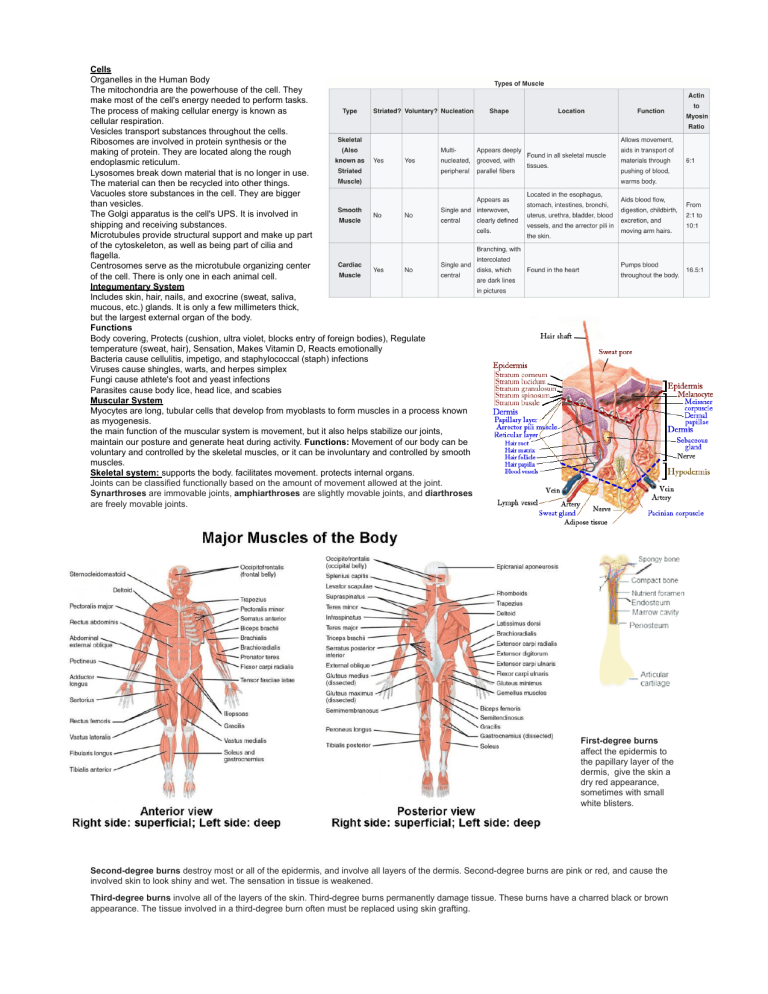
Cells Organelles in the Human Body The mitochondria are the powerhouse of the cell. They make most of the cell's energy needed to perform tasks. The process of making cellular energy is known as cellular respiration. Vesicles transport substances throughout the cells. Ribosomes are involved in protein synthesis or the making of protein. They are located along the rough endoplasmic reticulum. Lysosomes break down material that is no longer in use. The material can then be recycled into other things. Vacuoles store substances in the cell. They are bigger than vesicles. The Golgi apparatus is the cell's UPS. It is involved in shipping and receiving substances. Microtubules provide structural support and make up part of the cytoskeleton, as well as being part of cilia and flagella. Centrosomes serve as the microtubule organizing center of the cell. There is only one in each animal cell. Integumentary System Includes skin, hair, nails, and exocrine (sweat, saliva, mucous, etc.) glands. It is only a few millimeters thick, but the largest external organ of the body. Functions Body covering, Protects (cushion, ultra violet, blocks entry of foreign bodies), Regulate temperature (sweat, hair), Sensation, Makes Vitamin D, Reacts emotionally Bacteria cause cellulitis, impetigo, and staphylococcal (staph) infections Viruses cause shingles, warts, and herpes simplex Fungi cause athlete's foot and yeast infections Parasites cause body lice, head lice, and scabies Muscular System Myocytes are long, tubular cells that develop from myoblasts to form muscles in a process known as myogenesis. the main function of the muscular system is movement, but it also helps stabilize our joints, maintain our posture and generate heat during activity. Functions: Movement of our body can be voluntary and controlled by the skeletal muscles, or it can be involuntary and controlled by smooth muscles. Skeletal system: supports the body. facilitates movement. protects internal organs. Joints can be classified functionally based on the amount of movement allowed at the joint. Synarthroses are immovable joints, amphiarthroses are slightly movable joints, and diarthroses are freely movable joints. First-degree burns affect the epidermis to the papillary layer of the dermis, give the skin a dry red appearance, sometimes with small white blisters. Second-degree burns destroy most or all of the epidermis, and involve all layers of the dermis. Second-degree burns are pink or red, and cause the involved skin to look shiny and wet. The sensation in tissue is weakened. Third-degree burns involve all of the layers of the skin. Third-degree burns permanently damage tissue. These burns have a charred black or brown appearance. The tissue involved in a third-degree burn often must be replaced using skin grafting. allergen is an antigen that produces a rapid response from the immune system when introduced to the skin. An infection is an invasion of dermal tissue by disease-causing agents. Dermatitis is an inflammation of the skin due to a variety of factors. Eczema refers to any condition in which the skin becomes itchy or inflamed, but it is most often used to refer to atopic dermatitis. This condition typically begins in infancy or childhood and the skin becomes dry, flaky, and irritated near creases in the skin. Contact dermatitis produces red, burning, itching, or stinging rashes in response to allergens or other topical irritants. Seborrheic dermatitis (known as cradle cap in infants) produces scaly patches, dandruff, and incessant itching. Psoriasis is a condition resulting in red, flaky patches on the skin. There are five primary types: plaque, guttate, inverse, pustular, and erythrodermic. Psoriatic arthritis can also be considered