Nursing Care Plan: Hemorrhage Risk
advertisement
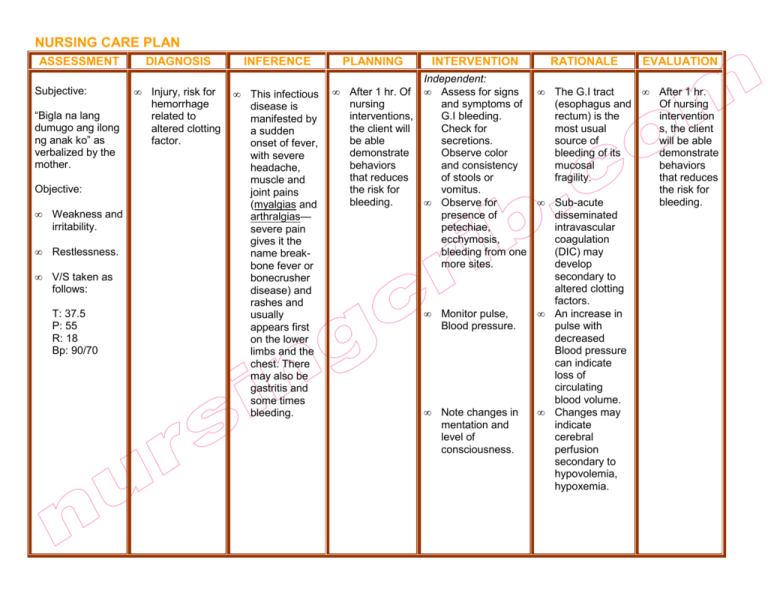
NURSING CARE PLAN ASSESSMENT Subjective: “Bigla na lang dumugo ang ilong ng anak ko” as verbalized by the mother. Objective: • Weakness and irritability. • Restlessness. • V/S taken as follows: T: 37.5 P: 55 R: 18 Bp: 90/70 DIAGNOSIS • Injury, risk for hemorrhage related to altered clotting factor. INFERENCE • This infectious disease is manifested by a sudden onset of fever, with severe headache, muscle and joint pains (myalgias and arthralgias— severe pain gives it the name breakbone fever or bonecrusher disease) and rashes and usually appears first on the lower limbs and the chest. There may also be gastritis and some times bleeding. PLANNING • INTERVENTION RATIONALE Independent: After 1 hr. Of • Assess for signs • and symptoms of nursing G.I bleeding. interventions, Check for the client will secretions. be able Observe color demonstrate and consistency behaviors of stools or that reduces vomitus. the risk for bleeding. • Observe for • presence of petechiae, ecchymosis, bleeding from one more sites. • Monitor pulse, Blood pressure. • • Note changes in mentation and level of consciousness. • EVALUATION The G.I tract • (esophagus and rectum) is the most usual source of bleeding of its mucosal fragility. Sub-acute disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC) may develop secondary to altered clotting factors. An increase in pulse with decreased Blood pressure can indicate loss of circulating blood volume. Changes may indicate cerebral perfusion secondary to hypovolemia, hypoxemia. After 1 hr. Of nursing intervention s, the client will be able demonstrate behaviors that reduces the risk for bleeding. • Avoid rectal temperature, be gentle with GI tube insertions. • • Encourage use of soft toothbrush, avoiding straining for stool, and forceful nose blowing. • • Use small needles for injections. Apply pressure to venipuncture sites for longer than usual. • • Recommend avoidance of aspirin containing products. • Prolongs coagulation, potentiating risk of hemorrhage. • Indicators of anemia, active bleeding, or impending complications. Collaborative: • Monitor Hb and Hct and clotting factors. Rectal and esophageal vessels are most vulnerable to rupture. In the presence of clotting factor disturbances, minimal trauma can cause mucosal bleeding. Minimizes damage to tissues, reducing risk for bleeding and hematoma.











