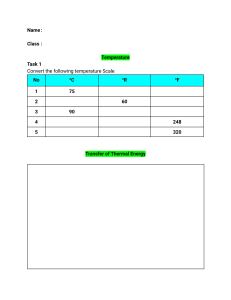
Heat, Temperature, and Heat Transfer Cornell Doodle Notes FREE SAMPLER TEACHER NOTES These Cornell Doodle Notes combine two effective note-taking strategies and can be used to introduce or review the concepts of temperature, heat, and the types of heat transfer: conduction, convection, and radiation. The notes begin by defining temperature and heat to make clear that temperature is a measure of the average kinetic energy of an object or substance while heat is the flow of energy from hotter to cooler places. The notes define and give real-life examples of conduction, conductors, insulators, convection and convection currents, and thermal radiation. The concepts align with the Disciplinary Core Ideas of NGSS MS-PS3-3, MS-PS3-4, and MS-PS1-4.. Cornell Notes are a note-taking strategy in which topic questions are written in a narrow left-hand column and definitions, explanations, and diagrams are filled in in the righthand column. At the bottom of Cornell Notes, there is typically a section included for reflection on the lesson’s main points. See the example to the right. Doodle Notes are another note-taking strategy for which pictures and graphics activate the visual pathways of the brain, which helps with retention of information when compared to standard note-taking. Your visual learners will really benefit from seeing and coloring in the pictures aside the main points of the notes! Doodle Notes is a registered trademark used with permission. See DoodleNotes.org for more details. See the Printing Tips on page 3 On the following pages, you will find 2 versions of the Cornell Doodle Notes: KEY The KEY : All notes and “answers” are included on this version Green Circle : Use this version for your lower-level students who need more support, take more time, or who are learning English as a second language…they will have to fill in missing words If you are satisfied with this FREE SAMPLER product, you of this may be interested in the resource, which includes: 1 A third version (Blue Square) of the notes for which students will write each of the topic questions in the left column and they will have to fill in more words and sentences throughout the notes 2 20-slide Powerpoint AND Google Slides presentations; this will make it possible to share the presentation with your students, which opens up opportunity for small group learning, leveled grouping using the scaffolded notes, and flippedclassroom learning! 3 A completely digital, Google Slides Version of the notes CLICK HERE Thank you very much for your business! If this product has met your needs, please consider leaving feedback at TeachersPayTeachers.com or feel free to email me at SunriseScienceTPT@gmail.com with any questions or concerns! © Sunrise Science 2020 You may also be interested in my other Cornell Doodle Notes products! Click on the picture to the right! Printing Tips! It depends how you’d like your students to use these notes. They can be printed onesided and folded up into an interactive notebook, or you can print them double-sided and have students keep them in binders/folders. If you print them double-sided, this is what I suggest doing: o In the print settings on Adobe/Reader, keep the “Auto Orientation” button selected o Click “FLIP ON LONG EDGE” and FIT to page o Type in the page numbers that you’d like to print and the number of copies o You can also print the pages one-sided and run them double-sided through your school’s copy machine! o Either way, I also suggest selecting “Fit to Printable Area” so that the notes take up the maximum amount of paper space! Printing the notes this way will avoid your students having to rotate their paper when they go to the next side. Instead, they will flip and the left and right columns will be in the same place! Example notes printed back-to-back (This is a different resource!) Name: ____________________________________________________________________ Class: ______________ Date: _____________KEY kinetic energy The energy of an object What is heat and how is it transferred from one place to another? because of motion. The word ‘kinetic’ stems from the Greek word for motion. The size of an object or the amount of a substance does not affect the temperature! Measures the average kinetic energy of the particles of an object or substance. It is like a What is temperature? Complete the temperature chart. These two pots of BOILING water have the SAME temperature-- speedometer for how fast particles are moving! Temperature is measured in degrees. The Celsius and Kelvin temperature scales are used in science. Celsius Kelvin Water Boils °C 100° 373 Body Temperature 37° 310 Room