Which amongst the following is not a composition of the earth
advertisement

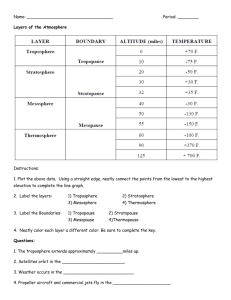
Which amongst the following is not a composition of the earth's athmosphere? A. Thin shell of air B. Water vapour C. Suspended particulates D. None of the choices Answer: As one moves upward from the ground, temperature of the various layers of Earth's atmosphere: A. Rises and falls B. Rises constantly C. Falls and rises D. Falls slowly Answer: Layer of the athmosphere characterized by decreasing temperature with height, appreciable vertical wind motion, appreciable water vapor content, and variable weather: A. Troposphere B. Stratosphere C. Ionosphere D. Mesosphere Answer: The atmospheric shell extending upward from the tropopause to the height where the temperature begins to increase in the 20 to 25 kilometer region. A. Troposphere B. Stratosphere C. Ionosphere D. Mesosphere Answer: Which layer of the athmosphere where the presence of charged particles in this region profoundly affects the propagation of certain electromagnetic radiation? A. Troposphere B. Stratosphere C. Ionosphere D. Mesosphere Answer: The athmospheric layer lying between the stratosphere and thermosphere is called: A. Troposphere B. Stratosphere C. Ionosphere D. Mesosphere Answer: Which of the following athmospheric layer has a temperature of over 1000 deg. A. Troposphere B. Stratosphere C. Ionosphere D. Thermosphere Answer: The transitional zone of maximum temperature between the stratosphere and the mesosphere is called: A. Stratopause B. Mesopause C. Tropopause D. Thermopause Answer: The boundary between the troposphere and the stratosphere is termed: A. Stratopause B. Mesopause C. Tropopause D. Thermopause Answer: The zone of minimum temperature between the mesosphere and thermosphere is called: A. Stratopause B. Mesopause C. Tropopause D. Thermopause Answer: Most of the weather events (e.g fog, cloud, dew, frost, hailstorm, storms, cloud-thunder, lightning etc) occur in this layer: A. Troposphere B. Stratosphere C. Ionosphere D. Mesosphere Answer: Passes through the athmosphere without appreciably warming it, the heat from the sun travels to the earth in the form of short wave: A. Ultraviolet rays B. Infrared light C. Radiation D. All of the choices Answer: Which regions of the earth athmosphere is where the flow of visible light into, and infrared light back out? A. Lower region B. Middle region C. Upper region D. Any of the choices Answer: The intensity of incoming solar radiation on an object is termed: A. Escalation B. Desolation C. Insolation D. Refraction Answer: Which of the following varies depending on time of year, solar declination, earth-sun distance, latitude, time of day and athmospheric condition? A. Refraction of Solar radiation B. Reflection of solar radiation C. Incoming solar radiation D. Cloud dissemination Answer: Insolation decreases with increased: A. Longitude B. Altitude C. Pressure D. Latitude Answer: A major environmental cue used by plants to time germination, leaf drop and prepare for winter (cold hardiness) is termed: A. Photoperiod B. Photofinish C. Photosynthesis D. None of the choices Answer: Water vapor can be produced from the following processes, except: A. Evaporation B. Boiling of liquid water C. Sublimation of ice D. None of the choices D. None of the choices Answe: The process of changing liquid water into water vapor or gaseous state is termed: A. Condensation B. Evaporation C. Sublimation D. Ionisation Answer: Which of the following generally occurs in the athmosphere when warm air rises, cools and loose its capacity to hold water vapor? A. Condensation B. Evaporation C. Sublimation D. Ionisation Answer: Latent heat is the heat necessary to change 1 kg. of water to one kg. of vapour at: A. Boiling point B. Saturation temperature C. Vaporisation D. Condensation Answer: When a volume of air at a given temperature holds the maximum amount of water vapour, the air is said to be: A. Evaporated B. Condensated C. Sublimated D. Saturated Answer: Unsaturated air can become saturated in three ways as follows, except: A. By evaporation of water into the air B. By the mixing of two gasses of air of different temperatures C. By the mixing of various gasses of air of different temperatures D. By cooling the air Answer: If cooled at constant pressure the temperature at which air becomes saturated is termed: A. Freeezing point B. Dew point C. Saturation point D. Vaporization point Answer: It is defined as the mass of water vapor divided by the volume of associated moist air and generally expressed in grams per cubic meter: A. Absolute humidity B. Water vapor density C. Either A or B D. Neither a Nor B Answer: The ratio of the actual vapor pressure to the saturation vapor pressure to the saturation vapour pressure at the air temperature, expressed as a percentage is termed: A. Absolute humidity B. Water vapor density C. Relative humidity D. Moisture content Answer: The partial pressure of a given sample of moist air that is attributable to the water vapour is called: A. Water vapor content B. Water vapor density C. Vaporization process D. Vapor pressure Answer: The atmospheric pressure on a unit area of a surface is equal to the weight of the "air column" extending from that surface to the outer fringes of the: A. Atmosphere B. Troposphere C. Stratosphere D. Ionosphere Answer: Atmospheric pressure decreases with height: A. Below the atmosphere B. Above sea level C. Below sea level D. Above the atmosphere Answer: Atmospheric pressure acts in: A. Clockwise direction B. Counter clockwise direction C. All directions D. Advance or backing direction Answer: