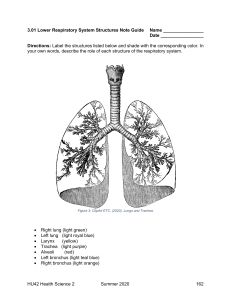
Chapter 53: Introduction to the Respiratory System Copyright © 2013 Wolters Kluwer Health | Lippincott Williams & Wilkins Anatomy of the Respiratory System Components o Upper respiratory tract o Lower respiratory tract Function o Brings oxygen into the body o Allows for the exchange of gases o Expels carbon dioxide and other waste products Copyright © 2020 Wolters Kluwer • All Rights Reserved The Respiratory Tract Copyright © 2020 Wolters Kluwer • All Rights Reserved Structures of the Upper Respiratory Tract Nose and Nasal Cavity Sinuses Pharynx Larynx Trachea Bronchi Copyright © 2020 Wolters Kluwer • All Rights Reserved Protective Features of the Upper Respiratory Tract Hairs filter the air Goblet cells produce mucus to trap material Cilia move the trapped material toward the throat for swallowing The blood supply close to the surface warms air and adds humidity to improve gas movement and gas exchange The cough and sneeze reflexes clear the airways Copyright © 2020 Wolters Kluwer • All Rights Reserved Cough Reflex The walls of the trachea and conducting bronchi are highly sensitive to irritation. When receptors in the walls are stimulated, a central nervous system reflex is initiated. Cough causes air to be pushed through the bronchial tree under tremendous pressure, clearing the airway of foreign irritant. Copyright © 2020 Wolters Kluwer • All Rights Reserved Sneeze Reflex Initiated by receptors in the nasal cavity Forces foreign materials directly out of the system Copyright © 2020 Wolters Kluwer • All Rights Reserved Cilia Copyright © 2020 Wolters Kluwer • All Rights Reserved Layers of the Bronchial Tubes Cartilage Muscle Epithelial Cells Copyright © 2020 Wolters Kluwer • All Rights Reserved Question #1 Please answer the following statement as true or false. The purpose of the cough and sneeze reflexes are to clear the airways. Copyright © 2020 Wolters Kluwer • All Rights Reserved Answer to Question #1 True Rationale: The cough and sneeze reflexes clear the airways. Copyright © 2020 Wolters Kluwer • All Rights Reserved Lower Respiratory Tract Composed of the smallest bronchioles and the alveoli Considered the functional unit of the lungs Gas exchange occurs in the alveoli - ventilation Copyright © 2020 Wolters Kluwer • All Rights Reserved Components of the Respiratory Membrane and Gas exchange Gas exchange occurs at alveolar level. The alveolar sac holds the gas, allowing needed oxygen to diffuse across the respiratory membrane. It consists of the following: Capillary Endothelium Capillary Basement Membrane Interstitial Space Alveolar Basement Membrane Alveolar Epithelium Surfactant Layer Copyright © 2020 Wolters Kluwer • All Rights Reserved Structures in the Respiratory Membrane Copyright © 2020 Wolters Kluwer • All Rights Reserved Process of Respiration Controlled through the medulla in the central nervous system Depends on a balance between the sympathetic and parasympathetic systems Depends on a functioning muscular system Copyright © 2020 Wolters Kluwer • All Rights Reserved Controls Over the Respiratory System Parasympathetic nerve stimulate the diaphragm contraction and inspiration Vagal stimulation leads to bronchoconstriction Sympathetic stimulation leads to increased rate and depth of respiration and dilation of the bronchi to allow free flow of air through the system Copyright © 2020 Wolters Kluwer • All Rights Reserved Upper Respiratory Tract Conditions The Common Cold Seasonal Rhinitis Sinusitis Pharyngitis and Laryngitis Copyright © 2020 Wolters Kluwer • All Rights Reserved Question #2 Sympathetic stimulation of the respiratory system leads to what? A. Decreased respiratory rate B. Decreased depth of respirations C. Increased respiratory rate D. Increased perfusion of lungs Copyright © 2020 Wolters Kluwer • All Rights Reserved Answer to Question #2 C. Increased respiratory rate Rationale: Sympathetic stimulation leads to increased rate and depth of respiration and dilation of the bronchi to allow free flow of air through the system. Copyright © 2020 Wolters Kluwer • All Rights Reserved Lower Respiratory Tract Conditions Atelectasis Pneumonia Bronchitis Bronchiectasis Obstructive Pulmonary Diseases- CF, COPD, and RDS Copyright © 2020 Wolters Kluwer • All Rights Reserved Atelectasis Definition o The collapse of once-expanded lung tissue Occurrence o Result of outside pressure against the alveoli o Most commonly occurs as a result of blockage of the airway Copyright © 2020 Wolters Kluwer • All Rights Reserved Pneumonia Definition o Inflammation of the lungs Causes o Bacterial or viral invasion of the tissue o Aspiration of foreign substances into the lower respiratory tract Manifestations o Localized swelling, engorgement, and exudation of protective sera Copyright © 2020 Wolters Kluwer • All Rights Reserved Bronchitis Definition o Narrowed airway during the inflammation Causes o Occurs when bacteria, virus, or foreign material infect the inner lining of the bronchi Copyright © 2020 Wolters Kluwer • All Rights Reserved Bronchiectasis Definition o Chronic disease characterized by dilation of bronchial tree and chronic infection and inflammation of bronchial passages. Causes o Often underlying medical condition that makes them more susceptible to infections Signs & Symptoms o Acute infection: fever, malaise, myalgia, arthralgia, and a purulent, productive cough(exam) Copyright © 2020 Wolters Kluwer • All Rights Reserved Obstructive Pulmonary Diseases Asthma Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) Cystic Fibrosis Respiratory Distress Syndrome (RDS) Copyright © 2020 Wolters Kluwer • All Rights Reserved Asthma Copyright © 2020 Wolters Kluwer • All Rights Reserved Distended and Destroyed Alveoli Versus Normal Alveoli Copyright © 2020 Wolters Kluwer • All Rights Reserved Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) Definition o Permanent, chronic obstruction of airways(damaged lung) Causes o Often related to cigarette smoking/Marianna o Emphysema and chronic bronchitis Manifestations o Airflow obstruction on expiration o Overinflated lungs and poor gas exchange Copyright © 2020 Wolters Kluwer • All Rights Reserved Cystic Fibrosis(Caucasian) Definition o A hereditary disease involving the exocrine glands of the respiratory, gastrointestinal, and reproductive tracts. CF results in the accumulation of copious amounts of very thick secretions in the lungs. o Causes o Heredity Treatment is aimed at keeping the secretions fluid and moving and maintaining airway patency as much as possible. Copyright © 2020 Wolters Kluwer • All Rights Reserved Respiratory distress syndrome (RDS) Seen in premature infants who are delivered before their lungs have fully developed and while surfactant levels are still very low Characterized by progressive loss of lung compliance and increasing hypoxia Treatment: give surfacntant until they can breath on their own. Copyright © 2020 Wolters Kluwer • All Rights Reserved Question #3 An elderly Native American woman has tested positive for tuberculosis. The woman refers to TB by another name. What is that name? A. Bronchiectasis B. Emphysema C. COPD D. Consumption Copyright © 2020 Wolters Kluwer • All Rights Reserved Answer to Question #3 D. Consumption Rationale: Tuberculosis is a bacterial infection. Once known as consumption, this disease has been responsible for many respiratory deaths throughout the centuries. Copyright © 2020 Wolters Kluwer • All Rights Reserved