Temperature 20° 293 Water Freezes 0° 273 K 100°C! But this little match has a temperature of 700°C! However, the bigger pot Because there are more DOES have more energy molecules in motion in the big pot than in the little pot or in overall…why? the match.. Color the arrow to show that heat moves from hotter (near camel) to cooler (near penguin). The flow of energy from warmer places to What is heat? cooler places due to difference in temperature. Heat travels from your hand into the ice cube and the ice cube melts. The skin on your hand will feel cold © Sunrise Science 2020 because thermal energy has left it. It’s important to remember that an object or system does not HAVE heat. Heat is the TRANSFER (or flow) of thermal energy due to temperature difference. Thermal equilibrium happens when heat flows from a higher temperature object to a lower temperature object until the two objects have an equal temperature. What is thermal equilibrium? 100°C 0°C heat flows from hotter block to cooler block until . . . KEY For example: Heat will continue to flow out of this kettle until the kettle and the air around it reach the same temperature (thermal equilibrium). 50°C 50°C Color the 100°C block red and the 0°C block blue. Color both 50°C blocks purple. is the transfer of heat through a solid What is conduction? When your feet touch hot sand on the beach, heat conducts from the sand to your skin. material by direct contact of particles. As the particles are heated, they move faster and bump into one another, creating more heat. Color the particles to show how heat is transferred through the material by conduction. When your cell phone screen feels warm, heat conducts from the phone to your fingertips. Materials that don’t allow heat Materials that allow heat energy to move What are conductors and insulators? through them efficiently are called conductors. well are called insulators. People The particles in good use insulators to keep heat in or conductors are typically close to keep heat out. Feathers, wool, together (dense), like in metals. © Sunrise Science 2020 energy to pass through them and rubber are good insulators. is the transfer of heat in a fluid (a gas or a liquid) caused when hotter, less What is convection? dense fluids rise and cooler, more dense fluids sink. Moving fluids result in a transfer of heat in a cycle called a convection current. KEY When you boil water in a pot, the water near the burner gets hot and becomes less dense. It rises up and pushes the cooler water out of the way. That cooler water sinks, gets heated, becomes less dense, and rises up. This creates a convection current. When a baseboard heater is used in a room, heat is distributed throughout the air in the room due to convection currents. Heat is transferred from the sun to the Earth by thermal radiation. The sun’s rays travel through the empty space between the sun and our planet. is the transfer of heat through empty What is radiation? space by invisible electromagnetic rays. No matter is required for the heat transfer to occur. Radiation travels at the speed of light in straight lines. This is also known as thermal radiation. Do The heat that you feel radiating from a fire to warm your hands is thermal radiation. Draw one picture and/or write one phrase below each of these terms that will help you to remember them best: © Sunrise Science 2020 Name: _________________________________________________________________________ : 1) Thermal Imaging https://bit.ly/2TSmkOm Class: ______________ Date: ______________ KEY Write a $2 summary of the video! Each word costs 10¢! Thermal imaging cameras use white to show the ‘hottest’ places and black to show the ‘coldest’ places as heat Classify each of the following words/phrases as having to do with HEAT TRANSFER transfers in everyday situations.. (H) or TEMPERATURE (T). Write H or T on the line! T speed of moving particles ________ T degrees Celsius ________ H convection current ________ H flow of energy ________ H warmer to cooler areas ________ H electromagnetic rays ________ H insulation ________ T Kelvin scale T not dependent on size/amount ________ ________ Circle the type of heat transfer that is responsible for each of the scenarios below: RADIATION 6) A very dense metal rod and a wooden stick are both placed on a heated surface. The metal rod feels much hotter much faster than the wooden stick. CONDUCTION CONVECTION RADIATION 5) The ocean circulates around the Earth as cool water sinks and pushes less dense, 7) Circle ALL of the following statements that are TRUE: a. a burning match has a higher temperature than a warmer water out of the way. CONDUCTION CONVECTION © Sunrise Science 2020 