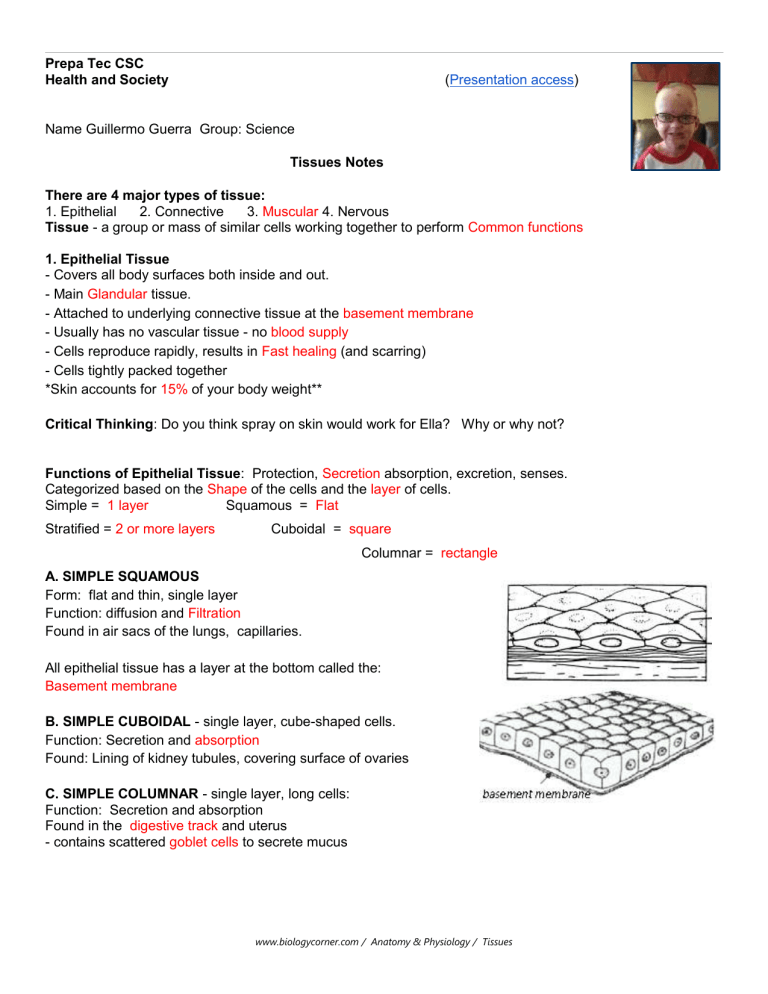
Prepa Tec CSC Health and Society (Presentation access) Name Guillermo Guerra Group: Science Tissues Notes There are 4 major types of tissue: 1. Epithelial 2. Connective 3. Muscular 4. Nervous Tissue - a group or mass of similar cells working together to perform Common functions 1. Epithelial Tissue - Covers all body surfaces both inside and out. - Main Glandular tissue. - Attached to underlying connective tissue at the basement membrane - Usually has no vascular tissue - no blood supply - Cells reproduce rapidly, results in Fast healing (and scarring) - Cells tightly packed together *Skin accounts for 15% of your body weight** Critical Thinking: Do you think spray on skin would work for Ella? Why or why not? Functions of Epithelial Tissue: Protection, Secretion absorption, excretion, senses. Categorized based on the Shape of the cells and the layer of cells. Simple = 1 layer Squamous = Flat Stratified = 2 or more layers Cuboidal = square Columnar = rectangle A. SIMPLE SQUAMOUS Form: flat and thin, single layer Function: diffusion and Filtration Found in air sacs of the lungs, capillaries. All epithelial tissue has a layer at the bottom called the: Basement membrane B. SIMPLE CUBOIDAL - single layer, cube-shaped cells. Function: Secretion and absorption Found: Lining of kidney tubules, covering surface of ovaries C. SIMPLE COLUMNAR - single layer, long cells: Function: Secretion and absorption Found in the digestive track and uterus - contains scattered goblet cells to secrete mucus www.biologycorner.com / Anatomy & Physiology / Tissues - microvalli increase surface area www.biologycorner.com / Anatomy & Physiology / Tissues D. STRATIFIED SQUAMOUS - multi-layered, squamous cells Functions in protection. Lines body cavities; Skin, Canal, esophagus, vaginal and mouth E. PSEUDOSTRATIFIED COLUMNAR - appear "stratified" but really a single layer with nuclei at various levels giving the appearance of layered cells. -Can have cilia (tiny, hair-like projections that sweeping materials) ---and goblet cells, which secrete mucus - Function: secretion and aided movement - Location: lining air passages like the trachea, tubes of the reproductive system Critical Thinking: What happens if the cilia of cells do not work properly? F. Glandular Epithelium Cells specialized in Release substances They make up the body’s gland Exocrine Glands (Examples): Salivary, sweat Endocrine Glands (Examples): Hormones Identify the type of Epithelial Tissue 2. Connective Tissue -Most abundant tissue in your body; Binds structures together -Provides support, protection, framework, fills space, stores fat, produces blood cells, fights infection -Composed of scattered cells within a matrix www.biologycorner.com / Anatomy & Physiology / Tissues -Made up of a ground substance and fibers -Most have a good blood supply Main types of fibers: -collagenous fibers: Strong, flexible, but not very elastic Found in: Bones, ligaments, and tendons - elastic fibers - Not as strong, but very elastic; Found in: ears, vocal cords What is wrong with Ella’s Skin? Mutations in the COL7A1 gene affects the protein collagen Collagen is the “glue” that holds tissues together. It anchors the epidermis to the dermis Skin Label -- Epidermis | Dermis | Blood Vessels | Fatty Tissue | Oil Gland Hair What happens when the dermis pulls away from the epidermis? Blister form Collagen and elastin are types of connective tissue. Categories of Connective Tissue www.biologycorner.com / Anatomy & Physiology / Tissues Melanocytes | Sweat Gland | A. LOOSE C.T.- binds skin to underlying organs and organs to organs Forms thin membrane throughout the body B. ADIPOSE TISSUE - aka FAT, beneath the skin, Function: Protective cushion, insulation to preserve body heat, stores energy C. FIBROUS Connective Tissue. - thick collagenous fibers and fine network of elastic fibers. Few cells, poor blood supply, thus slow healing Tendons = connect muscle to bone Ligaments = connects bones D. CARTILAGE (all cartilage cells are called chondrocytes HYALINE CARTILAGE Location: covers joints ELASTIC CARTILAGE Location: external ear and larynx FIBROCARTILAGE – Tough, shock absorbing. Location: between vertebrate E. BONE TISSUE – osseus tissue. Rigid due to mineral salts. F. BLOOD TISSUE - circulates throughout the body 3. Muscle Tissue Skeletal - skeletal muscles - voluntary, striated Cardiac - wall of the heart - striated, involuntary Smooth - in hollow organs, stomach - involuntary 4. Nerve Tissue - Found in brain, spinal cord, nerves Sketch: Neuron Neurons - transmit signals | Neuroglia - protection, support www.biologycorner.com / Anatomy & Physiology / Tissues