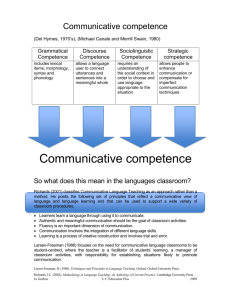
Spolsky (1989) stated that the development of theory about communicative is somewhat response to Chomsky’s limiting range of meaning to linguistic competence. As Hymes proposed it, Communicative competence is particularly for individuals that is interested in learning a second language. Also, it is stated the different language tests that involves measuring the individual’s knowledge of, proficiency in, the use language has the same manner to communicative competence because the theory deals with such knowledge and proficiency. Savignon (1983) made a model for communicative competence that she based on Canale and Swain’s framework that includes four areas of knowledge and skill which is grammatical competence, sociolinguistic competence, discourse competence, and strategic competence. Savignon made a diagram that shows the possible relationship of the four constituent areas. She stated that "an increase in one component interacts with the other components to produce a corresponding increase overall communicative competence". She made a valid and interesting point when she insist that sociolinguistic competence and strategic competence authorize a person or learner to reach a certain degree in communicative competence before he/she acquires any grammatical competence. She also stated that strategic competence is present in four areas of knowledge and skill. Barbora Dvořáková (2011, 2012) stated that Communicative Competence plays a big role in Communicative Language Teaching (CLT). It goes far further than the linguistic competence and it uses language as an instrument to achieve a premeditated objective through verbal processing. CLT understand language as tool to attain a certain goal and interpersonal communication. Back when this approach was first used they gave more value to ability of second language learners to effectively communicate in Target Language (TL) (Brown, 2001).