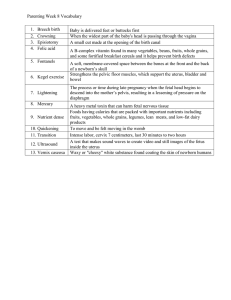
ATI Nursing Maternal Newborn Key Points Table of Contents Vital Signs/Lab Values ............................................................................................................ 1 Nursing Interventions ............................................................................................................. 3 Nursing Assessments for Diseases/Labor ................................................................................ 3 Medications ......................................................................................................................... 10 Surgical Implications ............................................................................................................ 11 Nursing Treatment Modalities .............................................................................................. 12 Newborn and Mother Vaccines ............................................................................................. 13 Nursing Education ................................................................................................................ 14 Vital Signs/Lab Values 1. Respiratory Rate: a. Neonate and Infant: 30-60 bpm b. Toddler: 20-40 bpm 2. APGAR Scores: a. 0-2 i. 1 is a weak result ii. 3. Neonate: a. HR: 100-160 b. RR: 30-60 c. Weight: 2.5-4 kg d. Glucose: 45+, 40-60 e. Head Size: 32-36.8 cm i. ↓ may be due to toxoplasmosis, rubella, cytomegalovirus. 4. Newborn: a. Hgb: 14-24 b. Platelets: 150-300K c. Bilirubin: 2-6 d. Glucose: 40-60 Nursing Interventions 1. Place a hat on baby’s head d/t heat loss. 2. Umbilical Cord Bleeding: Check the clamp. 3. Ultrasounds: a. During the 1st Trimester: Tell Mother to have a FULL bladder for visualization. 4. Cold Stress: newborn temperature should be kept within normal limits and NOT cold. a. ↓ in Neonate Temperatureà Take Glucose Level. 5. Language Barriers: a. Comfort measures are still good regardless of language barriers. 6. Rotating fetus anteriorly: a. Squat during contractions. b. Get on hand and knees during contractions. c. Lay on the same side as fetal spine. Nursing Assessments for Diseases/Labor 1. Always ask cultural preferences. 2. Preterm infants have abundant lanugo. 3. Risk for preterm labor, decreased muscle tone, ↓ Progesterone Levels. 4. Hypertonic uterus, assess pain and work on pain management. 5. ↑ Estrogen Levels, assess for nasal stuffiness. 6. Postpartum Depression (PPD) risk factors a. Gestational Diabetes, Infertility Treatment, Complicated Pregnancy, Preterm labor, History of Mood Disorders. 7. Strep Testing is done at 35-37 week before labor. 8. Risk factors for Necrotizing Enterocolitis (NEC) is ARDS/Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome. 9. During an amniocentesis always apply the fetal heart monitor. 10. Postpartum Depression can be seen through ↓ sex interest/libido. 11. Postpartum diaphoresis can cause and can be caused by a weight loss of over 2.25 kg a week. 12. Fundal Height: a. After 2 weeks postpartum it should be NONPALPABLE. b. At birth it is 2 cm above umbilicus. c. After birth 1 cm above umbilicus and drops 1-2 cm every 24 hrs. 13. Parental Assessments during trimesters a. 1st Trimester: Accept Pregnancy. b. 2nd Trimester: Accept Baby c. 3rd Trimester: End of Pregnancy and Start of Parenthood. 14. Bishop Scoring: a. Over 8 is sufficient for inducing labor. 15. Risk factor for intraventricular hemorrhage, fetus born before 34 weeks’ gestation. 16. Cyanosis assessment: a. Central=bad b. Acrocyanosis=okay 17. Hemophilia is a X Linked Recessive Trait and men with parent carriers have a 50% chance of acquiring it. 18. Uterine Atony: a. Assess for: Magnetism Sulfate usage, Distended Bladder, or Prolonged Labor. 19. HELLP: a. Low Hemoglobin b. ↑ Liver Function Test c. ↓ Platelets 20. Newborns with congenital diaphragmatic hernias will exhibit a Barrel-Shaped Chest. 21. Tonic Neck Reflex: The baby will turn their head to the side while sleeping. 22. With Hyperemesis Gravidarum, CHECK KETONES in URINE. 23. Infant in septic shock S&S: ↓BP, ↑HR, ↑RR, Mottled gray-skin, cool extremities. 24. Large For Gestational Age (LGA) baby. Monitor ↓ Blood Glucose. a. S&S: Jittery, lethargic, ↓muscle tone, crying. 