RADIATION pot of boiling water b. a burning match has more energy than a large pot of boiling water c. a small pot of boiling water has the same temperature as a large pot of boiling water 4) Your computer leaves the desk feeling very hot after you’ve been using it for awhile. CONDUCTION CONVECTION RADIATION How are you feeling about your understanding of heat and heat transfer? Circle one: I don’t get it. RADIATION CONVECTION I think I get it. CONVECTION CONDUCTION I got this! 2) A house’s attic is always warmer than its basement. CONDUCTION 3) The sun’s energy reaches Earth from millions of miles away. Name: ____________________________________________________________________ Class: ______________ Date: _____________ _______________ energy The energy of an object What is ________ and how is it __________________ from one place to another? because of ______________. The word ‘_____________’ stems from the ___________ word for motion. The __________ of an object or the _____________ of a Measures the average ______________ energy of substance does ________ affect the temperature! These two pots of __________ water have the _______ temperature-- the _______________ of an object or substance. It is like a ______________________ for how _________ What is _________________? particles are ______________! Temperature is measured in ______________. The ____________ and Complete the temperature chart. ____________ temperature scales are used in ____________. °C Celsius Water Boils Water Freezes Kelvin _____°C! But this little match has a temperature of _____°C! 100° Body Temperature Room Temperature K 310 20° However, the bigger pot DOES have more energy overall…why? Color the arrow to show that heat moves from hotter (near camel) to cooler (near penguin). The __________ of ____________ from ____________ places to What is ________? _____________ places due to ____________________ in temperature. Heat ______________ from your __________ into the ________ cube and the ice cube ___________. The __________ on your hand will _________ © Sunrise Science 2020 ________ because ____________ energy has left it. It’s important to remember that an object or system does not HAVE heat. Heat is the __________ (or flow) of thermal _________ due to temperature difference. ______________ equilibrium happens when ________ flows from a ___________ temperature object to a __________ temperature object until the two objects have an __________ temperature. What is thermal ___________________? 100°C 0°C For example: _____ will _________ to ____ out of this kettle until the kettle and the air around it reach the _____ temperature (thermal equilibrium). heat flows from _______ block to _______ block until . . . 50°C 50°C Color the 100°C block red and the 0°C block blue. Color both 50°C blocks purple. When your feet _______ hot _____ on the beach, heat _________ from the sand to your skin. is the _______________ of heat through a _________ What is ________________? material by _____________ contact of ______________. When your cell phone screen feels ______, heat _________ from the phone to your _____________. As the particles are ____________, they ________ ____________ and ________ into one another, creating more heat. Color the particles to show how heat is transferred through the material by conduction. Materials that _________ allow heat What are ________________ and ________________? © Sunrise Science 2020 Materials that __________ heat ____________ to move through them _________________ are called conductors. The particles in _________ conductors are typically _________ together (dense), like in ____________. energy to ________ through them well are called ________________. People use insulators to keep heat _____ or to keep heat _______. Feathers, _________, and ____________ are good insulators. is the transfer of heat in a __________ (a _______ or a ___________) caused when hotter, _______ dense fluids ________ and What is ___________, more __________ fluids ________. _________________? Moving fluids ____________ in a _____________ of heat in a __________ called a ___________________ _______________. is the transfer of heat through __________ space by ______________ electromagnetic What is ________________? When a baseboard __________ is used in a room, heat is _____________ throughout the _____ in the room due to convection currents. Heat is transferred from the _____ to the Earth by _________ ___________. The sun’s rays travel through the empty _______ between the sun and our planet. rays. _______ matter is _______________ for the heat transfer to occur. ______________ travels at the __________ of _________ in ______________ lines. This