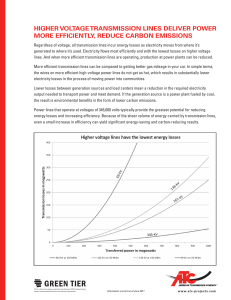
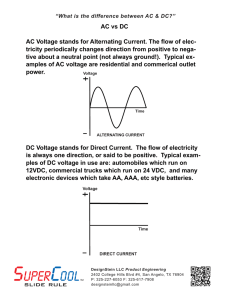
About the research point entitled (Improving the power factor in homes) Power Factor Improvement: The power factor is defined as the ratio of the effective capacity to the total capacity, and it is an indicator of the efficiency of electrical energy consumption in the facility’s equipment. Electricity and other problems at the subscriber’s internal network in addition to the public network. The power factor can be improved by using capacitors that are installed in parallel with the equipment, which is beneficial in the following aspects: • An additional increase in the carrying capacity of the factory network. • Network voltage stability. • Reducing the electricity bill by reducing losses and avoiding fines resulting from low power factor (below the permissible level). • Improving the power factor (not less than 0,9) to reduce waste and make full use of the equipment. Power factor information: The power factor is defined as the ratio of the effective power and its unit (KW) to the apparent power and its unit (KVA). And your low PF index means that there is a lost difference between the two capacities called the unproductive capacity (KVAR) that burdens the electrical network in your facility and requires you to expand it further. If you do not directly pay compensation for the unproductive energy in the monthly consumption bill, you will pay indirect expenses and costs as a result of the low power factor, as long as you have a distribution network, circuit breakers and other electrical equipment in your facility. Benefits of improving the power factor (PF) on the plant: 1- Increasing the carrying capacity of the facility’s network: You often need to expand the equipment of your facility, which requires an increase in the required electrical capacity, and thus an increase in investment in expanding the electrical network in your facility. Improving the power factor (PF) provides you with a significant amount of the carrying capacity of your current network, and allows you to add additional loads Without the need to increase the size of the network and thus reduce the financial expenses needed to change or modify the network to keep pace with the development of your loads. 2- Voltage stability: • Improving the power factor will avoid the plant's voltage drop problems, which are as follows: • Low engine speed and high temperature. • Cables heat up as a result of high current. • The work of the electronic control devices is affected by the improvement of the power factor, the electric voltage in the branches of the network increases. 3- Reducing the electricity bill: Since the losses in the network (IR) are inversely proportional to the power factor, improving the power factor (PF) at all load points will reduce the unproductive current passing through the factory network, and therefore less current will pass through the network and the result is less kilowatt-hours (Kwh) in your bill.