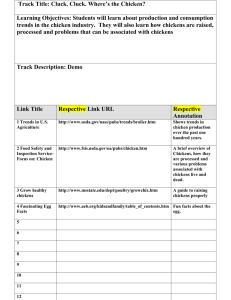
Introduce ourselves Talk about the farm and how chickens are part of it. We get fresh eggs, chickens eat unwanted bugs and weeds, and we get fertilizer from their droppings. Chicken welfare – what do chickens need to survive: ask class to guess. food water fresh air/sunshine/access to the outdoors coop/house/shelter fence - protection from predators – have students guess predators – “Hawks, bobcats, coyotes, snakes, skunks, owls, raccoons, foxes, and opossums. Some predators are tricky and can get through the fence, so we have a guardian dog. Louie: Great Pyrenees dog breed’s goal in life is to protect livestock, people, children, grass, flowers, the moon, the lawn furniture, bird feeders, and any real or imaginary predators that may intrude on his personal space. There for he barks all night and half the day. Oh yeah, and he gives unconditional love. CHICKEN FACTS: Chickens are domestic or farm birds. What does domestic mean? “Trained to live or work for humans as pets or on a farm.” Poultry is domestic fowl not just chickens. The term poultry includes, chickens, turkeys, ducks, ostriches, emus, quail, pheasants, and geese, that can be raised for meat or eggs. On our farm we raise chickens, ducks, and turkeys for their eggs and meat. Male chickens are called what? “Roosters” come in may sizes from 12 pounds down to 22 ounces. Female chickens are called? “Hens” and are smaller than roosters. There are over 150 breeds of poultry and 340 different color combinations. Chickens may have either 4 or 5 toes depending on the breed. There are more chickens in the world than any other bird and are raised on every continent. Humans started keeping chickens over 10,000 years ago. Chickens can only fly short distances Let’s talk about the parts of a chicken: Hold chicken and name each part – refer to poster. Count how many toes the chicken has. Life cycle of a chicken: 1. Egg – hold up eggs 2. Embryo – Show Poster and talk about baby chicken growing inside egg. 3. Chick – show baby chick – covered in down. 4. Pullet – is a chicken that half grown and is getting feathers but not old enough to lay eggs. 5. Adult chicken is full grown and egg laying. What do chickens eat: Chickens are omnivores and eat insects, grains, vegetables, weeds, and many other foods. Chickens don’t have teeth. They swallow their food without chewing and then it is ground up in their gizzard. The gizzard, which is part of the stomach contains tiny stones to help grind up the food. Chickens need grit (stones) in their diet to produce eggs. A hen must eat 3.5 pounds of feed, vegetables, bugs, or weeds to make a dozen eggs. Show what 3 ½ pounds of food looks like. Anatomy of an Egg: Refer to poster Break 2 eggs in two bowls. Have the students look for the parts. Have the teachers and Taya take around so kids can see. (Save to use for the next groups, replace if egg yoke gets broken.) EGG FACTS 1. Eggs are natural, delicious, nutritious, and provide protein (to help you built muscle), healthy fats, vitamins, minerals, antioxidants that fight cancer and reduce the effects of aging. 2. An egg’s shell color doesn’t indicate the quality or nutritional value of an egg, but rather the breed of the hen that laid it. 3. The yolk color is determined by the diet of the hen. Grain only produces yellow yokes; free range diet on bugs, vegetables, weeds and grain produces orange yokes. 4. Long shelf life. Your eggs should be edible for 3-4 weeks past the sell by date on the carton. Show the Julian date on the carton. 5. The average American eats 250 eggs per year. 6. Unlimited cooking options. MEET THE CHICKENS - LET STUDENTS TOUCH THEM – DON’T LET THEM HOLD THEM! ALWAYS WASH HANDS AFTER HANDLING CHICKENS OR UNCOOKED EGGS