Cell Structure: Prokaryotes, Eukaryotes, Organelles, Cell Types
advertisement

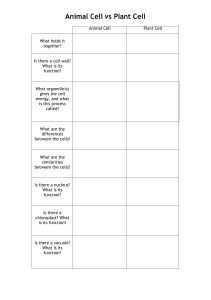
structure of the cell prokaryotes - do not have a real cell nucleus -Frequently unicellular -a few microns in size 1-2 µm -The genome lies freely in the cytoplasm -Mostly only one DNA molecule: plasmid -The cell wall is made of murein, a peptidoglycan eukaryotes -Real cell nucleus with shell -various organelles -DNA is in the form of chromosomes -Lysosomes are used to digest various substances -Different connections exist between the cells such as the desmosomes and the gap junctions -In plant cells there are also the vacuole and the cell wall -The vacuole serves to maintain the pressure of the plant cell -The chloroplasts are used for photosynthesis organelles -Cell nucleus: genetic material in the form of chromosomes -Endoplasmic reticulum: protein biosynthesis and signaling -Ribosomes: Proteins containing rRNA are used for translation -Golgi apparatus: binding and conversion of proteins into vesicles -Mitochondria: Serve to provide energy through ATP synthesis cell types Red blood cells (erythrocytes) White blood cells (leukocytes) nerve cells (neurons) muscle cells (myocytes) Bone cells (osteocytes) Platelets (thrombocytes) skin cells Germ cells or sex cells (gametes) epithelial cells Cartilage cells (chondrocytes)