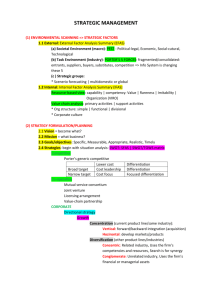
3. PART III: STRATEGY FORMULATION 1.1 Strategy formulation It is the art and science of formulating, implementing, and evaluating cross-functional decisions that enable an organization to achieve its objectives. It is performed to create unique competitive advantage by setting the organization mission, analysing the competitive situations both external perspective and internal perspective, and then developing the strategies that fits in the environments.is in essence and entrepreneurial activity. 3.2 There are 3 levels of the strategies. Grand strategy or corporate strategy is the highest level. It is very essential for setting the organizational direction whether firm wants to grow, stable or exit. Business strategy is the second that the company should describe the company’s characteristics making competitiveness among the competitors whether it wants to differentiate by offering the superior values for customers, offering the affordable price by gaining the low cost advantage, or creating distinctive values for its concentrated customers. Consequently, the company will contribute its grand strategy and business strategy to each business functions in order to craft functional strategies. 3.3 Improved performance Strategic management can improve performance for the following reasons: Strategic management helps to identify and develop a competitive advantage .managers know what edge their business has over the competition. It provides a long –term indication of the direction that top management visualizes for the business. Managers know where to place more effort. It sets priorities which may serve as a guideline for the allocation of the limited resources. Business that do formal strategic planning perform considerably better than similar businesses that do not .The advantages of strategic planning are particularly noticeable in the results of business that function in a complex rapidly changing environment. 3.4 The level of strategic planning The nature, size and diversification of a business determine the kind of strategic planning process that will be used .Large, diversified businesses that operate in different industries, find that it becomes increasingly difficult to allocate resources effectively and to formulate a strategy for the different industries. Three levels of strategy planning can be distinguished. 3.4.1 Strategic planning at corporate level Strategy formulation at corporate level comprises the consideration of the overall nature and aim of the activities of the business and the allocation of its resources to the various units in different industries. Top management is responsible for the formulation of the overall strategy of the business and must make important decisions about the mission of the business, what diversified product range to offer, what market segments to serve, what industry to be involved in or to leave, and the overall philosophy to be followed. The most important tasks are the formulation of a mission and deciding on the strategies that will lead to the fulfilment of the mission. 3.4.2 Strategic planning at strategic business units (SBU) To facilities the management of large businesses similar or related activities in an industry are grouped together in a strategic business unit and treated as separate units for the purpose of strategic planning. Strategic business unit can, for example, exist for the business’s activities in the clothing, shoe, furniture, beer, television and steel industry. The strategy at this level indicates how the strategic business unit will function in the specific industry. Decisions must be made about the strategic business unit’s products or services and market segments and how it can help within the parameters of the corporate strategy and philosophy to achieve the mission of the business. 3.4.3 Strategic planning for function activities Where a strategic human unit is organized on the basic of the functional activities such as human resource management, purchasing management production management , administrative management, marketing management and financial management , functional strategies must be decided upon that will indicate those policies and procedures which lead to success financial policy should indicate policy and procedures for budgets accounting practice and investment . Strategy formulation is only concerned with giving general long-term direction. 3.5 The strategic planning process No single approach to strategic planning will necessarily be ideal for all businesses in all circumstances. Individualistic approaches at certain stages my produce the best results in a specific situation. 3.5.1 Evaluation of present performance and strategy The steps in the model for strategic planning of new business start with the identification of the vision and mission. In the case of an existing business, present performance and strategy must be evaluated. This step enables the business to determine is current strategic profile and posture. It is important to know where the business is at present, where it is going and how it is going to bridge the gap. To prevent a planning gap from developing, a gap analysis should be done. A gap analysis comprises a comparison of the actual results and chosen strategy to determine trends and is done with the help of feedback from control activities (strategic tactical and operational) by means of the database of the management information system. Trends, growth rate, goals, functional strategies and other information are analyzed. If the actual performance has not led to the achievement of the goals and mission the strategy should be adjusted. However, care must be taken that using the present performance and strategy as point of departure does not lead to insufficient adjustment of the strategy. The ideal is to develop a new strategy and to overcome the gap by replacing the existing strategy with the new strategy and implement the new strategy accordingly. Strategic planning can be seen as an annual course adjustment to ensure that the business continues to proceed in the right direction. 