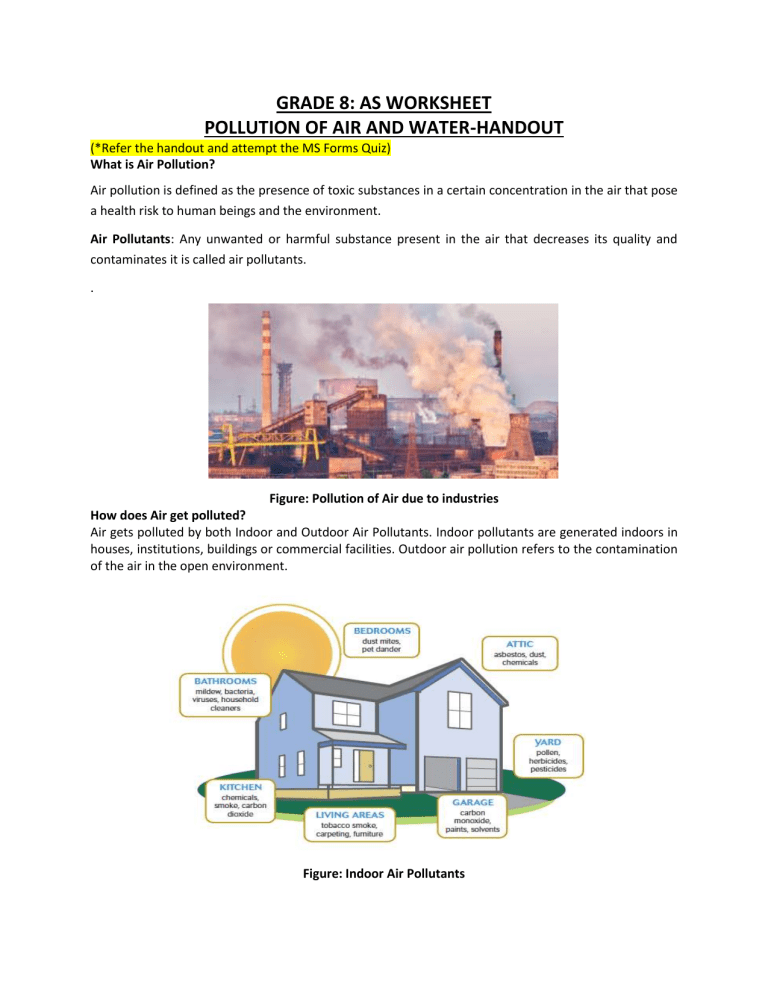
GRADE 8: AS WORKSHEET POLLUTION OF AIR AND WATER-HANDOUT (*Refer the handout and attempt the MS Forms Quiz) What is Air Pollution? Air pollution is defined as the presence of toxic substances in a certain concentration in the air that pose a health risk to human beings and the environment. Air Pollutants: Any unwanted or harmful substance present in the air that decreases its quality and contaminates it is called air pollutants. . Figure: Pollution of Air due to industries How does Air get polluted? Air gets polluted by both Indoor and Outdoor Air Pollutants. Indoor pollutants are generated indoors in houses, institutions, buildings or commercial facilities. Outdoor air pollution refers to the contamination of the air in the open environment. Figure: Indoor Air Pollutants Figure: Outdoor Air Pollution Sources Causes of Air Pollution Air pollution from Natural Sources: sometimes Dust storms in desert areas, forest fires or volcanic eruptions can lead to the release of an excess of smoke and dust in the atmosphere. Automobile Emissions: The vehicles release smoke which contains carbon monoxide, carbon dioxide and also lead. Industrial emissions: Burning of fossil fuels like coal and petroleum used in industries release harmful substances in the air such as carbon monoxide, nitrogen oxides, sulphur dioxide, smoke and even dust. Suspended and Particulate Matter (SPM): These are minute solids present in the air in the form of smoke or dust that can remain suspended for long periods and are also the main source of haze that reduces visibility. Particulate matter can be divided into two types- coarse particles (coming from road dust, construction activities) and fine particles (due to burning of fuel in automobiles and power plants). Chlorofluorocarbons (CFC): This is an organic compound that contains carbon, chlorine and fluorine. It causes damage to the ozone layer that protects the Earth form the Sun’s UV radiation. Agricultural activities: usage of insecticides, fertilizers and pesticides lead to release of chemicals in the air. Agricultural activities also lead to the release of ammonia in the atmosphere which is extremely hazardous for us. Pollution due to households: paints, cleaning products, air conditioners, refrigerators and other appliances used in houses also contribute to air pollution. The air conditioners and refrigerators release chlorofluorocarbons that damage the ozone layer of the earth. Burning of wood and cow dung cakes in rural areas also leads to air pollution. Mining activities: mining results in the release of a large amount of dust and chemicals in the air. Effects of Pollutants on the Environment Pollutants Source Effects Carbon monoxide It is produced due to improper ● Poisonous gas combustion of fuels ● Decreases blood’s oxygen carrying capacity Smog It is a combination of fog and ● Causes difficulty in breathing Reduces visibility and forma a layer of haze in the atmosphere smoke ● Can cause asthma, wheezing, cough Eyes and nose irritation. ● Leads to decreased visibility Sulphur dioxide Produced mainly due to the ● Leads to respiratory problems combustion of coal Causes acid rain. ● Can cause lung damage Chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs) Produced from air conditioners, ● Deteriorate the Ozone Layer refrigerators and aerosols Suspended particulate Produced due to the burning of ● Cause decrease visibility matter (SPM) fuels ● Lead to problems in breathing Air pollution and the case study of the Taj Mahal We know that air pollution can severely affect the environment. One great example of the harmful effects of air pollution can be viewed on the Taj Mahal, the most famous and beautiful tourist attraction of India. It has been seriously damaged by the extreme climatic conditions and monsoon rains which lead to water infiltration and erosion of white marble exterior. The pollution in that region from heavy traffic and factories has led to decolourization of the white marbles of the Taj Mahal. Figure: Effect of Air Pollution on Taj Mahal Causes of air pollution in Agra and effects on the Taj Mahal The main sources of pollutants in the air around Taj Mahal are the industries around Agra. The Mathura oil refinery and other industries including automobiles, rubber processing and chemicals are releasing harmful substances in the air. The major pollutants are Nitrogen dioxide and Sulphur Dioxide. These pollutants lead to acid rain in the Agra region. When Nitrogen dioxide combines with water it forms nitric acid and when Sulphur Dioxide combines with water it forms sulphuric acid. The rainwater which falls on the Taj Mahal leads to decay of the marble. This is also called ‘marble cancer’. The Mathura oil refinery is a major source of suspended particulate matter (SPM) in the air around the Taj Mahal which is making the white marble look yellow in colour. Steps were taken to reduce air pollution in the area near Taj Mahal 1. The industries are switching to clean fuels such as CNG and LPG to prevent air pollution and protect the monument. 2. Also, unleaded petrol should be used in automobiles to prevent harmful smoke from the vehicles near the Taj Mahal area. 3. To reduce pollution a green buffer zone (tree plantation) has been created around Taj. 4. The vehicles are strictly checked for pollution and the traffic around Taj has been banned. The parking is kept at a safe distance. Prevention of Air Pollution 1. Switching to cleaner fuels like CNG and LPG can lead to decreased air pollution. 2. Generating awareness among people about air pollution and its harmful effects will encourage them to participate in preventing it. 3. Increasing the usage of solar energy, wind energy and hydropower. 4. Planting more and more trees around the cities in rural areas. India celebrates ‘Van Mahotsav’ in July every year where people come together and plant trees on a large scale. 5. Instead of burning dry leaves and other organic materials they should be dumped into compost. 6. Using gas stoves instead of burning coal or wood to cook food. 7. Sharing vehicles or using public transport to reduce the number of vehicles on the road and hence the air pollution and also using unleaded petrol to minimize air pollution. 8. Using eco-friendly paints and cleaning products for household and other buildings. 9. Enforcing smoke emission test and certification to all motor vehicles.