25. Signs & Symptoms of Pregnancy: a. Presumptive: are symptoms patient reports, like Nausea and Vomiting in the morning. b. Probable: tests or exams or procedures with objective data. c. Conclusive: Fetal heart rate. 26. Heroin Baby S&S: incessant crying, jittery, ↑CNS, ↓ feeding, ↑HR, ↑ Yawning, ↑ Sneezing. 27. Neonatal Abstinence Syndrome S&S: CNS Hyperactivity, ↑ reflexes, ↑ muscle tone, RR of ↑ 60 bpm. a. Avoid stimulation: No eye contact, No talking to them. 28. Eclampsia Look for swelling of face, fingers, or sacrum. 29. Preeclampsia ↑ risk for seizures: Report ↑ CNS like: ↑ Deep Tendon Reflexes d/t ↑CNS. a. S&S: HA, Swelling Face, Eyes, and Fingers, Vision Changes, Epigastric Pain. 30. Calculating Estimated Delivery Date: a. Subtract 3 months b. Add 7 days c. Add 1 year 31. Fundal Massages: The fundus should be FIRM and MIDLINE. a. How to do it: i. Patient will lay on their back with knees flexed. ii. Hand on symphysis pubis iii. Hand on top of fundus. iv. Rotate hand to massage. v. Apply slight downward pressure to compress fundus. b. If deviated or soft: Massage and ensure the patient is voiding. i. After 24 hours, if the fundus is above the umbilicus…Take the patient to the restroom or insert a foley. 32. Risk for ↑ Bilirubin: a. Blood Types i. Seen with Type O Mothers Carrying A/B/AB Baby(s). b. Infection c. Diabetes Mellitus d. Oxytocin Administration 33. Nuchal Cord Wrapping: a. Assessment: i. Petechia: small-pin point red-purple sports 1. Are found in the neck or above the wrapped area, but REPORT anywhere else d/t Risk of Infection. 34. Newborn Respiratory Distress: a. Grunting, Nasal Flaring, Substernal and/or Intercostal Retractions. 35. For Cardiac issues with pregnant woman, Assess Lungs especially COUGH! 36. Uterine Rupture Risk includes History of C-Sections. S&S include onset of pain with decelerations in FHT. 37. Rupture of Membranes: a. Meconium: a stained fluid green-brown color, prepare for fetal resuscitation. 38. Nonstress Test (NST): a. Takes about 20-30 minutes. b. Take sips or eat a snack during the test to stimulate fetus. c. The test is intended to assess the health of the fetus NOT the contractions. 39. Stages of Labor: a. First: i. Latent: 0-3 cm dilated ii. Active: 4-7 cm dilated with contractions every 3-5 minutes lasting 40-70 seconds. iii. Transition: 8-10 cm dilated with contractions every 2-3 minutes lasting 45-90 seconds. 1. Attempt to contract for 60 seconds with rest periods of 3 minutes with contractions every 4 minutes. b. Second: Complete dilation to birth. i. Encourage changing positions frequently b/c it helps ↑ fetus descending through the vaginal canal. 40. Fetus Positions: a. Occiput/Vertex: Occipital bone presenting. b. Transverse: Shoulder presenting. c. Breach: Buttocks or feet presenting. d. Mentum: Chin Presenting. 41. Doppler can detect HR at 12 weeks or 10 weeks (sometimes) after 1st trimester. 42. Fetal Heart Monitor: a. Frequency of monitoring during stages of labor: i. Stage 1: Q15 minutes. ii. Stage 2: Q5 minutes. b. Late Decelerations: Signals Uteroplacental Insufficiency, this means the baby has ↓ O2 levels. i. Spontaneous Rupture of Membranes (SROM): 1. Manually apply upward pressure intravaginally to release umbilical cord. a. Look for ↓15 bpm in HR. c. Early Decelerations: Signal Head Compression, this is normally not a threat. i. No interventions are required, just monitor Q15minutes. d. Variable Decelerations: Signal Cord Compression, reposition mother. e. Types: i. Continuous: Used to monitor variability. ii. Intermittent: Used when continuous monitoring is not required. 1. Palpate mom and hear monitor to ensure it is the fetus and NOT the mom. 2. Listen for 30-60 seconds after contraction. 3. Place in fetus’ back. 43. Oligohydramnios is usually due to a RENAL issue. 44. Moro Reflex: a. “C” form in the thumb and forefinger b. Extend leg before being pulled upwards. c. Abduct arms (extend away). d. Startle trigger movement of arms forward. 45. Categorizing Fetal Heart Tones: a. Category 1: Expected FHT. b. Category 2: Intermediate FHT. D/C Oxytocin and Administer Terbutaline. c. Category 3: Abnormal FHT. D/C Oxytocin and Administer Terbutaline. i. Tachysystole: Position on the Left Side-lying to ↑ Perfusion. 