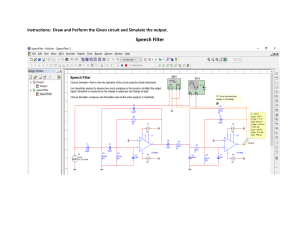
Electronics III Exercise4 Filters Concepts: effect of frequency on Capacitive Reactance: As the frequency increases, Xc decreases. Concepts: What is the basic operation of filters? Concepts: Passive Filters Low pass filter Concepts: Passive Filters High pass filter Concepts: Passive Filters Band pass filter Concepts: Terminology The critical frequency, (also called the cutoff frequency) defines the end of the passband and is normally specified at the point where the response drops (70.7%) from the passband response. Filters that use op-amps as the active element provide several advantages over passive filters (R, L, and C elements only). The op-amp provides gain, so the signal is not attenuated as it passes through the filter. The high input impedance of the op-amp prevents excessive loading of the driving source, and the low output impedance of the op-amp prevents the filter from being affected by the load that it is driving. Active filters are also easy to adjust over a wide frequency range without altering the desired response. Concepts: Active Filters Low pass filter Non-Inverting case Inverting case Concepts: Active Filters High pass filter Non-Inverting case Inverting case Concepts: Active Filters Band pass filter Non-Inverting case Inverting case Q1: Design a non-inverting active low pass filter circuit that has a gain of 10 at low frequencies, a high frequency cut-off or corner frequency of 159Hz and an input impedance of 10KΩ. Q2 A first order non-inverting active high pass filter has a pass band gain of 2 and a cut-off corner frequency of 1kHz. If the input capacitor has a value of 10nF, calculate the value of the cut-off frequency determining resistor and the gain resistors in the feedback network. Q3: In the figs below. determine(a) the filter type ,(b) the corner frequency(s), and (c) the DC gain