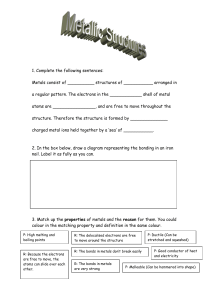
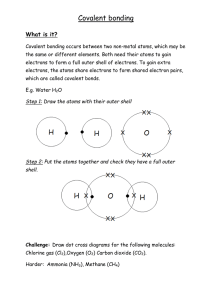
PART I ATOMS AND BONDING Go to: http://www.teachersdomain.org/asset/lsps07_int_ionicbonding/ 1. Describe what happens when two negatively charged particles interact with one another. 2. When will oppositely charged atoms stick together? 3. A. What is an ion? (Look this up online) B. What is a cation and where can you find it on the periodic table? C. What is an anion and where can you find it on the periodic table? 4. Describe how ionic compounds form crystals: COVALENT BONDS Go to: http://www.teachersdomain.org/asset/lsps07_int_covalentbond/ 1. If an atom, such as hydrogen, is able to form a covalent bond, describe what happens when the electron shells of two atoms overlap: a. What happens when the two atoms are fairly close? b. What happens when the two atoms are TOO close? 2. What does the nucleus of an atom want to do to its own electrons? 3. What does the nucleus of one atom want to do to the electrons of a nearby atom? 4. Are the atoms really “sharing” electrons? 5. What type of atoms form covalent bonds? 6. Draw a graph showing the change in potential energy when atoms form covalent bonds. 7. What happens to the stability of atoms when they form covalent bonds? 8. A line can be used to represent a covalent bond between two atoms. Diagram pairs of atoms that can form single, double, and triple bonds. 9. Can every atom form each of these kinds of bonds? PART II Introduction to Acids & Bases: A WebQuest 1. http://www.visionlearning.com/en/library/Chemistry/1/Acids-and-Bases/58 The word acid comes from the Latin word _____________________ meaning __________________. Boyle stated that acids taste ___________________, are corrosive to _____________________, change the color of litmus to _______________,and become less acidic when mixed with _______________. He described bases as feeling ________________________, changing litmus to the color ______________, and becoming less basic when mixed with an ___________. About 200 years later, Arrhenius proposed that water can dissolve many compounds by separating them into their individual _____________. He suggested that acids contain _____________ and can dissolve in water to release _________________. Bases dissolve in water to release _______________________ ions into the solution. http://www.chem4kids.com/files/react_acidbase.html Every liquid has __________ & ____________ traits. One exception might be __________________________. It is just water. However, the ____________ ions and _________________ ions cancel each other out. 3. https://www.thoughtco.com/formulas-of-common-acids-and-bases-603663 Give the formula for the following acids: Hydrofluoric AcidHydrochloric AcidHydrosulfuric AcidNitric AcidSulfuric AcidAcetic AcidBoric AcidGive the formula for the following bases: Sodium HydroxidePotassium HydroxideCalcium HydroxideIron (II) Hydroxidehttps://www.thoughtco.com/acids-and-bases-definitions-603664 Scroll down to Properties of Acids. Complete the following sentences for Acids Tastes _________________ Changes litmus from blue to _____________. Solutions are __________________________ (conduct electricity). React with bases to form ___________________ + _______________. Neutralization Create _______________ gas when reacting with an active metal. Five (5) Common acids (scroll down): Properties of Bases Tastes _____________________. Feels _______________________________. Don’t change the color of __________________________. Solutions are _____________________________ (conduct electricity). React with acids to form ____________________ + ______________________. Neutralization Four (4) Common Bases: https://www.thoughtco.com/ph-of-common-chemicals-603666 and https://www.visionlearning.com/en/library/Chemistry/1/Acids-and-Bases/58 Scroll down on the site above until you get to the pH scale Using the sites above, answer the questions below: pH range of acids ______________________ pH of a neutral substance ______________ pH of a basic (alkaline) substance ______________________ https://www.thoughtco.com/acids-and-bases-quiz-4045347 Take the quiz. Place score here __________________. PART III Motions Web Quest http://www.ducksters.com/science/physics/speed_and_velocity.php What is the measurement of how fast an object moves relative to a reference point? What is the formula for speed? How do we measure or think of speed in the United States? In science and physics, what is the standard unit of measure for speed? What is the speed of an object at a given moment? Give an example of instantaneous speed. What is the average speed of a car that travels 40mph for 1 hour and 60 mph in another hour? What is the rate of change in an object’s position? What two parts make up velocity? Who was the first scientist to measure speed as distance over time? What is good example of instantaneous speed? Scroll to the bottom of the page and click on “Acceleration.” What is the measure of a change in an object’s velocity? What is the equation for acceleration? What is the standard unit of measure for acceleration? What do we call the precise spot where an object is located? What is how fast an object’s speed is changing? What is how fast an object is moving? PART IV Periodic Table Complete the following table using information from this website. http://allperiodictables.com/ClientPages/AAEpages/aaeHistory.html Scientist Contribution to the development of the periodic table Greek thinkers Lavoisier John Dalton Doberiner Dechancourt ois Cannizaro Newlands Meyer Mendeleyev Moseley Seaborg GETTING THE LAY OF THE LAND: PERIODICALLY ORGANIZED http://www.chem4kids.com/files/elem_pertable.html 1. Why are the elements placed in specific places on the Periodic Table? 