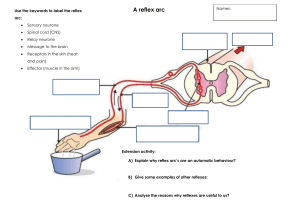
The Nervous System PNS: Nerves, Senses, and Responses Peripheral Nervous System Form & Function Two major jobs: Carries signals between the CNS and the rest of the body Regulates involuntary body functions and responses 4 major groups of nerves, organized by spinal cord: Cervical Thoracic Lumbar Sacral Both are involuntary Sympathetic: “arousing” reactions Ex. Heartbeat increase, digestion inhibition, Autonomic NS: Parasympathetic vs Sympathetic pupils dilate, epinephrine released Parasympathetic: “calming” reactions Ex. Heartbeat slows, digestion stimulated, saliva produced Together they’re responsible for “fight/flight/freeze” responses and their opposites Two-way pathways between sensory input and motor responses Afferent (sensory) pathway: sensory organ Somatic NS: Sensory and Motor CNS Efferent (motor) pathway: CNS muscle/motor response Both voluntary and involuntary Voluntary: See a penny, pick it up Involuntary: Reflexes See cat… …must pet Reflexes Reflex arc simple path, only includes a few neurons (involuntary, instantaneous) Knee-jerk reflex maintains uprightness Withdrawal reflex avoidance of painful stimuli acoustic reflex - In response to high sound intensities, contraction of the stapedius and tensor tympani muscles in the middle ear. blushing - A reddening of the face caused by Some more human reflexes embarrassment, shame or modesty. corneal reflex - Blinking of both eyes when the cornea of either eye is touched. rooting reflex - Turning of an infant's head toward anything that strokes the cheek or mouth. shivering - Shaking of the body in response to early hypothermia in warm-blooded animals. vestibulo-ocular reflex - Movement of the eyes to the right when the head is rotated to the left, and vice versa. Neurons! Synapse Cell Body Dendrite Axon Neuron Structure Neurons - masses of nerve cells that transmit information Each neuron is connected in long chains They don’t actually touch! Space between = synapse Cell Body - contains the nucleus and two extensions Dendrites – extend from the cell body and receive information Axons - long section, transmits impulses Myelin - insulation surrounding axons Protects and speeds up signals – think like an insulated wire! Multiple sclerosis = degradation of myelin (immune) Nodes of Ranvier - gaps in the insulation Signals “jump” between nodes = super speedy! Neuron Structure White vs. Grey matter White matter – myelinated axons Grey matter – unmyelinated Why might one be more myelinated than the other? Longevity – can live and function for a lifetime Do not divide – fetal neurons lose their ability to undergo mitosis; neural stem cells are an exception Neuron Facts! High metabolic rate – require abundant oxygen and glucose The nerve fibers of newborns are unmyelinated - this causes their responses to stimuli to be coarse and sometimes involve the whole body. Try surprising a baby! Neurotransmitters To complete the signal, a NEUROTRANSMITTER is released at the gap to signal the next neuron. Receptors on the dendrite receive the chemical message Types of neurotransmitters Over 100 different kinds Acetylcholine - stimulates muscle contraction Monoamines - Norepinephrine & Dopamine (sense of feeling good, low levels = depression) Serotonin - sleepiness and mood Endorphins - reduction of pain, good mood Neurotransmitters Weak point of nervous system Any substance that affects neurotransmitters or mimics them affects nerve function • gases: nitrous oxide, carbon monoxide • mood altering drugs • Stimulants: amphetamines, caffeine, nicotine • Depressants: alcohol • hallucinogenic drugs • poisons Curare - poison made from frog skin and causes paralysis by blocking Ach receptors at the neuromuscular junction. Uses: indigenous weapons Botulinum toxin – produced by bacteria Neurotoxins Clostridium botulinum, inhibits Ach release. “Food poisoning” Uses: BOTOX Brain plasticity "I Listen to Color" - Neil Harbisson Reflex activity! Pupillary Response Exercise Perform this exercise with a partner. Dim the room lights. After a few minutes, look at the eyes of your partner and note the pupil sizes (the black center spots in the middle of the eyes). Turn on the room lights. Check the pupil sizes again. The pupils should now be smaller. This is called the pupillary reflex response. This reflex “automatically” keeps out excessive light that may damage the eyes, and thus protects your eyes for you!