46. Biophysical Profile (BPP): a. 4 or Lower: good for delivery b. 6 or lower seen at or later than 36 weeks. 47. Hip dysplasia can cause LIMITED abduction of hip. 48. Vaginal Bleeding: a. Assess the Uterine Tone: i. Placenta Previa (a position issue): Uterus is Soft, and Bleeding is Painless. 1. Assessment: No Pain, Bright Red Blood, Soft Uterus, Abnormal Fetus Position. a. Note that Placenta Previa will have a ↑ higher fundal height. ii. Abruptio Placenta (detachment issue): Uterus is Firm, and Bleeding is Painful. 1. Assessment: Dark Red Blood, Tender, Shock Risk, May Cause DIC. iii. Cervical Laceration: A tear in the cervix during labor. 1. Assessment: Bright red bleeding, Slow Trickle of blood, FIRM fundus. Medications 1. Oxytocin: ↑ Contractions. a. Risk for fetal asphyxia. b. Contraindicated for ACTIVE HERPIES. c. STOP it if contractions are 2 minutes or more OR 5 contractions in 10 minutes. 2. Terbutaline: ↓ Contractions. a. High risk Tachycardia. 3. Erythromycin given within 1-2 hours of birth 4. Vitamin K Injection given in the thigh. 5. Betamethasone: used for lung maturity in the fetus. a. Note it may cause HYPOglycemia. 6. Magnesium Sulfate: Used for preterm labor by ↓ contractions. a. ANTIDOTE: Calcium Gluconate. b. Tell mom she WILL FEEL WARM, this is NORMAL. 7. Meperidine Hydrochloride: an opioid used for pain. a. ↓BP, ↓RR, ↑Sedation, ↑Constipation, ↑Urine Retention. 8. Prostaglandin E2 Gel administration. Teach patient to stay on their side for 30-40 minutes. 9. Ferrous Sulfate is given with Hgb levels <10.5. 10. Nitrous Oxide: a. ONSET: Rapid within 1 minute. b. No effect on fetus. c. No Level of Conscious changes. d. Continuous administration with facemask. 11. Methylergonovine is CONTRAINDICATED in PREECLAMPSIA and HTN. 12. Rhogam Rh(D) antibody is given at 28 weeks gestation. Surgical Implications 1. Pelvis shapes and C-Section Necessity a. Ideal Shape for Vaginal birth i. Gynecoid Pelvis b. Shapes that Warrant a Possible C-Section i. Android ii. Anthropoid iii. Platypelloid 2. Circumcision Care: Use petroleum jelly to protect the incision from urine and feces. Nursing Treatment Modalities 1. ↓ Hgb: Add Iron and Vitamin C to Diet/POC to ↑ Hgb. 2. For perineal area lacerations, try to ice the area first THEN a sitz bath. 3. Epidurals that are placed too early will PROLONG labor. 4. For the Leopards Maneuver the nurse needs to be on their dominant side. 5. A decrease in Platelets (<150K) may be due to: a. Preeclampsia b. HELLP 6. Intrauterine Pressure Catheter is used to measure intensity of contractions. 7. Vibracoustic Stimulator is used for 3 seconds to wake up the fetus. 8. Engaging a Fetus to Correct Position: a. External cephalic version is when they rotate the fetus from the outside, but needs a relaxed uterus. b. Internal Version is when they turn the fetus with provider’s hands inside the uterus. 9. Epidural side effects include ↓perfusion to placenta. 10. Complication of oxygen in preterm newborn is retinopathy. 11. Amniocentesis in a Rh-Negative Mother: Immunoglobulins are NEEDED to prevent isoimmunization. 12. Premature infant treatment: a. Encourage skin to skin (kangaroo) care. b. Allow sleep c. Provide a low light environment. 13. Pain during Labor: Nonpharmacological Pain Management: Counterpressure to the back. a. Effleurage: a light massage on the abdomen (or if they have a monitor on the chest, thigh, or sides of abdomen). b. Warm baths decrease pain too. c. Heat on the lower back is okay for pain management too. d. Types of pain control: i. Lamaze: Think of “Lazy” and just learning to breathe. ii. Dick-Read: ↓Fear iii. Bradley: involve both partners 14. Infant jaundice TX: phototherapy to ↓ Bilirubin. a. During therapy change newborn’s position Q2-3H. b. ↑ bilirubin level with weight loss of UP TO 10% is OKAY i. More=BAD Newborn and Mother Vaccines 1. Hepatitis B Vaccine: Informed consent is needed for vaccine. a. HIV babies can get all live vaccines including Hep B. 2. Common Allergies with Vaccines: a. Influenza: Eggs b. MMR: Gelatin c. Hepatitis B: Yeast 3. Rubella Vaccine, POSTPARTUM: a. Avoid pregnancy b/c it is a live virus and birth defects. i. Wait 1 month (28 days) before conceiving b. They CAN breastfeed. c. Is indicated postpartum if they had a negative titer. d. 1 dose Subcutaneous, Check after 3 months titer (if on Rhogam). Nursing Education 1. Afternoon insulin dosages: a. ↓ during 1st Trimester b. ↑ during 2nd and 3rd Trimester c. ↓ after birth 2. IUD ↑ the risk for ectopic pregnancies. 