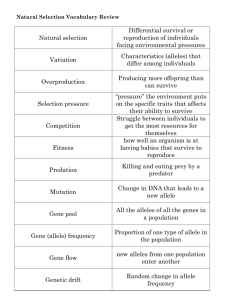
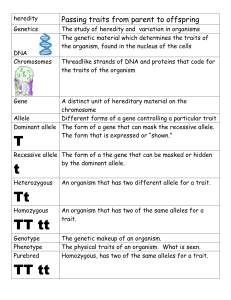
8th Grade Vocabulary Review - for Bingo Earth and Space Science Axis Rotation Revolution Orbit Gravity Tides Spring Tide Neap Tide Convergent Boundary Divergent Boundary Transform Boundary Pangea Air Mass Front Convection Weather Climate Round 1 Round 2 Round 3 Round 1 Round 2 Round 3 an imaginary line that passes through a planet’s center and its north and south poles the spinning motion of a planet on its axis the movement of an object around another object the path of an object as it revolves around another object in space the attractive force between objects the periodic rise and fall of the level of water in the ocean the tide with the highest highs and lowest lows due to the sun, moon, and Earth being aligned the tide with the least difference between highs and lows due to the sun, moon, and Earth being in a perpendicular shape a plate boundary where two plates move toward each other a plate boundary where two plates move away from each other a plate boundary where two plates move past each other in opposite directions the name of the single landmass that began to break apart 200 million years ago and gave rise to today’s continents a large volume of air that has a specific temperature and humidity the area where two or more air masses meet the transfer of thermal energy by the movement of a fluid conditions of the atmosphere over a short period of time patterns in the atmosphere over long periods of time Physical Science Atom Molecule Element Compound Mixture Acceleration the smallest particle of an element that has the properties of that element two or more atoms held together by bonds a substance that cannot be broken down into any other substances by chemical or physical means a substance made of two or more elements chemically combined in a specific ratio two or more substances that are together in the same place but their atoms are not chemically bonded the rate at which velocity changes Mass Chemical Reaction Thermal Energy Reactant Product the amount of matter in an object the process in which substances change into new substances with different properties the total energy of the motion of all the particles in an object a substance that enters a chemical reaction a substance formed as a result of a chemical reaction Newton’s First states that an object in motion will stay in motion Law and an object at rest will stay at rest unless acted upon by an outside force Newton’s states that force is calculated using the mass and Second Law acceleration of an object Newton’s Third states that for every action, there is an equal and Law opposite reaction Inertia the tendency of an object to resist a change in motion Force a push or pull on an object Life Science Round 1 Genetic factor a gene that influences an organism’s growth, traits, or survival Environmental any factor (biotic or abiotic) that influences living factor organisms Organic the molecules of life that are built around chains of Compound carbon that are often quite long. Carbohydrate an energy-rich organic compound that is made of the elements carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen Protein large organic molecule made of carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, and sometimes sulfur Lipid an energy-rich organic compound, such as fat, oil, or wax, that is made of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen Asexual a reproductive process that involves only one parent Reproduction and produces offspring that are identical to the parent Sexual a reproductive process that involves two parents that Reproduction combine their genetic material that produces an offspring that differs from both parents Mitosis the second stage of the cell cycle during which the cell’s nucleus divides into two new nuclei and one set of DNA is distributed into each daughter cell Round 2 Round 3 Meiosis the process that occurs in the formation of sex cells (sperm and egg) by which the number of chromosomes is reduced by half DNA the genetic material that carries information about an organism and is passed from parent to offspring Chromosome a threadlike structure within a cell’s nucleus that contains DNA Gene a sequence of DNA that determines a trait and is passed from parent to offspring Alleles the different forms of a gene Mutation any change in the DNA of a gene or a chromosome Heredity the passing of traits from parents to offspring Dominant an allele whose trait always shows up in the organism when the allele is present Recessive an allele that is hidden whenever the dominant allele is present Pedigree a chart that shows the presence or absence of a trait according to the relationships within a family across several generations Homozygous having two identical alleles for a particular gene Heterozygous having two different alleles for a particular gene Evolution change over time; the process by which modern organisms have descended from ancient organisms Natural the process by which organisms that are best adapted Selection to their environment are most likely to survive and reproduce Artificial the intentional reproduction of individuals in a Selection population that have desirable traits Fitness the ability of an organism or population to survive and pass its genes to its offspring Adaptation an inherited behavior or physical characteristic that helps an organism survive and reproduce in its environment Winners: