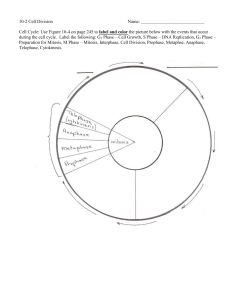
a) Identify, with a reason, whether the cell is (i) Prokaryotic or eukaryotic: eukarotic: no visible cell wall and genetic material seems to be packed (nucleus) (ii) Part of a root tip or a finger tip: finger tip: no vacuoles for osmosios or diffusion (iii) In a phase of mitosis or in interphase: interphase: no supercoiling/ condensed genetic material b) The magnification of the drawing is 2,500 x (i) Calculate the actual size of the cell Mag= image size/ actual size 2500= (ii) Calculate how long a 5 μm scale bar should be if it was added to the drawing 5 x 2500 = how many cm 1 cm= 10,000 micromatere (104) 5 x 10-4 x 2500 = cm c) Predict what would happen to the cell if it was placed in a concentrated salt solution for one d) hour. Include reasons for your answer: The solution, depending on whether it is hypertonic or hypotonic would affect the osmolarity of the cell. It can cause the cell to burst, or shrink In human secretory cells, for example in the lung and the pancreas, positively charged ions are pumped out, and chloride ions follow passively through chloride channels. Water also moves from the cells into malfunction and too few ions move out of the cells. The liquid secreted by the cells becomes thick and viscous, with associated health problems. a) State the names of the processes that (i) Move positively charged ions out of the secretory cells: exocytosis (ii) Move chloride ions out of the secretory cells: facilited diffusion (iii) Move water out of the secretory cells: osmosis b) Explain why the fluid secreted by people with cystic fibrosis is thick and viscous (4): gene mutation , chromosome number, recessive autosomal, common in children less chlorine so less water hence more viscous . water follows concentr The amount of DNA present in each cell nucleus was measured in a large number of cells taken from two different cultures of human bone marrow (Figure 8). a) For each label (I, II, III) in the Sample B graph, deduce which phase of the cell cycle the cells could be in (i.e. prophase, interphase) I: (non-dividing) II: ????? b) III: telophase? c) Estimate the appropriate amount of DNA per nucleus that would be expected in the following human cell types (i) Bone marrow at prophase (ii) Bone marrow at telophase