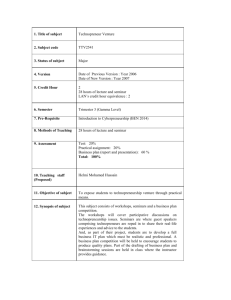
Technopreneurship BEE4613 BEE4613 Technopreneurship Syllabus Chapter 1: • Technopreneur & Technopreneurship Chapter 2 • Business Opportunities: Identification, Evaluation & Selection Chapter 3 • Innovation and Technopreneurship BEE4613 Technopreneurship Chapter 4 • Forms of Business Entities, Regulations and Business Support System Chapter 5 • Business Plan Chapter 6 • Management of a Small Business BEE4613 Technopreneurship Chapter 7 • Marketing Chapter 8 • Operations Management Chapter 9 • Financial Plan Chapter 10 • Issues on Technopreneurship BEE4613 Technopreneurship Assessment Test 1 Test 2 Presentation Business Plan Report Final Exam TOTAL : 15% : 15% : 30% : 40% : 0% : 100% BEE4613 Technopreneurship References i. ii. iii. iv. UiTM Entrepreneurship Study Group (2004). “Fundamentals of Entrepreneurship.” Pearson Prentice Hall. Peter F.Drucker (1993). “Innovation and Entrepreneurship”. HarperBusiness W.Chan Kim, Renee Mauborgne (2005). “Blue Ocean Strategy”. Harvard Business School Publishing Corporation David H.Bangs, Jr (2001). “The Business Planning Guide”, Advantage Quest Publications. BEE4613 Technopreneurship Subject assignment • Business proposal – – A group consists of max 6 students Register group members • CEO/manager – Brain storming session • Type of business • Type of product • Commercial value.. BEE4613 Technopreneurship How great we are? BEE4613 Technopreneurship BEE4613 Technopreneurship BEE4613 Technopreneurship BEE4613 Technopreneurship Are they any business opportunities from this scenery? BEE4613 Technopreneurship How many business should be established to have all this stuffs inside BEE4613 Technopreneurship your kitchen? How about this messy room? BEE4613 Technopreneurship How about communication industry? BEE4613 Technopreneurship How about airlines industry? BEE4613 Technopreneurship Why we need an entrepreneur? BEE4613 Technopreneurship • Identify how many of – – – Business items (we have to pay)…. Non-business items (free of charge)… Inside this lecture room??? • Percentage…??? % = Business items – non-business items x 100% Business items BEE4613 Technopreneurship What Can BEE4613 Technopreneurship Entrepreneur, Technopreneur, Intrapreneur, Innovator, Manager BEE4613 Technopreneurship Earlier Viewpoints (17001950s) • The word entrepreneur comes from French word ‘entreprendre’ • “Entreprendre” – individuals who undertake (the risk of new ventures). BEE4613 Technopreneurship Entrepeneur • Entrepreneur invests, transforms and makes (profit or loss) [Richard Cantillon, French economist] – In other words, goods are bought at a certain price, value is added by transforming (the least being to repack) the goods, and the goods are then sold at an uncertain price. BEE4613 Technopreneurship • “The task of forming an organisation for commercial purposes” [Adam Smith 1977] • In his book, Wealth of Nations “The ability to foresee potential through changes in the economy, and to act on the demand thereby created” BEE4613 Technopreneurship • “The entrepreneur was said to influence society by forming enterprises and was in turn influenced by society to recognise needs and to fulfil through skilful management of resources” [Jean Babtiste Say, 1903, French Economist] BEE4613 Technopreneurship • “Entrepreneurs are economic agents who transform resources into goods and services, thereby creating an environment conducive to industrial growth” [Carl Menger, 1871, Principles of Economics] BEE4613 Technopreneurship D elivered baked bread is highest value use P riority1 B read at bakery for sale has high value Priority 2 Priority3 Milled flour for baker has high value Intermediate Priority 7 Priority 8 Menger’s Model of Value-Added Transformation of Resources steps in trans form ation B ulk grain from farmer has low value Grain in field has very low value Source: David H.Holt. Entrepreneurship. New Venture Creation Englewood Cliffs, NJ: Prentice-Hall 1992, p.5 BEE4613 Technopreneurship • “Entrepreneurship is a creative destruction force that sees the destruction of usual ways of doing things by the introduction of new improved ways” [Joseph Schumpeter, 1934, Austrian] BEE4613 Technopreneurship • Entrepreneurship is a process, and the entrepreneur is an innovator who uses processes to challenge existing norms via combinations of new resources and methods in commerce. BEE4613 Technopreneurship Technopreneur • They are entrepreneurs who used “technology” as their driven factor in transforming resources into goods and services, creating an environment conducive to industrial growth”… BEE4613 Technopreneurship • Innovations are not confined to tangible products but also include services and processes. – The continuous improvement in financial sector – City bank, Air Asia… BEE4613 Technopreneurship BEE4613 Technopreneurship • Entrepreneur seem to be the starters and managers the followers – Initially, entrepreneurs also assume the role of manager, but later the managerial roles are delegated to the managers. • Managers do not start businesses, they only manage them. BEE4613 Technopreneurship • In the world of corporate business, intrapreneurs emerge as that breed who is a cross between managers and entrepreneurs. – They work for the corporation but are given the task of starting new ventures. BEE4613 Technopreneurship Any Questions? BEE4613 Technopreneurship What Is Entrepreneurship? Nature of Entrepreneurship • It is a socio-economic phenomenon. • Engine of economic growth • Creator of wealth and employment. What is Entrepreneurship? • It is a creative and innovative human act. • Ability to create and build a vision from practically nothing. • Vision requires willingness to take calculated risks. • It is a discipline, hence it can be learned – Peter Drucker BEE4613 Technopreneurship Definition of Entrepreneurship “ Entrepreneurship is the ability to create and build a vision from practically nothing. Fundamentally, it is a human, creative act. It is the application of energy to initiating and building an enterprise or organization, rather than just watching or analyzing. This vision requires a willingness to take calculated risks – both personal and financial, and then to do everything possible to reduce the chances of failure. Entrepreneurship also includes the ability to build an entrepreneurial or venture team to complement your (the entrepreneur) own skills and talents. It is the knack for sensing an opportunity where others see chaos, contradiction, and confusion. It is possessing the knowhow to find, marshal and control resources, often owned by others.” BEE4613 Technopreneurship Professor Jeffrey Timmons (1990) Entrepreneur Are Made and Not Born “The entrepreneurial mystique? It’s not magic, it’s not mysterious and it has nothing to do with the genes. It is a discipline. And like any discipline, it can be learned.” …Peter Drucker BEE4613 Technopreneurship Why People Become Entrepreneurs? • Definition of an entrepreneur – French word “entreprende” meaning ‘go between’ or ‘enter to undertake’. A person who undertakes to organize, manage and assume risks of business • How people become entrepreneur ? – By Necessity and Opportunity, Design and Default • Triggered by ‘Social Disruption or Interruption” • Entrepreneurs are created in good and bad economic times. • Achievements and Financial Rewards for an Entrepreneur. • Many begins but few make it. BEE4613 Technopreneurship Who Are The Entrepreneurs? • Paradigm shifters, innovators and opportunists – creative destroyers • Key change catalysts and agents • Wealth and employment creators • Economic engine drivers • Key actors of the Malaysian Economy • Entrepreneurs are made and not born – entrepreneurial propensity • You can be the entrepreneur - if you have what it takes • People who like to be their own boss • People who has experienced a “social disruption”? • Necessity and opportunity entrepreneurs BEE4613 Technopreneurship Entrepreneurial Traits (1) Most Important for Success: • Innovative & Opportunistic • Willingness to take risk • Initiative • Self reliance • Perseverance (keep trying to achieve something) • Need to achieve • Self confidence BEE4613 Technopreneurship Entrepreneurial Traits (2) Important for Success: • Leadership • Competitiveness • Good physical health • Creative • High level of energy • Versatility BEE4613 Technopreneurship Entrepreneurial Traits (3) Least Important for Success: • Ability to get along • Patience • Well organized • Desire for money • Tolerate uncertainty • Need for power • Need for affiliation BEE4613 Technopreneurship Difference Between Entrepreneurship And Small Business Entrepreneurship Small Business • Innovation • Little innovation • Fast growth • Static growth • Vision • Little vision • Employment creation • Family business • Money making machine • Earning a livelihood • Higher risk • Low or minimum risk BEE4613 Technopreneurship