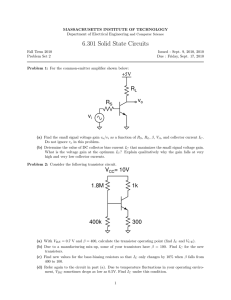
Transistor as Switch Objective Theory Transistor is a three terminal, bipolar, current controlled device. It works in three different regions: Active, Cutoff and Saturation according to applied biasing condition. Transistor as switch: ON Transistor will become ON (saturation) when a sufficient voltage V is given to input. During this condition the Collector Emitter voltage Vce will be approximately equal to zero, ie the transistor acts as a short circuit. For a silicon transistor it is equal to 0.3v. Thus collector current Ic = Vcc/Rc will flow. Transistor as switch: OFF Transistor will be in OFF ( cutoff ) when the input Vin equal to zero. During this state transistor acts as an open circuit and thus the entire voltage Vcc will be available at collector. Schematic In this circuit, a square wave input is applied. When input is high, the transistor is turned on and works in saturation region. So maximum current IC flows through transistor as well as LED. Hence LED emits the light. When input is low (low means not enough to turn on the transistor), the transistor remains in cutoff. So current IC is zero thus LED does not emit the light. As the input is square wave, the LED will turn on and off alternately. If output is observed on CRO from the collector, then it will be also a square wave but out of phase by 180° with input. Thus transistor is working as a switch which can be made on or off by an external input. Procedure Connect the circuit as shown in figure. Apply 1 Hz square wave signal to the base and ground from function generator. Apply 5V VCC to collector and ground. Observe the indication of LED and see the output waveforms on CRO. Observations Draw input and output waveforms. Conclusion The transistor switching operation is performed based on the voltage applied at the base terminal of a transistor. When a sufficient voltage is applied between the base and emitter, collector to emitter voltage is approximately equal to 0. Therefore, the transistor acts as a short circuit. The collector current flows through the transistor. Similarly, when no voltage or zero voltage is applied at the input, transistor operates in cutoff region and acts as an open circuit. In this type of switching connection, load (LED) is connected to the switching output with a reference point. Thus, when the transistor is switched ON, current will flow from source to ground through the load(LED). Graph 3.2: Output for Inverting Voltage Amplifier Phase Shift=_____________ Questions What is the effect as Rf is increased? How does the voltage gain vary as the op amp is changed? Does the inverting voltage amplifier exhibit a predictable and stable voltage gain? What can be said about the input impedance of this type of amplifier? Based on the simulation, what is the relationship between gain, feedback and distortion for this circuit?