Pharmacology Reference: Sedatives, Anticoagulants, Parkinson's Meds
advertisement

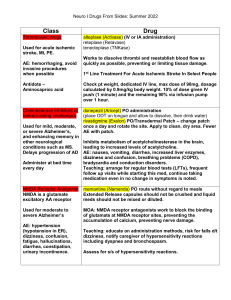
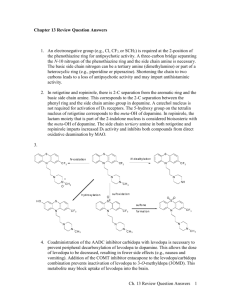
Sedatives (Propofol) Adrenergic Phenylephrine) Calcium Channel Blocker (Diltiazem) Mechanism of Action CNS depression by activating GABA receptor Vasoconstriction, inotropic effects (^ CO) • Dilates coronary/ peripheral arteries • Slow SA/AV node conduction Therapeutic effect Sedation Increase BP Decrease BP, slow HR Side effects Bradycardia, hypotension, Apnea Tachycardia, decrease peripheral perfusion Hypotension, bradycardia, heart block Special considerations Onset:15-30min Half life: 1-8 min • Will alter neuro assessment • IV Onset: minutes IV *Must be given through central line 1 Mechanism of Action 1Anti-Coagulants • Heparin • Warfarin • Rivaroxaban • Dabigatran etexilate Anti-platelets • Clopidogrel • Aspirin Glucocorticosteroid • Dexamethasone • Methylpredisone Calcium Channel Blockers • Nimodipine H: Prevents conversion of Platelet aggregate Decreases inflammation/ normal immune response Relaxing narrowed blood vessels in the brain fibrin-> fibrinogen/ Prothrombin-> thrombin W: Depresses hepatic synthesis of vitamin K. Therapeutic effect for these patients Blood thinner, allows the blood to easily get through narrowed arteries Prevents further stenosis of diseased vessels. Decreases cerebral edema Preventing cerebral vasospasm post CVA Side effects/ Adverse Reaction BLEEDING BLEEDING Hypertension, hyperglycemia, weight gain, decreased immune response Hypotension, bradycardia Thrombocytopenia Special considerations Reversal agents • Heparin-protamine • Warfarin- vitamin K • Rivaroxaban & Dabigatran etexilate: NONE Need to be tapered down, abrupt withdrawn causes acute adrenal insufficiency. • Monitor INR for Warfarin. • Monitor aPTT for heparin. 2 Anti-Parkinson agent (Levodopa/Carbidopa) Pharmacokinetics Side effects/ Adverse effects -Converted to dopamine in the brain. -Carbidopa added to protect the premature metabolism of levodopa before it can reach the brain. Stimulate dopamine receptors in the brain. • • -N/V • • • Teaching/ Special considerations Dopamine Agonist (pramipexole, ropinirole) N/V Cardiovascular effects (tachycardia, palpitations) Orthostatic hypotension Discoloration of sweat/urine Dyskinesia *“On/off effect”: sudden return of symptoms, treated with a drug holiday or manipulating doses. -Psychiatric effects (impulse disorders) -Psychosis -Sedation -Orthostatic hypotension -Not as effective, worse side effects. -Therapeutic effect: 2mos -Change position slowly “Wearing off”: therapeutic effects of medications may wear off right before the next dose is due. Schedule is important. 3 Anticholinergic (benztropine mesylate) Pharmacokinetics Side effects/ Adverse reactions COMT Inhibitors (entacapone & tolcapone) MAO-B Inhibitor (Selegiline & Rasagiline) Blocks acetylcholine receptors. Diminishes excess cholinergic effect from acetylcholine. Stimulate dopamine receptors in the brain. Increase the duration of action of levodopa within the brain. Increase “on” time, decrease “off” time. -Inhibits breakdown of dopamine. -Urinary retention, dry mouth, constipation. -N/V -Psychiatric effects (impulse disorders) -Psychosis -Sedation -Orthostatic hypotension -Orthostatic hypotension -GI symptoms -Discoloration urine/sweat • Hypertensive crisis -Not as effective, worse side effects. -Therapeutic effect: 2mos -Change position slowly -Change position slowly -Dark urine is common. • Avoid foods high in tyramine (aged cheese, cured meat, beer, soy) -N/V -Sedation Teaching/ Special considerations Dopamine Agonist (pramipexol,ropinirole) -Controls tremors & rigidity but does not help bradykinesia. -Change position slowly ->Hypertensive crisis 4