Entrepreneurship Statistics… Do You Know? US Situation About 1 million businesses are formed each year in the US Between 70 to 80% failed the first year of start-up 10% to 20% last through the next 5 years Venture investment 1:10 success rate Venture capitalists expects between 5 to 10 times return Source : US Statistics BEE4613 Technopreneurship Entrepreneurship Statistics Do You Know? 6 in a million with a high tech business idea eventually becomes a successful company that goes public / IPO. Fewer than 20% of the funded starts-up go public. Bankruptcies occur for 60% of the high tech companies that succeed in getting venture capital. Venture capital investors own a large part of the start-up by the time it goes public: 70 % of hardware companies, 60% of software companies and 50% of internet companies. Source: US Statistics BEE4613 Technopreneurship Malaysian Setting & Global Scenario BEE4613 Technopreneurship Mewujudkan masyarakat saintifik dan progresif, masyarakat yang mempunyai daya perubahan tinggi dan memandang ke hadapan, yang bukan sahaja menjadi pengguna teknologi tetapi juga penyumbang kepada BEE4613 Technopreneurship tamaddun saintifik Malaysia: Enterprising Culture And Nation Economic Paradigm Shifts 1950s to 2000s. Wawasan 2020 Ministry for International Trade & Investment - SMIDEC Ministry for Entrepreneurs & Co-0perative Development. Multimedia Super Corridor – 7 Flagships. MSC Status Privileges & Incentives. Strong Economic Growth & Social Innovation Rapid Infrastructure Development. Industry Promotion of Entrepreneurship: Enterprise 50 Awards, Ernst & Young Malaysian Entrepreneur of the Year Award, Venture 2002, MSC-IHL Business Plan Competition, MAVCAP’s Cradle Investment Programme BEE4613 Technopreneurship MSC Flagship Applications Smart Schools Multipurpose Card Telehealth Electronic Government Technopreneur Development R&D Cluster E-Business Borderless Marketing BEE4613 TechnopreneurshipWorldwide Centre Manufacturing Web Malaysia Economic Transformation & Drivers Source : Malaysia’s National Economic Action Council Knowledge-based Knowledge-driven KNOWLEDGE BASED / INTELLECTUAL CAPITAL HIGH TECHNOLOGY / SERVICES High-tech Manufacturing & Services Productivity-driven Medium-tech Manufacturing & Services Investment-driven Assembly-type Manufacturing TECHNOLOGY / FOREIGN DIRECT INVT Labour-driven Primary Commodities Labour-driven 1960 INDUSTRIAL / IMPORT SUBSTITUTION AGRICULTURE / PRIMARY COMMODITY 1970 1980 BEE4613 Technopreneurship 1995 1996 2005 2020 • Value creation through knowledge products and industry • ICT as a sector • Information as commodity Now NITA Vision Economic • Competitive, dynamic, robust & resilient • Fair & equitable distribution of wealth • Knowledge economy non i o t i ta a m r iteyty m r o of ie InIfn SoScoc 2020 l i v Ci iety c o S e g e egd l d le ieyty ow w n o oicet K n s K oSc n a S IC e m s a T • Connectivity of • Empowered citizens networks • Self-regulating • Equitable access to • Self-controlled information • Fostering creativity • Culture of learning • Inclusive society • InformationBEE4613 literate Technopreneurship • Strong families Social • United • Developed & secure • Strong moral and ethical values • Democratic and liberal • Tolerant & Progressive Strategic Framework For balanced development through innovation, the ‘ICT4D Framework’ shown, which draws on the principles highlighted thus far, can be used as a guide. ICT as an ENABLER Malaysia’s ICT4D program for Innovating towards a K-nation Innovation for BALANCED SOCIETAL DEVELOPMENT Innovation for GOOD GOVERNANCE BEE4613K-society Technopreneurship Industry Society ICT as a SECTOR Innovation for WEALTH CREATION Govern -ment Information & Communication Technology K-economy Framing the Strategic ICT R&D Agenda: Strategic Intent • Innovation for WEALTH CREATION - All sectors of the Malaysian economy creating value and wealth through successful participation in the emerging knowledge-driven global economy - Key focus: Knowledge-driven economy • Innovation for BALANCED SOCIETAL DEVELOPMENT – Inclusive community development through provision of life changing ICT applications – Key focus: Knowledge society • Innovation for GOOD GOVERNANCE – Foster form of accountability and transparency in the process of governance that enhance the quality of life of Malaysians – Key focus: Participating in governance for quality of life BEE4613 Technopreneurship Any Questions? BEE4613 Technopreneurship