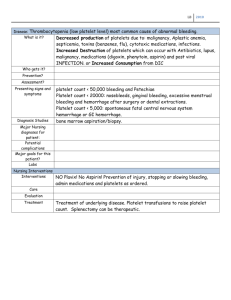
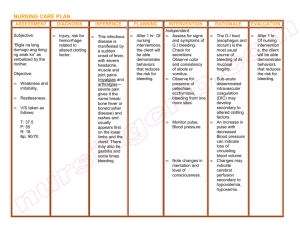
Part 1 A 6 month old baby was brought to his pediatricians office due to an injury that would not stop bleeding . Briefly, the baby had tried to follow his 3 year old sister up the stairs when he slipped and fell, hitting his mouth on the linoleum floor of the kitchen. The mother reported a small wound on the child’s gum, but with copious amounts of blood loss. She applied cold compresses for 15 minutes, the bleeding eventually stopped, but minutes later, the bleeding started again. During a thorough checkup of the baby, the pediatrician noticed bruises on the legs and arms. Upon examination of the injured gum area, bleeding started again. The pediatrician asked the mother if there was a history of bleeding disorders on the maternal side of her family. The mother was not sure, although she thought she may have had a great uncle who died when he was young of a blood disorder. 1, What 3 physiological processes are activated to reduce or stop bleeding? 2. What steps are required to form a platelet plug? 3. What 3 pathways are involved in coagulation? 4. What activates the extrinsic pathway? 5. What activates the intrinsic pathway? 6, What are the steps of the common pathway? 7. What is the end result of the clotting cascade? The child is found to have a lack of von Willebrand factor. What is the purpose of Von Willebrand factor? How would this be expected to affect platelet plug formation? How would this be expected to affect clotting? Name 3 ways that an anticoagulant could act to interfere with the clotting mechanisms ( it does not have to be a real drug mechanism, but just a rational approach) Part 2 Determine whether each of the following will increase/stabilize clot formation, decrease clot formation or dissolve clots that have formed Activation of antithrombin III Activation of plasminogen Inhibition of factor X Inhibition of platelet activation Inhibition of thrombin Activation of fibrinogen