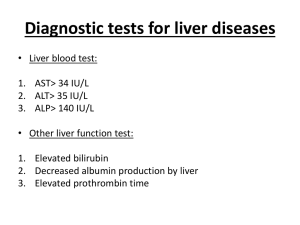
Approach to a patient with jaundice Dr Ali Tumi Jaundice • Yellow discoloration of skin & sclera due to excess serum bilirubin. >40umol/l, (3mg/dl) • Conjugated & Unconjugated types • Obstructive & Non Obstructive (clinical) • Pre-Hepatic, Hepatic & Post Hepatic types • Jaundice - Not necessarily liver disease * Bilirubin Metabolism •Blood •Conjugated & Unconjugated •Urine – Urobilinogen •Stool – Stercobilin Common Causes of Jaundice • Pre Hepatic (Acholuric) - Hemolytic – Unconjugated/Indirect Bil, pale urine • Hepatic – Viral, alcohol, toxins, drugs – Liver damage - unconjugated – Swelling, canalicular obstruction Conjugated • Post Hepatic (Obstructive) – Stone, tumor – Conjugated/Direct Bil, High colored urine, Critical Questions in the Evaluation of the Jaundiced Patient • Acute vs. Chronic Liver Disease • Hepatocellular vs. Cholestatic – Biliary Obstruction vs. Intrahepatic Cholestasis • Fever – Could the patient have ascending cholangitis? • Encephalopathy – Could the patient have fulminant hepatic failure? Evaluation of the Jaundiced Patient HISTORY • • • • • • • Pain Fever Confusion Weight loss Sex, drugs, R&R Alcohol Medications • • • • • • • • • pruritus malaise, myalgias dark urine abdominal girth edema other autoimmune dz HIV status prior biliary surgery family history liver dz Evaluation of the Jaundiced Patient PHYSICAL EXAM • • • • • • • • BP/HR/Temp Mental status Asterixis Abd tenderness Liver size Splenomegaly Ascites Edema • • • • • • Spider angiomata Hyperpigmentation Kayser-Fleischer rings Xanthomas Gynecomastia Left supraclavicular adenopathy (Virchow’s node) Cirrhosis Clinical Features Yes Treat Evaluation of the Jaundiced Patient LAB EVALUATION • • • • • • • • AST-ALT-ALP Bilirubin – total/indirect Albumin INR Glucose Na-K-PO4, acid-base Acetaminophen level CBC/plt • • • • • • • Ammonia Viral serologies ANA-ASMA-AMA Quantitative Ig Ceruloplasmin Iron profile Blood cultures Evaluation of the Jaundiced Patient • Ultrasound: – More sensitive than CT for gallbladder stones – Equally sensitive for dilated ducts – Portable, cheap, no radiation, no IV contrast • CT: – Better imaging of the pancreas and abdomen • MRCP: – Imaging of biliary tree comparable to ERCP • ERCP: – Therapeutic intervention for stones – Brushing and biopsy for malignancy New Onset Jaundice • • • • • • • • Viral hepatitis Alcoholic liver disease Autoimmune hepatitis Medication-induced liver disease Common bile duct stones Pancreatic cancer Primary Biliary Cirrhosis (PBC) Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis (PSC) Jaundiced Emergencies • Acetaminophen Toxicity • Fulminant Hepatic Failure • Ascending Cholangitis Jaundice Unrelated to Intrinsic Liver Disease • • • • • Hemolysis (usually T. bili < 4) Massive Transfusion Resorption of Hematoma Ineffective Erythropoesis Disorders of Conjugation – Gilbert’s syndrome • Intrahepatic Cholestasis – Sepsis, TPN, Post-operation HBV Serology HBSAg HBcAb HBcAb HBSAb IgM IgG Acute HBV Resolved HBV Chronic HBV HBV vaccinated + + - + - + + - + + Jaundice Jaundice Yellow hands on top, red palms underneath - a sign of liver damage Ascitis in Cirrhosis Ascitis in Cirrhosis Gynaecomastia in cirrhosis