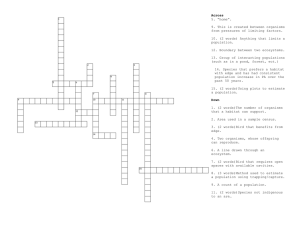
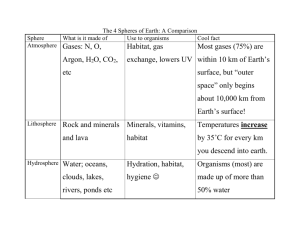
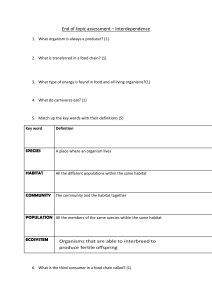
Answer ALL questions. 1. Define the term sampling.(3) Sampling is a method used to determine population size, relationships between organisms and their environment or interactions organisms have within their community. It is done by extracting a small quantity of a species for research or in other words taking a sample from the ecosystem. 2. Discuss what you understand by the term “ecological succession”. (4) Ecological succession is understood by me to be a process in which organisms inhabit an area and overtime change the state of the environment thus resulting in the original occupants to be replaced by other species. 3. Explain four (4) actions of humans that may affect species diversity. (10) Four human actions that affect species diversity are: loss of habitat, pollution, exploitation and habitat fragmentation. Habitat loss is the complete destruction of a habitat, such as cutting down trees in a forest. Pollution of water bodies can result in decrease in oxygen content and harm fish and other aquatic species and cause a loss of plant biodiversity. Exploiting can lead to depletion of resources and put a number of threatened and endangered species at risk of extinction.Habitat fragmentation is described as a habitat that is broken into smaller discontinuous segments of land for development, an example of this would be placing a road in the middle of a habitat. 4. Examine the impacts of a non-native introduced species to a new environment.(8) Non-native or invasive species in a new environment negatively impacts the original wildlife. Non-native species may not have any natural predators or controls. It can also breed and reproduce quickly, thus dominating the new environment. Native organisms also have not evolved a defense mechanism against the non-native species, or they may not be able to compete with a species that has no predators. The direct threats of invasive species include preying on native species, outcompeting native species for food or other resources, causing or carrying disease, and preventing native species from reproducing or killing a native species' young. TOTAL 25 MARKS