Tolerance Field Calculation Homework: Metrology & Standardization
advertisement

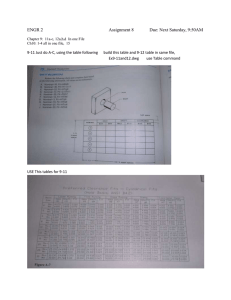
OPTIONS homework on the calculation of tolerance fields in the discipline "Metrology, Qualimetry and Standardization" for students of the academic groups BGBi-19-01, BGRi-19-01, BGBi-18-01 and BGRi-18-01 1 Homework Terms For the homework option specified in table 1: 1) draw out graphically the disposition of tolerance fields of coupling according to the original dates presented in table 1; 2) determine in which system (hole-basis fit system or shaft-basis fit system) the original coupling of machined workpieces is performed; 3) determine the mode of coupling clearance fit, interference fit or transition fit; 4) by international or interstate standard select the standard fit and indicate its designation; 5) determine the standard values of the upper and lower limits of size deviations of the shaft and hole, the standard limits of size tolerances of the shaft and hole, the maximum dimensions of the shaft and hole, the minimum and maximum values of the clearance or interference in the coupling; 6) check in the correct choice of the fit; 7) draw up a layout diagram of tolerance fields containing standard deviations, graphically selected by calculation. 8) indicate the value of the roughness of the machined surfaces of the shaft and the hole. Table 1 Homework options for calculating of tolerance fields Size deviations No. Nominal size A method of workpiece machining size, m option of coupling hole shaft 1 40 +19 -16 Finishing turning 2 45 -25 -15 Fine cylindrical grinding 3 28 +52 -13 Semi-finishing turning 4 280 +48 +45 Finishing face milling 5 20 +41 -40 Semi-finishing reaming +41 -40 6 20 Fine face milling -20 -62 +48 7 20 +21 Fine planning +35 +21 8 20 +16 Finishing reaming +20 +98 9 25 -45 Finishing grinding +65 10 32 +63 Semi-finishing grinding 23 +23 11 60 Finishing broaching 45 +16 -65 12 25 Drilling on the jig 35 -98 13 32 -62 +45 Drilling 14 14 +55 -55 Semi-finishing reaming 15 28 +13 +10 Finishing countersinking 16 42 +42 +26 Polishing 17 55 +30 +49 Honing 18 90 -28 +28 Finishing plane milling 19 70 +32 Rough slotting 25 No. option Nominal size of coupling 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 10 100 16 20 35 68 90 140 190 270 350 450 630 720 900 500 160 100 38 125 39 63 40 320 41 42 80 280 43 560 44 630 45 2000 46 1400 47 80 48 100 49 125 50 160 Size deviations size, m hole shaft +45 -25 +120 - 100 -16 -12 +18 -80 +10 +15 +23 +12 +48 +35 +85 +60 +50 +20 -190 -400 -62 -96 -230 -400 -450 -151 +265 -480 +300 +185 +155 +145 -12 +27 -14 +58 +180 -270 +120 -700 -40 +50 +44 128 +38 -230 +46 +81 28 +220 +70 +125 -76 +110 -146 +500 -400 +450 -500 -150 +195 -110 +438 -305 -25 +23 -80 -44 -54 +110 -40 31 -110 A method of workpiece machining Drilling on the jig Finishing reaming Planning finishing Drilling Fine turning Semi-finishing turning Finishing turning Rough turning Flat thin grinding Cutting off with a power saw End thin milling Turning semi-finishing End milling, semi-finishing End thin milling Finishing chiseling Planning finishing Drilling on the jig Finishing turning Fine turning Round fine grinding Flat grinding, semi-finishing Thin scraping Countersinking semi-finishing End milling finishing Rough milling with cylindrical cutter Rough milling, semi-finishing Face thin milling Finishing broaching End finishing broaching Finishing broaching Round fine grinding 2 Example homework on the calculations for selection the tolerance fields of the coupling Original dates for computations: +0,016 D = 20+0,021 ; Type of workpiece machining finished reaming +0,002 ; d = 20 Define the values of the nominal size of the coupling and limits of size of the shaft and the hole. The nominal size of the coupling is D = 20 mm. Upper limit of deviation and lower deviation of the hole: ES = +210 μm = 0,021 mm; EI = 20 μm (1) Upper limit of deviation and lower limit deviation of the haft: es = 0,016 mm = 160 μm; ei = 0 μm (2) Upper limit of sizes and lower limit of sizes of the hole and shaft: D max = 20,000 + 0,021 = 20,021 мм, Dmin = 20,000 + 0,002 = 20,002 мм, d max = 20,000 + 0,016=20,016 мм, dmin= 20,000 – 0 = 20,000 мм (3) (4) Define the values of interference and clearance of the coupling. Maximum interference: N max = d max – Dmin= 20,016 – 20,002 =-0,014 мм = 140 мкм (5) Maximum clearance: Smax = Dmax – dmin = 20,021 – 20,000 = 0,021 мм = 210 мкм (6) Determine the mode of coupling and system in which the initial coupling of machined workpieces is performed. The mode of coupling is transition fit because there are both an interference and clearance: Nmax = 140 μm, Smax = 210 μm. The fit is non-standard, since in a standard fit one of the values of the deviations of the hole or the shaft must correspond to the value of the fundamental deviation of the basic hole (H) or the fundamental deviation of the basic shaft (h). Define the tolerances of the hole and the shaft, span of a fit. Hole tolerance TD = Dmax - Dmin = 20,021 - 20,002 = 190 μm (7) Shaft tolerance Td = dmax – dmin = 20,016 - 20,000 = 160 μm (8) Span of a clearance fit TS = Smax - Smin = 20,021 – 20,002 = 190 μm (9) Span of an inteference fit ТN = dmax – Dmin = 2,016 – 20, 002 = 140 μm (10) Span of a transition fit TI = Smax + Nmax = 210 +140 = 350 μm (11) Based on the calculation results, draw a diagram (figure 1) of the tolerance fields of the coupling. e s = 160 E I = 20 Е S = 210 Figure 1 Diagram of tolerance fields according with original dates The values of the standard fit parameters for the nominal size D = 20 mm should be as close as possible to the values of the basic parameters of the original dates. According to the international (ISO) or interstate standard (GOST), the parameters of the standard fit will be chosen in the hole-basis fit system: - tolerance class of a hole Ø20H10 = Ø 20+0,070; - tolerance class of a shaft Ø20js13 = Ø20± 0,0165; - fit designation Ø20H10 / js13. Evaluate the correctness of the choice of the fit: Maximum interference fit: Nmax = dmax - Dmin = 20,0165 – 20,000 = -0,0165 mm = 165 μm (12) Maximum clearance fit: Smax = Dmax - dmin = 20,0070 - (-20,0165) = 0,0235 mm = 235 μm (13) e i = 165 e s = 165 E S = 70 Conclusion: The standard fit is chosen correctly, since the limit deviation values of the fit are as close as possible to the values specified by international and interstate standards (the interference and clearance values differ by 25 μm). The span of a fits diagram corresponding to a standard fit are presented in figure 2. For a given method of workpiece machining determine the roughness parameters of the shaft and which equal to Ra 3.2 μm according to the corresponding reference books. Figure 2 Diagram of standard tolerance fields REFERENCES 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Балабанов, А.Н. Технологичность конструкций машин / А.Н. Балабанов. – Москва : Машиностроение, 1987. 336 с. Гжиров, Р.И. Краткий справочник конструктора : Справочник / Р.И. Гжиров. – Ленинград : Машиностроение, 1983. – 464 с. ГОСТ 25346-2013 (ISO 286-1:2010) Основные нормы взаимозаменяемости. Характеристики изделий геометрические. Система допусков на линейные размеры. Основные положения, допуски, отклонения и посадки = Basic norms of interchangeability. Geometrical product specifications. Code system for tolerances on linear sizes. General provisions, tolerances, deviations and fits. Допуски и посадки: Справочник / В.Д. Мягков, М.А. Палей, А.Б. Романов и др. – В 2-х ч. – 6-е изд. – Ленинград : Машиностроение, 1982. Мягков, В.Д. Допуски и посадки: Справочник / В.Д. Мягков. – 4-е изд., перераб. и доп. Москва : Машиностроение, 1966. – 772 с. Общетехнический справочник / Под ред. Е.А. Скороходова. – 4-е изд. – Москва : Машиностроение, 1990. – 496 с. Якушев, А.И. Взаимозаменяемость, стандартизация и технические измерения. – 6-е изд., перераб. и доп. / А.И. Якушев. – Москва : Машиностроение, 1987. – 352 с. Professor 25.12.2021 Ferdinand Sh. Zabirov