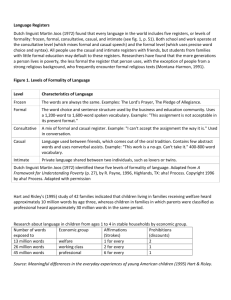
Speech Styles •Casual •Intimate •Formal •Frozen •Consultative CASUAL STYLE • Informal interaction among communicators • Characterized by a certain degree of familiarity among colleagues, friends, and acquaintances. INTIMATE STYLE • Used among very close friends, family members, and loved ones. • Persons you are talking with accept you as you are, no matter what you say and how you say it. • Use codes peculiar/ common to you and the person you are talking with. FORMAL STYLE • Follows form or structure • Speakers prepare in advance so that the content of his/her speech is logically organized and the structure is polished. • Has limited interaction with the participants • Feedback and reaction, if the communication situation allows, usually happen at the end of the speech delivery. • Public communication e.g. seminars and conferences FROZEN STYLE • Lack of participation and feedback from the receiver's end. • Often seen in formal ceremonies and rituals e.g. weddings, baptism, and other proclamations with formulaic statements. • The content is pro-forma and can be repeated in another similar occasion. • By virtue of the power vested upon me, I now…. • …so help me God • By the decree… • We anoint you with the oil of salvation… - The content of frozen speech style is often kept intact until the community involved decides to revise it. CONSULTATIVE STYLE • Evident among communicators who are not very familiar to each other or between two parties who have different social positions. • Examples: Workers who come from different departments, between a subordinate and an authority, or between an expert and a lay person. • Public information such as office policies, business transactions, plans and matters that need to be decided. • Follows certain degree of formality TYPES OF COMMUNICATIVE STRATEGY Nomination Turn-Taking Topic Control Topic Shifting Repair Termination