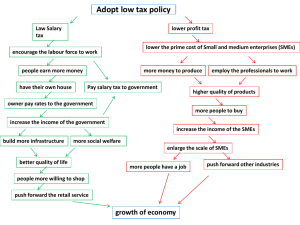
Lesson 2 Small and Medium Scales Enterprises Week 2 What are Small and Medium Enterprises? Small and medium enterprises (SMEs) are very important in the economy of the country because they maintains revenues, assets or a number of employees below a certain threshold. The definition of SMEs may vary depending on the country. Certain size criteria must be met occasionally by the industry where the company operates. SMEs play an important role in the economy, employing vast numbers of people and helping to shape innovation. (Liberto, 2019) Small and medium enterprises represent 90% of businesses and more than 50% of employment worldwide. Formal SMEs contribute up to 40% of national income (GDP) in emerging economies. These numbers are significantly higher when informal SMEs are included. According to our estimates, 600 million jobs will be needed by 2030 to absorb the growing global workforce, which makes SME development a high priority for many governments around the world. In emerging markets, most formal jobs are generated by SMEs, which create 7 out of 10 jobs. However, access to finance is a key constraint to SME growth, it is the second most cited obstacle facing SMEs to grow their businesses in emerging markets and developing countries. (Liberto, 2019). According to the definition of Bureau of Small and Medium Business Development (BSMBD), Department of Trade and Industry (DTI) SMEs can be classified based on the number of employees or the total assets. In the Philippines, SMEs are defined as any enterprise with 10 to 199 employees and/or assets valued from P3 million to P100 million. In the Philippines, the definition of small enterprises is according to the size of assets, size of equity capital, and number of employees. It defines a small business as any enterprise or business activity engaged in the major sectors of the economy. Whether a single proprietorship, cooperative, partnership or corporation whose total assets are ranging from more than P3,000,001 to P15,000,000. Small enterprise has a total number of employee of 10 to 99 workers. Bakeshops and convenience stores are examples of small business enterprise. Medium scale enterprises has total assets of P15,000,001 to P60,000,000 and employs 100 to 199 workers. Food manufacturing corporation and a furniture company are examples of medium enterprises. (DTI, 2018) Advantages of Having SMEs (Segundo, 2017) • SMEs are closer to their customers-Small and medium enterprises has direct dealing with their customers that will enable them to meet their needs more accurately and to offer a more individualized service. • SMEs are more flexible-Due to their size and simpler structure, SMEs have a greater capacity to adapt to changes. • SMEs are able to better detect and take advantage of small market niches-SMEs will have a greater capability to detect and satisfy very specific needs of its customers. • SMEs can make decisions faster-In SMEs, decision-making will normally fall on a person or a small group. • It is easier to link the staff to the company-Greater proximity to management and a more global vision of the business will make it easier to emotionally connect the worker with the company’s objectives. St. Scholastica’s Academy Grade 10 – Business Arts Page 6 • Everyone knows each other-Within a small and medium-sized company it is easier to form bonds and know the qualities of others. This can be used to increase performance and improve teamwork. • Communication will be easier-This will enable new ideas to flow and problems to be solved as a team. Disadvantages of Having SMEs (Segundo, 2017) • SMEs have more difficulties to find funding-Normally SMEs do not have the financial power that large companies have. For this reason, they will usually need external financing, which will also be more limited in worse condition. • It may be difficult to reach a large number of customers and earn their trust-The financial power of large companies allows them to make themselves known through mass media by advertising. • The costs are higher-SMEs will have enormous impediments to benefit from the economy of scale which will cause cost to be higher in certain types of business. • It is not easy to endure prolonged periods of crisis-The lack of financial capability can cause more problems for an SME if it is forced to endure long periods of crisis. • Low bargaining power with suppliers and customers-For an SME, it is more difficult to achieve beneficial conditions and are often forced to give in or they would like to. • Access to less skilled personnel-Given the greater limitations that an SME usually offers to develop a career (there will be fewer possibilities of advancement), it will be more difficult to attract talented and well-prepared workers. Formative Assessment What Have I Learned So Far? Use activity sheet # 3 1. Define small and medium enterprises. 2. Determine the number of employees for small and medium enterprises. III. Integration St. Scholastica’s Academy Grade 10 – Business Arts Page 7