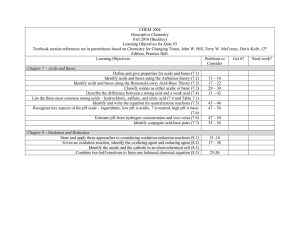
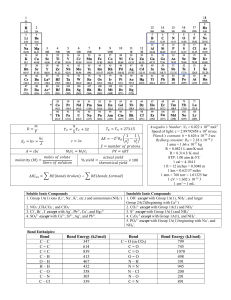
Acids and Bases Practice Questions 1. a) State the definition of an Arrhenius acid and of a Bronsted-Lowry Acid. b) Write the chemical equation for what happens when HNO3 is dissolved in water according to each theory. 2. A scientist states that methylamine (N2H4) is a base. Which acid-base theory are they using to make this claim, and how do you know? 3. For each of the following reactions, identify the Brønsted-Lowry acids and bases and identify the conjugate acid-base pairs: a) CH3COOH + NH3 � NH4+ + CH3COO – b) H2CO3 + H2O � H3O+ + HCO3 – c) NO2 – + NH4+ � HNO2 + NH3 4. A compound is tested in the lab to determine if it is an acid or a base. The results are shown below: Tests carried out on an unknown sample to determine if it is an acid or a base Test Result solubility in water when sample was placed in water it disappeared electrical conductivity of solution reacted with Mg(s) reacted with NH4Cl(s) solution was electrically conductive bubbles observed no reaction a) Use the data in the table to identify whether the substance is an acid or a base and explain which tests were NOT useful in reaching your conclusion. b) Based on your identification in (a), predict the observations if i) litmus paper was placed in the solution ii) the solution was tasted (do NOT do this in the lab!!) 5. Identify these substances as acids or bases, and compare the [H+] for each pair. a) b) Solution A pH 5 and Solution B pH 2 Solution C pH 11 and Solution D pH 13 6. Calculate the pH of the following solutions: a) b) c) d) A 3.42 x 10-4 mol/L solution of nitric acid A 4.4575 x 10-5 mol/L solution of sulfuric acid A 1.65 x 10-2 mol/L solution of potassium hydroxide A 7.995 x 10-6 mol/L solution of barium hydroxide 7. Calculate the pH of a solution made by dissolving 0.500g of KOH to a final volume of 500.0 mL.