3.6 Types of strategies 3.6.1 Cost leadership The business tries to outmatch its competitors by emphasizing productivity .To be a low-cost producer the business will build efficiently scaled facilities with a low break –even point, set control objectives and become cost conscious in all sections of the business. Lower costs will make it possible it charge lower prices that can possibly generate larger sales and higher profits. The strategic planning process and organizational design should facilitate overall cost leadership. 3.6.2 Differentiation This strategy is concerned with the creation of product that are perceived to be exceptional or unique. The differentiation can be based on factors such as product features, brand image, customer service or distribution channels. Effective differentiation requires creativity, basic research, innovation, effective marketing and a reputation for quality. This strategy should incorporate a flexible response to changing perceptions and preferences as well as cost control. 3.6.3 Focus The focus strategy strives to achieve cost leadership and differentiation or both in a particular target market. The business focuses on one market segment rather than completing throughout the whole market. A business pursing this strategy is willing to serve customers with special financing, inventory or service needs, to supply customers in isolated geographic areas or to meet unique demands or supply small quantities. Businesses that use this strategy achieve success as a result of their willingness to serve particular target markets. 3.6.4 A maintenance strategy Top management is satisfied with the success of the business and continuous with the present stable grow str4ategy .This is a low risk strategy and is particularly suited to business that concentrate on one industry where the environment does not change quickly .Characteristic of maintenance strategy is that it is aimed at achieving the same objective and growth rate in the same marker with the same products. Businesses grow by maintaining their market share in a slowly growing market or with very little medication to their product range market or geographical area. 3.6.5 A growth strategy The values of top have a great influence on the choice of a strategy many managers see the growth and progress of their business as indicative of their personal success. When top management owns shares in the business, growth in dividends and increased share prices become even more since management stand to gain directly. Shareholders and investors find business that follows a growth strategy an attractive investment opportunity. Growth should be the result of effective management, while unplanned and excessive growth should be guarded against .the choice of a growth strategy is inevitably associated with risk. A growth is based on the expansion of activities by means of one or more the following eight strategies: 3.6.5.1 Concentration on product line The strategy assumes a more rapid increase of sales, profit and marker share that in the past.it is based on a single product line, market and technology and is particularly successful where the market for the product is large and still growing. The strategy utilizes the skills and completive advantage of the business. Concentrating on a single product line holds the smallest risk in in terms of additional resources, but poses a major if for some reason the demand for the product drops drastically better exploitation of the market can occur by extending the product line and distributing the product line in new geographical areas and by finding new retail outlets and other market segment by means of pricing strategies, product differentiation and advertising. 3.6.5.2 Market development Next to concentration on one product line, market development holds the least risk for the business .This strategy is based on the marketing of the present products, mostly with small changes, in related markets through additional distribution channels or by changing the content of advertisements or the advertising media. The opening of further branches in other cities and towns and the increased use of advertising media are important elements of this strategy. 3.6.5.3 Product development This strategy is aimed at extending the product life cycle of utilizing a favourable reputation and successful trade mark or brand name .The business introduces new products to satisfy customers by making fundamental changes to existing distribution channels to existing customers. Examples this are new model motorcar or a new, improved washing powder or toothpaste. 