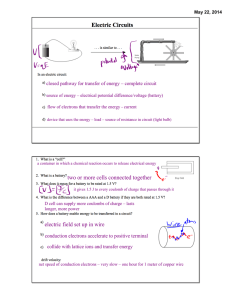
Science Notes Electricity: - Electrons in current electricity move in a steady flow through a conductor A continuous path for electron flow is called an electric circuit - Components of a simple electrical circuit o Load ▪ Device that transports electrical energy into other usable forms of energy, such as a bulb or a heater o Energy Source ▪ An energy source o Conducting Wires ▪ Join all parts of a electrical circuit ▪ Pathway for electrons to flow ▪ Normally made of aluminum or insulated copper o Switch ▪ Controls current flow in a circuit ▪ Closed = On ▪ Open = Off - Electrical Cells o Electrical Cell: Portable device that converts chemical energy into electrical energy o Electrical cells are made of two electrodes in a conducting solution called an electrolyte ▪ Electrodes are the conductors with different charges o Primary Cells: Cannot be recharged because chemical reactions used to produce energy aren’t reversible o Secondary Cells: Can be recharge and reused due to the chemical reactions being able to be reversed - There are Two different forms of electrical currents: o Direct Current (DC) ▪ Electrons flow in one direction, battery provides electrons to loads o Alternating Current (AC) ▪ Electrons move back and forth, alternating their direction ▪ AC produced through generators ▪ Able to travel longer distance than DC - There are many ways to produce energy o Electrical generating stations convert mechanical energy into electrical energy. ▪ An external energy source is used to push the blades of a turbine which moves a generator ▪ Generator has a coil of wire inside between two poles of a magnet ▪ When turbine spins, so does coil of wire and electrons are transmitted into the wire o Constant flow of electrons through a generator was discovered by Michael Faraday o Electrical energy production can be controlled - Electrical Power: o Electrical Power: The rate at which electrical energy is produced or consumed in a given time ▪ Unit for electrical power is the Watt (W) ▪ W = J/S o Electrical Generating Stations measures in Watt-hours (W-h) and kilowatthours (kW-h) and gigawatt-hours (GW-h) ▪ kW-h = W-h x 1000 ▪ GW-h =kW-h x 1000000 - Electric Current: Rate of electron flow past a specific point in a circuit Potential Difference or Voltage: Difference in potential energy per unit of charge Electrical Resistance: The opposition to the movement of electrons as they flow through a circuit o Factors that affect resistance ▪ Material • Conductivity leads to lower resistance ▪ Cross-sectional area - • ▪ ▪ ▪ Thicker wires have less resistance as there are more places to move Length • Resistance increases the longer the wire Temperature • Warmer wire means higher resistance