3. Pruritus Gravidarum SLOWLY ↑ Sunlight to help ↓ itching. 4. A fetus at 20 weeks will look like a human. 5. Daily fetal Movement Count (DFMC) should be counted at bedtime or after eating for 2 hours until 10 movements are counted for good health. 6. Phenylketonuria (PKU) is a autosomal RECESSIVE gene. a. Need 2 carrying parents 7. If Hydatidiform mole is present: DO NOT get pregnant for 1 year due to risk of CARCINOMA. 8. Teach Umbilical cord care, AVOID antimicrobials and moisture on the umbilical cord to avoid infection and prolonged drying. 9. Breastfeeding a Newborn. Teach that sessions would be Q2-3 hours or 812 sessions per day. a. ↑ Vitamin C in diet to help build baby’s immune system and tissue growth and repair. b. Breastfeeding ↑ Uterine Contractions and Cramps, this is NORMAL. 10. Pseudomenstration is possible with female newborns due to the decrease in maternal hormones 11. Urinary Frequency during pregnancy will occur during the 1st and 3rd Trimesters. Why? The fetus is growing upwards with the uterus during the 1st trimester and drops during the 3rd trimester adding pressure to the bladder. 12. Recommended Values for nutrition: a. Carbohydrates: 55% b. Protein: 20% c. Fats 25% i. Saturated Fasts: 10%. 13. If breastfeeding report the following: a. Cracking of the nipples, bleeding, or blisters on the nipples. 14. If mother is having difficulty sleeping due to growing belly, USE pillows to support belly this is normal due to the fetal growth. 15. Infertility: Encourage support groups. 16. If mother has Mastitis they can continue to breastfeed BUT Avoid ill family members. 17. Wight gain during pregnancy: a. If the patient is obese before conceiving: gain 5-9 kg during pregnancy b. If the patient is overweight before conceiving: gain 6.8-11.3 kg. during pregnancy. c. If the patient is normal before conceiving: gain 11.3-15.9 kg during pregnancy. d. If the patient is underweight before conceiving: gain 12.7-18.1 kg during pregnancy. 18. Breast engorgement PREVENT WITH ice packs. 19. Types of fetal movements: a. Lightening: head of the fetus engages in the cervix ↓respiration efforts and ↑urination in mother. b. Quickening: the first fetal movements. i. Fetus will begin moving around 18-20 weeks (during the 2nd trimester) 20. Graafian follicle releases Ovum. 21. True contractions begin irregular then turn regular and increase in frequency and duration. 22. C-Section if they get gas pain- AMBULATE. 23. Teach parents to BOIL bottles and caps prior to use then run them on the dishwasher for cleaning, USE sterilized tap water (boiled) for 1-2 MINUTES, and DISCARD within 48 hours of opening a new bottle. 24. Swaddle the baby until they are able to roll over at 2 months. 25. IUD is contraindicated with ABNORMAL rrhagias, and history of ectopic pregnancy. 26. For weight loss postpartum, TEACH lose 1 kg per month to avoid ↓ milk production. 27. Teach Oral Contraceptives INTERACT with HIV, TB, Seizure, and antifungal medications. a. Oral Contraceptives are contraindicated in SMOKERS. b. Okay after 4 weeks postpartum. i. Note that Progestin Oral Contraceptives or Injection is Okay when breastfeeding 6 WEEKS postpartum. 28. Caput Succedaneum: sucked head shape seen in vacuum assisted birth and lasts 3-5 days. 29. Cow’s formula is preferred for newborns, as alternative to breastmilk. 30. Crib Rails should be less than 2.25 inches or 6 cm wide. 31. Formula babies, teach 1 scoop of formula for 2 ounces of water. 32. Diaphragms: a. Replace Q2 years. b. Keep inside for 6 hours. 33. Four Stages of labor a. Frist stage: uterus getting ready to push. b. Second stage: birth c. Third stage: birth of placenta d. Fourth stage: post labor marked by a decrease in UO. 34. Nutrition During Pregnancy: a. Alcohol during pregnancy is NOT recommended. 35. Car seat Safety a. Face rear until 2 years old. b. Retainer clip at the armpits. c. Have at 45 degrees. d. Shoulder harness at the level of shoulders or slightly below. ↓↓↑↑↓↓↑↑↓↓↑↑↓↓↑↑↓↓↑↑↓↓↑↑