3.6.5.4 Innovation In a rapidly changing environment consumer expect changing and improved products all the time. It is risky for businesses not to be and stay at their forefront of change .The business chooses the strategy of innovation and utilises the originality of new products by applying the skimming –the-cream prizing policy to initially make large profits on every new product of a similar kind outdated and almost redundant. The appearance of the first Polaroid camera or new generation of computers are good examples of innovation. 3.6.5.5 Integration Horizontal integration consist of the takeover of a business at the same stage of production or a business the manufactures related products. Thus a competitor is eliminated and entry into new market is obtained. This can be done through the purchase of a competitor’s shares or by the takeover of a competitor’s assets. The amalgamation of banks and build societies to form ABSA and an Amcar and ford are typical examples of horizontal integration. Vertical integration as a growth strategy is based on the extension of the business’s activities in the following two possible directions: Forward integration is aimed at owning a business in the direction of consumer or the marketing of the products. There are numerous examples of manufactures that have their own retail outlet. Backward integration consists of the take of supplier that delivers the business’s input.one of the main reasons for backward integration is to ensure the supply of important raw materials. 3.6.5.6 Joint venture It sometimes happens that a business does not have sufficient resources at its disposal to start a large project on its own .By forming a joint venture the skills that are lacking (such as marketing) and resource (such as capital) can be obtained. A business can also form a joint venture with a business in another country or area with the aim of obtaining important raw material s or marketing is products. 3.6.5.7 Concentric diversification This strategy implies the addition of related new products to the business’s product range. It utilizes the business’s knowledge and experience in technology, markets, distribution channels customer base. The addition of related products should maintain synergistic benefits and complement the existing products. A business marketing clothing summer sportswear may, for example, decide to marker winter sportswear as well. 3.6.5.8 Retrenchment strategies A retrenchment strategy is usually followed when a business performs poorly for some or other reason. It can be a result of an economic recession, a technological breakthrough, entry of competitors or ineffective and inefficient management, marketing or product. Also called the defensive strategy focus on the desire or need to reduce organizational operations, usually through cost reduction or asset reductions. Retrenchment strategy includes many types of retrenchment such as harvest, turnaround, divestiture, bankruptcy, and liquidation. A retrenchment strategy can take place by means of one or more of the following three sub strategies. (1) Harvest entails minimizing investments while attempting to maximize short run profits and cash flow, with the long-run intention of exit the market. It is often used when future growth in the market is doubtful or will require investment that does not appear to be cost effective. (2) Turnaround is designed to reverse a negative trend and restore the Organization to appropriate levels of profitability. It is used for shifting from a negative direction or a positive one. A company will push an effort to reserve it resources in order to make a big turnaround. (3) Divestiture involves an organization’s selling or divesting of a business or part of a business. There are 2 different effects on this strategy. A company may have a positive effect on the price of the firm’s stock but conversely it may have a negative effect if divestitures are conducted in the absence of clear strategic goals. (4) Bankruptcy is a means whereby an organization that is unable to pay its debts can seek court to protection from creditors and from certain contract obligations while it attempts to regain financial stability. (5) Liquidation entails dissolving an organization by disposing of all its assets and settling its remaining debts. It usually occurs when serious difficulties, such as bankruptcy cannot be resolved. 3.6.5.9 A combination strategy Various of the above strategies are used for different strategic business units or product line/services. Thus a maintenances strategy can be applied for a particularly successful product line, a growth strategy for flagging product line. Many businesses apply a form of a combination strategy for their product range or activities. 3.7 Management and success The different levels of management must lead the business to success, taking consideration continual changes in external environment. In order to make this possible, all employees must know exactly what they are striving for and how the resources of the business are to be applied. The strategic plan gives direction it provides the strategy, goals and business policy. The participation of each member of staff in the implementation of the chosen plan is necessary. To make this possible, each subordinate, in conjunction with his manager, must determine what he must achieve within the overall plan .this done by allowing the worker to decide on an end result to be achieved. He/she must then continually monitor his progress towards attaining the objectives and make adjustment where necessary. Thus each worker’s performance can be determined effectively and remunerated accordingly.