a variation of this disorder. Many cases of psoriasis are hereditary, but other risk factors include weight or obesity, smoking, medications, infections, alcohol consumption, vitamin D deficiency, and stress. The most common type of psoriasis, plaque psoriasis appears as raised, red, scaly patches on the skin. guttate psoriasis manifests as tiny lesions or teardrops on the skin Inverse, flexural or intertriginous psoriasis, intertriginous psoriasis manifests on "flexor surfaces" or in skin folds. Pustular Psoriasis As the name suggests, raised bumps filled with pus (pustules) accompany the telltale psoriatic scales. Erythrodermic Psoriasis is described as aggressive and is considered the most severe form of psoriasis. It involves a full body rash that can spread quickly from the initial site Arthritis is an inflammation of the joints, and psoriatic arthritis involves scaly rashes along with joint stiffness and pain. Skin cancer| Basal cell carcinoma is the most common type It is curable if found early, especially because it rarely metastasizes (spreads to other organs). BCCs look like smooth, pearly bumps which are mostly found on the face, neck, and back. Squamous cell carcinoma occurs on parts exposed to the sun. SCC looks like firm red bumps susceptible to bleeding and crusting. Melanoma is deadly if not found early because it metastasizes quickly. It is most common in the southern hemisphere where the ozone layer is thin. Melanoma looks like irregular dark spots with a different appearance than a patient's moles. Polio: Poliomyelitis is a viral disease that affects the nerves and can lead to paralysis. There are four types of polio: paralytic, bulbar, spinal, and bulbospinal polio. Muscular Dystrophies: Muscular dystrophies are a group of inherited diseases that are characterized by weakness and deterioration of muscle tissue. The tissue is slowly replaced by fat, rendering the patient immobile. Myasthenia gravis is a chronic autoimmune disease that causes weakness and rapid fatigue of voluntary muscles. Tetanus is an extremely rare and serious bacterial infection that causes painful muscle spasms and often leads to death. Myositis is a term that refers to inflammation of muscles. Carpal tunnel syndrome is a numbness and tingling in the hand and arm caused by a pinched nerve in the wrist. Botulism is an extremely rare and potentially fatal poisoning caused by a bacterial infection. Fibromyalgia, or fibrositis, is a disease causing widespread musculoskeletal pain, fatigue, and issues with sleep, memory, and mood. Chronic fatigue syndrome, or myalgic encephalomyelitis, is characterized by fatigue worsened by activity and unimproved by rest. Osteoarthritis: The protective cartilage that cushions the ends of your bones wears down over time; extra strain on joints and joint injuries contribute. Osteoporosis: The body loses too much bone or produces too little bone. Herniated discs are caused by wear and tear, injuries, and excess strain on intervertebral discs. Scoliosis may be caused by neonatal pathologies, attained injuries, infections, and other things. An ACL tear occurs when your anterior cruciate ligament is sprained or torn. MCL damage occurs when the medial collateral ligament is stretched. Spinal stenosis is caused by a narrowing of the spaces within your spine that can be attributed to osteoarthritis Achondroplasia is a congenital disease of dwarfism caused by a gene alteration in the FGFR3 gene. Spinal stenosis is caused by a narrowing of the spaces within your spine that can be attributed to osteoarthritis. Juvenile rheumatoid arthritis is an autoimmune disease ankylosing spondylitis: reduced flexibility in the spine, which eventually results in a hunched-forward posture Osteosarcoma: bone pain and swelling