States of Matter Worksheet: Phase Changes & Particle Theory
advertisement

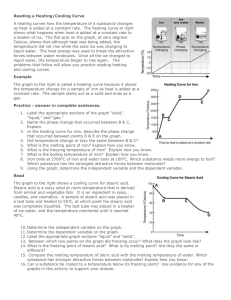
Archbishop’s Seminary States of Matter Worksheets Unit 1 Geraldine Fsadni Unit 1 Matter WORKSHEET 1. Which change of state is going on in the following processes: a. thawing snow ________________________ b. drying clothes ________________________ c. misting up windows ________________________ d. hoar-frost forming on grass on cold, clear nights ________________________ e. chips bubbling in a deep fat fryer ________________________ f. casting metals in a mould. ________________________ 2a. The statements below describe the usual size and shape taken by each state of matter. Fill in the correct state of matter. i) ………………….take any size or shape (fill all the space available). ii) ………………….have a fixed size and keep their shape, unless a force is applied. iii) …………………..have a fixed size but take the shape of the container that they are put in. (3 marks) b. i) Describe the arrangement and movement of particles in a solid. _____________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________________ ii) Describe what happens to the particles of a solid when it melts to a liquid. _____________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________________ (6 marks) c. The state in which a substance normally exists depends on its melting point and boiling point in relation to room temperature. If room temperature is 25°C, in which state of matter will each substance, given below, exist? Page 1 of 10 Substance Melting point Boiling point State Ethane -183°C -88°C ______________________ Naphthalene 80°C 218°C ______________________ Butanol -89°C 118°C ______________________ (3 marks) 3. In the following diagram (fig. 1), the gases ammonia and hydrogen chloride have been introduced at either end of a glass tube. After a short time a white smoke appears in the tube. a. Name or give the formula of the white smoke. ____________________________________________________________ b. Name the process by which the gases move in the glass tube. ____________________________________________________________ c. Suggest why ammonia moves more rapidly than hydrogen chloride. ____________________________________________________________ (3 marks) 4. Use the theory that matter is made of particles to explain the following observations. a) An inflated balloon always goes down in a few days. _____________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________ Page 2 of 10 b) Solids have fixed shapes. _____________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________ c) A closed syringe full of air can be easily compressed but if it is filled with water the plunger cannot be pushed down. _____________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________ d) Liquids stay at the bottom of the containers they are put in. _____________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________________ 5. Explain the following processes by describing what happens to the particles of matter in each case. a) Clothes drying on a line. _____________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________ b) Sugar dissolving in a cup of coffee. _________________________________________________________________________________________________________ ___________________ c) pumping up your bike tyres quite hard gives a smooth ride. Page 3 of 10 _____________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________ d) compressing a gas into half the volume will double its pressure. _____________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________ e) when two solids are placed on top of each other they do not mix. _____________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________ f) poisonous gases from a factory chimney can affect a large area. _____________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________ 6. A gas tap in a laboratory is turned on. Explain, in terms of particles: a) why only the people very near the gas tap smell the gas immediately. _____________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________ b) why everyone in the laboratory can smell the gas within a few minutes. _____________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________ 7. Ammonia is an alkaline gas that turns litmus blue. It is lighter than air. A test tube of ammonia gas is plaed over a test tube of air , like this: Blue litmus paper Ammonia gas Page 4 of 10 Air red litmus paper a. After a short time the red litmus paper in the lower test tube turns blue. Explain why. _____________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________ b. Would it make any difference if you reverse the test tubes? Explain your answer. _____________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________ c. What will you see if the test tube of air is replaced by one containing hydrogen chloride? _______________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________ 8. Give an explanation for the following statements Telephone wires always sag between poles, they are never stretched _________________________________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________ A gas filled thermometer is more sensitive than a liquid one. _________________________________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________ Page 5 of 10 In the olden days the metal ‘tyres’ for cartwheels were heated before being fitted on the wheel. _________________________________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________ Putting a screw-topped jar in hot water makes it easier to open. _________________________________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________ Furniture often creaks at night. _________________________________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________ Concorde is shorter before it takes off than when it is flying. _________________________________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________ 9. Mark the following as True or False Statement True False All matter is made up of particles There are limitless states of matter in which an object can exist The molecules of steam are identical to those of ice: they just have a higher energy Liquids take the shape of the whole container Page 6 of 10 A gas jar is opened in a room. The gas diffuses through the whole room Particles in a gas can change shape No solid can turn into a gas without first becoming a liquid When a solid is heated above its melting point it melts Water is heated from 20°C to 60°C. A change of state occurs Brownian motion supports the theory that everything around us is made up of continuously moving particles Particles in a solid vibrate A chemical change cannot be reversed Solid particles have strong forces of attraction between them Reading a Heating/Cooling Curve Worksheet Page 7 of 10 A heating curves how the temperature of a substance changes as heat is added at a constant rate. The heating curve at right shows what happens when heat is added at a constant rate to a beaker of ice. The flat spot on the graph, at zero degrees Celsius, shows that although heat was being added, the temperature did not rise while the solid ice was changing to liquid water. The heat energy was used to break the attractive forces between water molecules. Once all the ice changed to liquid water, the temperature began to rise again. The problems that follow will allow you practice reading heating and cooling curves. Example The graph to the right is called a heating curve because it shows the temperature change for a sample of iron as heat is added at a constant rate. The sample starts out as a solid and ends as a gas. Practice -answer the following 1.Label the appropriate sections of the graph “solid,” “liquid,” and “gas.” 2.Name the phase change that occurred between B & C. Explain what is happening and why the temperature is not increasing even though heat is being added. __________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ ______________________ 3. In the heating curve for iron, describe the phase change that occurred between points D & E on the graph. Page 8 of 10 __________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ ______________________ 5.What is the melting point of iron? Explain how you know. __________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ ______________________ 6.What is the freezing temperature of iron? Explain how you know. __________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ ______________________ 7.What is the boiling temperature of iron? Explain how you know. __________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ ______________________ 8. Iron boils at 2700oC of iron and water boils at 100oC. Which substance needs more energy to boil? Which substance has the strongest attractive forces between molecules? __________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ ______________________ Read The graph to the right shows a cooling curve for stearic acid. Stearic acid is a waxy solid at room temperature that is derived from animal and vegetable fats. It is an ingredient in soap, candles, and cosmetics. A sample of stearic acid was placed in a test tube and heated to 95oC, at which point the stearic acid was completely liquefied. The test tube was placed in a beaker of ice water, and the temperature monitored until it reached 40oC. 9.Label the appropriate graph sections “liquid” and“solid”. Page 9 of 10 10. Between which two points on the graph did freezing occur? What does the graph look like? __________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ ______________________ 11. What is the freezing point of stearic acid? What is its melting point? Are they the same or different? __________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ ______________________ 12. Compare the melting temperature of steric acid with the melting temperature of water. Which substance has stronger attractive forces between molecules? Explain how you know. __________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ ______________________ 13. Can a substance be cooled to a temperature below its freezing point? Use evidence for any of the graphs in this activity to support your answer. __________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ ______________________ Page 10 of 10