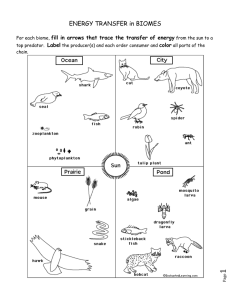
Introduction to Ecology Define ecology The scientific study of interactions among organisms and between organisms and the environment. Biosphere contains the combined portions of the planet in which all of life exist, including land, water and atmosphere Level of Organization of an Ecosystem Species • Species - group of organisms so similar to another that they can breed and produce fertile offspring Population • Population – same species and live in same area Community • Communities – different populations that live together in a defined area Ecosystem • Ecosystem – a collection of all organisms that live in a particular place together with their nonliving environment. Biome • Biome – a group of ecosystems that have the same climate and similar dominant communities. What shapes an Ecosystem? Biotic and Abiotic • Biotic and Abiotic factors determine the survival and growth of an organism and the productivity of the ecosystem in which an organism lives. Biotic Factors • Living Factors that influence an ecosystem • Plant life • Animal life Abiotic Factors • Physical, non-living factors that influence an ecosystem • Examplestemperature, precipitation, humidity, wind, nutrients, sunlight Other factors that affect an Ecosystem • The area where an organism lives is called its habitat. • Habitats provide populations of wildlife with food, water, shelter and space. • A niche is the full range of physical and biological conditions in which an organism lives and the way in which the organism uses those conditions. It is an organisms’ occupation. Cycles that affect Ecosystems Water Cycle Water Cycle Definitions • Evaporation – process of becoming a vapor; liquid to a gas • Condensation – state of matter from gas to liquid; reverse of vaporization • Precipitation – the amount of water that falls to earth as snow, sleet, hail, rain, mist • Transpiration – loss of water from a plant through its leaves • Runoff – the flow of water, from snow and rain • Infiltration – process by which water on the ground enters soil Carbon Cycle CO2 Cycle Description • Plants release O2 into atmosphere as a waste product • Animals release CO2 into atmosphere as a waste product • Factories and cars release CO2 into atmosphere through combustion. • Plants use CO2 during photosynthesis and animals use O2 for respiration. Energy Flow • Every organism needs energy to power life’s processes • The flow of energy through an ecosystem is one of the most important factors that determines the ability to sustain life Autotrophs • Captures energy from sunlight or chemicals and use that energy to produce food. • Other names are producers or plants. • Are essential for the flow of energy through the biosphere • Produce food through Photosynthesis Examples ofAutotrophs Heterotrophs • Organisms that rely on other organisms for their energy and food supply. • Consumer is another name • Types of Consumers • • • • • Herbivores Carnivores Omnivores Decomposers Detritivores Examples of Consumers Decomposers • Breaks down dead/decay matter • Bacteria and fungi are examples of decomposers • Detritivores feed on plant/animal remains • Millipedes and earthworms are detritivores Parasites A parasite is an organism that lives on or in a host organism and gets its food from or at the expense of its host. Example – Tick, Flea, Tapeworm Energy Flow Energy flows through an ecosystem in one direction from the sun to autotrophs (producers) and then to heterotrophs (consumers). Food Chains • A food chain is a series of steps in which organisms transfer energy by eating and being eaten. Food Web • A network of complex feeding relationships among the various organisms in an ecosystem Energy Pyramid • Trophic level is each step in a food chain/web • A diagram that shows the amount of energy or matter contained within each trophic level in a food chain/web • Only about 10% of the energy available within one trophic level is passed to organisms in the next trophic level. • Ecological Succession a series of predictable changes in an environment Succession • Primary Succession – succession that occurs on the surface where no soil exists • Pioneer Species first species to populate the area • Examples- lichen and moss Examples of Pioneer Species • Lichen Succession • Secondary Succession – following a disturbance that destroys a community without destroying the soil. • Example- land cleared and plowed for farming • Example – Fires set by lightning