is also known as ______________ radiation. Do When you _____ water in a pot, the water ______ the burner gets ____ and becomes ____ dense. It ______ up and ________ the cooler water out of the way. That cooler water ______, gets heated, becomes less dense, and ______ up. This ________ a convection current. The heat that you _____ radiating from a ______ to ______ your hands is thermal radiation. Draw one picture and/or write one phrase below each of these terms that will help you to remember them best: © Sunrise Science 2020 Name: _________________________________________________________________________ : 1) Thermal Imaging https://bit.ly/2TSmkOm Class: ______________ Date: ______________ Write a $2 summary of the video! Each word costs 10¢! Classify each of the following words/phrases as having to do with HEAT TRANSFER (H) or TEMPERATURE (T). Write H or T on the line! ________ speed of moving particles ________ degrees Celsius ________ convection current ________ flow of energy ________ warmer to cooler areas ________ electromagnetic rays ________ insulation ________ not dependent on size/amount ________ Kelvin scale Circle the type of heat transfer that is responsible for each of the scenarios below: RADIATION 6) A very dense metal rod and a wooden stick are both placed on a heated surface. The metal rod feels much hotter much faster than the wooden stick. CONDUCTION CONVECTION RADIATION 5) The ocean circulates around the Earth as cool water sinks and pushes less dense, 7) Circle ALL of the following statements that are TRUE: a. a burning match has a higher temperature than a warmer water out of the way. CONDUCTION CONVECTION © Sunrise Science 2020 RADIATION pot of boiling water b. a burning match has more energy than a large pot of boiling water c. a small pot of boiling water has the same temperature as a large pot of boiling water 4) Your computer leaves the desk feeling very hot after you’ve been using it for awhile. CONDUCTION CONVECTION RADIATION How are you feeling about your understanding of heat and heat transfer? Circle one: I don’t get it. RADIATION CONVECTION I think I get it. CONVECTION CONDUCTION I got this! 2) A house’s attic is always warmer than its basement. CONDUCTION 3) The sun’s energy reaches Earth from millions of miles away. Terms of Use © Sunrise Science Thank you for your purchase! The original purchaser of this document/product is granted permission to reproduce the pages in needed quantities for the purchaser’s classroom/home use only. By purchasing this resource, you are agreeing that the contents are the property of Sunrise Science and licensed to you only for classroom/personal use as a single user. I retain the copyright, and reserve all rights to this product. YOU MAY: o Use items (free and purchased) for your own classroom students, or your own personal use. o Reference this product in blog posts, at seminars, professional development workshops, or other such venues PROVIDED there is both credit given to myself as the author and a link back to my TPT store is included in your post/presentation. o Distribute and make copies of free items only to other teachers PROVIDED there is credit given to Sunrise Science and a link back to my TPT store. YOU MAY NOT: o Claim this work as your own, alter the files in any way (unless this has been advertised as an editable resource), or remove/attempt to remove the copyright/watermarks. o Sell the files or combine them into another unit for sale/free. o Post this document for sale/free elsewhere on the internet (this includes public classroom websites and Google Doc links on blogs). o Make copies of purchased items to share with others is strictly forbidden and is a violation of the Terms of Use, along with copyright law. o Obtain this product through any of the channels listed above. Thank you for abiding by universally accepted codes of professional ethics while using this product. If you encounter an issue with your file, notice an error, or are in any way experiencing a problem, please contact me at SunriseScienceTPT@gmail.com and I will be more than happy to help sort it out! Thank you ☺ Karla @ Sunrise Science /SunriseSciences @SunriseScience @SunriseScienceClassroom Credit for fonts and graphics Thank you to these amazing artists! Want to Save Money on Future Purchases? Earning ‘TPT Credit’ saves you money on future purchases! You can simply apply the credits you earn to a purchase at checkout. To earn your credit, go to your My Purchases on TeachersPayTeachers.com and click on ‘Provide Feedback’ underneath each purchase. You will be taken to a page where you can give a quick rating and leave a comment about the product. Easy peasy!