2. Periods are ________ that run from _______ to _______. 3. Elements in the same period have the same ________________________. 4. Every element in the first period has ________ shell for its _______. Every element in the second period has __________ for its ___________. See the pattern? 5. Groups are _______________ that run from ______ to _________. 6. The elements of a group have the same number of ____________ in their ___________ shell. 7. Every element in group one has _________ electron in its outer shell. Every element in group two has ___________ electrons in its outer shell. 8. Hydrogen is special because it can act like two groups, __________ and _________. 9. Hydrogen sometimes is ________________ an electron and sometimes it has an _____________ electron. 10.Although helium has only __________ electrons in its outer shell, it is grouped with elements that have ________________. 11. The green elements on this table are called ____________ elements. They each have two electrons in their outer shell. GETTIN'' TOGETHER WITH THE FAMILIES!!!! Use this site to fill in the blanks below: http.//chemicalelements.com/ 12. Click on Alkali Metals (left bar) and answer the following questions. a. What is the group number? __________ b. Are these metals reactive? __________ c. Do these metals occur freely in nature? __________ d. How many electrons are in their outer shell? ___________ e. What are the three characteristics of ALL metals? ___________________ f. Are these metals soft or hard? ________________________ g. Name the two most reactive elements in this group? _____________ and __________ h. What happens when they are exposed to water? ____________________ 13. Click on Alkaline Earth Metals (left bar) and answer these questions. a. What is the group number? __________ b. Are these metals reactive? __________ c. Do these metals occur freely in nature? ____________ d. How many electrons are in their outer shell? _________ 14. Click on Transition Metals (left bar) and answer these questions. a. How many elements are in this group? ____________ b. What are the group numbers? __________ through _______ c. What are valence electrons? ________________ d. Because the valence electrons are present in more than one _____________ transition metals often exhibit several common __________________. e. Name the three elements in this family that produce a magnetic field. _________, __________, and __________. 15. Click on Other Metals (left bar) and answer these questions. a. How many elements are in this group? ______________ b. What are the group numbers? _________ through __________ c. How are these other metals similar to the transition metals? ______________ d. How are these metals different than the transition metals? ________________ _______________________________________________________________ e. List three physical properties of these other metals. _________________________ 16. Click on Metalloids to answer these questions. a. Metalloids have properties of both ________ and _____________. b. Define semiconductor ___________________________________. c. Name two metalloids that are semi-conductors. ____________and __________. d. This property makes metalloids useful in ____________and ______________. 17. Click in Nonmetals to answer these questions. a. What are the group numbers? ___________ through ____________ b. List four characteristics of ALL nonmetals. ______________________________ c. What two states of matter do nonmetals exist in at room temperature? _________________________ d. The nonmetals have no _______________and do not ____________________. 18. Click on the Halogens (left bar) to answer these questions. a. What is the halogen group number? ___________________ b. Are halogens metals or nonmetals? ______________________ c. The term “halogen” means ____________________ and compounds containing halogens are called ____________________. d. How many electrons are in their outer shell? __________________ e. What states of matter do halogens exist in at room temperature? __________________________________ 19. Click on Noble Gases (left bar) and answer these questions. a. What is the group number? _________________ b. Why were these gases considered to be inert or stable? ________________________