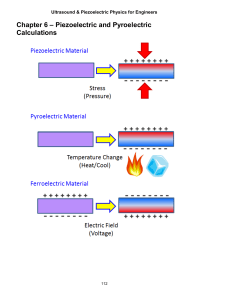
BY, SHEBINA. A ROLL NO: 15 Materials that respond to a stimulus in the form of a mechanical property change such as a dimensional or a viscosity change. Eg: Simple amplifier ( converts low energy signal into high power signal) Transducer( energy of the amplified control signal is converted into work) Actuator Material Classes Actuator Materials • • • • Shape Memory Alloys Magnetostrictive Materials Piezoelectric & Electrostrictive Materials Electrorheological & Magnetorheological Fluids Shape Memory Alloys • Ability of material to regain its original shape when heated to a temp, after being deformed at a lower temp. • Shape memory effect occurs in a no: of alloys, which undergo a special type of transformation called the ‘ • SMAs are useful for actuators as they change shape tiffness osition atural frequency and ther mechanical characteristics in response to temp or electromagnetic fields. The diverse applications for these metals have made them increasingly important Types:• Copper - aluminium - nickel • Copper - zinc - aluminium • Iron - manganese - silicon (nitinol) – most useful • Ni-Ti has that this alloy exhibits above transformation temperature ~ for a single cycle max 8% ~ for 10,000 cycles 4% 30 to 50degree celsius ~ austenite 100 micro ohms*cm ~ martensite 80 micro ohms*cm < 1.002 3.06 (youngs Modulus) ~ austenite 83GPa ~ martensite 28 to 41 Gpa Applications… • • • • • • • • Automobile transmissions Shock Absorbers Small Pumps Window Openers Automotive AerospaceMedical consumer • Materials which change shape when placed in magnetic field. Result of re-orientation of the magnetic domains, which produces internal strain in the material • Utilised in switches and sensors ~ materials of fixed structure metal, ceramic and polymeric composites Elastomers filled with ferromagnetic material powders (carbonyl iron) Solid magnetocaloric materials ~ Materials of variable internal structure MR Fluids Ferro Fluids Porous materials saturated with MR Fluids Electrical energy mechanical energy • Giant Magnetostrictive Materials such as rare earth-iron feature magnetostrains two orders of magnitude larger than Ni • Terfenol – D : commercially available • Positive microstrains of 1000 to 2000ppm are reported to terfenol-D • NiMnGa alloys offering a microstrain up 6% • • • • • Young's modulus- 2.5-3.5x1010 N/m3 Tensile strength- 28MPa Compressive strength- 300MPa Density- 9250kg/m3 Strain- 0.6% • Force : offer large force • Voltage : Its is adjusted by no:of turns in the coil. With high current and large section wires, required magnetic field produced with low voltage Applications • • • • • • • Active noise and vibration cancellation Sonar Fuel injection Medical Nozzle anti-clogging system (paper) Screening applications Metals casting industry • Sonar transducers – very high power transducers, long range transmissions and communication applications • Hydraulic valves – high speed valves • Inchworm motors – in low frequency sound transducers • Materials that exhibit an electrical polarization with an applied mechanical stress • 2 types ~ piezoceramic relatively stiff Large piezoelectric constant ~ piezopolymer Relatively flexible Large voltage capacity Property Curie temp (degree Celsius) Young's modulus (N/m2 ) Piezoelectric constant Maximum electric field PZT (Lead Zirconate Titanate) PVDF (PolyVinylidene Floride) 212 100 59.51 310 21210 2310 .41 4010 • A change in dimensions of material due to the application of electric field • Non – linear response • No hysteresis • A quick response time • Higher displacements with good reproducibility ~ APPLICATIONS • Micro positioned • Adaptive optics • Rheology is the science of the flow and deformation of matter. i.e., response of the matter to a force or stress • Viscous fluid can be altered by ER fluids by application of electric field. Response time is typically a millisecond • Colloidal suspensions of dielectric solids in non-conducting liquids • In absence of electric field, colloidal suspension –fine particle, uniformly distributed • Electric field applied – dielectric particles causes the particles to align with the electric field, causes them to adhere to adjacent particles which join to form fibrils • Fibrils modifies the viscosity of fluid • When electric field is removed, alignment disappears Applications • Tunable shock absorbers used in sports equipment FACTORS CONSIDERED FOR ACTUATOR MATERIALS • • • • • • • • • • • Actuation voltage Speed of actuation Actuation force Stored energy Electrical resistivity Mechanical quality factors Resistance to fracture Young’s modulus Density Stress Resistivity