way ANOVA followed by Newman-Keul’s post hoc test).